Abstract
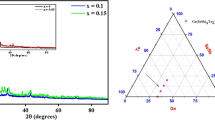
The structural properties of quaternary Ge10Te80Se10-xGax (x = 0 to 10) glassy alloy have been studied with XRD (X-ray diffraction) and FTIR (Fourier transform infrared) spectroscopy. The position of FSDP (first sharp diffraction peak) (2θ) and its FWHM (full width half maxima) have been utilized to estimate the local structure parameters of FSDP like repeating distance y and structural correlation length (L). The far-infrared (IR) transmission spectra of Ge10Te80Se10-xGax (x = 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10) have been analysed in the range 30–300 cm−1 to study the formation of bonds using chain crossing model, random covalent network model and chemical bond approach. The theoretical calculations have been executed for bond energies, force constants, wave number, etc., for probable bonds, and the results justify the experimental values. The present study contributes to the understanding of the composition-dependent structural property relationship of chalcogenide glasses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Yang, B. Bureau, T. Rouxel, Y. Gueguen, O. Gulbiten, C. Roiland, E. Soignard, J.L. Yarger, J. Troles, J.C. Sangleboeuf, P. Lucas, Correlation between structure and physical properties of chalcogenide glasses in the AsxSe1-x system. Phys Rev B - Condens Matter Mater Phys. 82, 1–8 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.82.195206
X.H. Zhang, Y. Guimond, Y. Bellec, Production of complex chalcogenide glass optics by molding for thermal imaging. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 326–327, 519–523 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(03)00464-2
S.A. Fayek, M.R. Balboul, K.H. Marzouk, Optical, electrical and thermal studies on (As2Se3)3–x(As2Te3)xglasses. Thin Solid Films 515, 7281–7285 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.03.039
V. Sharma, S. Sharda, N. Sharma, S.C. Katyal, P. Sharma, Chemical ordering and electronic properties of lone pair chalcogenide semiconductors. Prog. Solid State Chem. 54, 31–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2019.04.001
P. Sharma, N. Sharma, S. Sharda, S.C. Katyal, V. Sharma, Recent developments on the optical properties of thin films of chalcogenide glasses. Prog. Solid State Chem. 44, 131–141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2016.11.002
B.A.A. Wilhelm, C. Boussard-plédel, Q. Coulombier, J. Lucas, B. Bureau, P. Lucas (2007) Development of far-infrared-transmitting te based glasses suitable for carbon dioxide detection and space optics. 3796–3800. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200700823.
S. Danto, P. Houizot, C. Boussard-Pledel, X.H. Zhang, F. Smektala, J. Lucas, A family of far-infrared-transmitting glasses in the Ga-Ge-Te system for space applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 1847–1852 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200500645
P. Houizot, C. Boussard-Plédel, A.J. Faber, L.K. Cheng, B. Bureau, P.A. Van Nijnatten, W.L.M. Gielesen, J. Pereira do Carmo, J. Lucas, Infrared single mode chalcogenide glass fiber for space. Opt. Express. 15, 12529 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.15.012529
M.A. Popescu, Non-Crystalline Chalcogenides (Kluwer academic Publishers New York, Boston, Dordrecht, London, Moscow, 2001).
S. Maurugeon, B. Bureau, C. Boussard-plédel, A.J. Faber, X.H. Zhang, W. Geliesen, J. Lucas, Te-rich Ge – Te – Se glass for the CO2 infrared detection at 15µm. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 355, 2074–2078 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.01.059
Z. Yang, A.A. Wilhelm, P. Lucas, High-conductivity tellurium-based infrared transmitting glasses and their suitability for bio-optical detection. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1941–1944 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03686.x
K. Ramesh, S. Asokan, K.S. Sangunni, E.S.R. Gopal, Glass formation in germanium telluride glasses containing metallic additives. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 61, 95–101 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00239-5
K. N’Dri, D. Houphouet-Boigny, J.C. Jumas, Study of first sharp diffraction peak in As2S3 glasses by X-ray powder diffraction method. J. Non-Oxide Glas. 3, 29–37 (2012)
S.R. Elliott, Origin of the first sharp diffraction peak in the structure factor of covalent glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 711–714 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.711
C. Lin, G. Qu, Z. Li, S. Dai, H. Ma, T. Xu, Q. Nie, X. Zhang, Correlation between crystallization behavior and network structure in GeS2-Ga2S3-CsI chalcogenide glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1779–1782 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.12394
L. Calvez, M. Rozé, Y. Ledemi, H.L. Ma, J. Lucas, M. Allix, G. Matzen, X.H. Zhang, Controlled crystallization in Ge-(Sb/Ga)-(S/Se)-MX glasses for infrared applications. J. Ceram. Soc. Japan. 116, 1079–1082 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.116.1079
E. Sharma, H.H. Hegazy, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Topological behavior and glassy framework of GeTeSeGa chalcogenide glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 562, 100–106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.03.019
E. Sharma, P.B. Barman, P. Sharma (2020) Evaluation of optical linear and non-linear parameters of thermally deposited GeTeSeGa thin films in NIR (1 µm–2.6 µm) wavelength range from their transmission spectra. Optik. 219; 165181. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165181.
J. Bicerano, S.R. Ovshinsky, Chemical bond approach to the structures of chalcogenide glasses with reversible switching properties. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 74, 75–84 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(85)90402-8
T.S. Kavetskyy, O.I. Shpotyuk, V.T. Boyko, Void-species nanostructure of chalcogenide glasses studied with FSDP-related XRD. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 68, 712–715 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.02.009
P.H. Gaskell, Medium-range structure in glasses and low-Q structure in neutron and X-ray scattering data. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 351, 1003–1013 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.01.011
O.P. Rachek, X-ray diffraction study of amorphous alloys Al-Ni-Ce-Sc with using Ehrenfest’s formula. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 352, 3781–3786 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2006.05.031
L. Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond and the Structure of Molecules and Crystals (Cornell University Press, London, 1960).
E. Sharma, R. Sharma, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Cohesive energy calculation of quaternary Ge-Te-Se-Ga chalcogenide glasses using chemical bond approach. AIP Conf. Proc. 2050, 10–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5083595
I. Quiroga, C. Corredor, F. Bellido, J. Vkzquez, P. Villares, R.J. Garay (1996) Infrared studies of a Ge0.20Sb0.05Se0.75 glassy semiconductor. J. Non-Crytstalline Solids. 196; 183–186. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(95)00583-8.
L. Tichý, H. Tichá, A. Pačesová, J. Petzlt, On the infrared spectra of GeBiSe(S) glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 128, 191–196 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(91)90513-6
W. Gordy, A relation between bond force constants, bond orders, bond lengths, and the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 14, 305–320 (1946). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1724138
G.R. Somayajulu (1958) Dependence of force constant on electronegativity, bond strength, and bond order. VII, J. Chem. Phys. 28; 814–821. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1744276.
A. Rana, B.P. Singh, R. Sharma, Structural and chemical changes in Ga doped Ge-S glassy alloy. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 523, 119597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119597
G. Lucovsky, F.L. Galeener, R.C. Keezer, R.H. Geils, H.A. Six, Structural interpretation of the infrared and Raman spectra of glasses in the alloy system Ge1-xSx. Phys. Rev. B. 10, 5134–5146 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.10.5134
P. Tronc, M. Bensoussan, A. Brenac, C. Sebenne, Optical-absorption edge and raman scattering in GexSe1-x glasses. Phys. Rev. B. 8, 5947–5956 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.8.5947
G.J. Ball, J.M. Chamberlain, Infrared structural studies of GeySe1-y glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 29, 239–248 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(78)90118-7
P. Němec, V. Nazabal, M. Dussauze, H.L. Ma, Y. Bouyrie, X.H. Zhang, Ga-Ge-Te amorphous thin films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 531, 454–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2013.01.096
P. Sharma, S.C. Katyal, Far-infrared transmission and bonding arrangement in Ge10Se90-xTex semiconducting glassy alloys. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 354, 3836–3839 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.05.010
E.M. Vinod, A.K. Singh, R. Ganesan, K.S. Sangunni, Effect of selenium addition on the GeTe phase change memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 537, 127–132 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.05.064
D.R. Goyal, A.S. Maan, Far-infrared absorption in amorphous Sb15GexSe85 - x glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 183, 182–185 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)00550-8
P. Jóvári, I. Kaban, B. Bureau, A. Wilhelm, P. Lucas, B. Beuneu, D.A. Zajac (2010) Structure of Te-rich Te-Ge-X (X = I, Se, Ga) glasses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 22. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/22/40/404207.
I. Voleská, J. Akola, P. Jóvári, J. Gutwirth, T. Wágner, T. Vasileiadis, S.N. Yannopoulos, R.O. Jones (2012) Structure, electronic, and vibrational properties of glassy Ga 11Ge 11Te 78: Experimentally constrained density functional study. Phys. Rev. B - Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 86; 1–9. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.86.094108.
S. Sen, E.L. Gjersing, B.G. Aitken, Physical properties of GexAs2xTe100 - 3x glasses and Raman spectroscopic analysis of their short-range structure. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 356, 2083–2088 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.08.013
N. Dong, Y. Chen, N. Wei, G. Wang, R. Wang, X. Shen, S. Dai, Q. Nie, Optical and structural properties of Ge-Ga-Te amorphous thin films fabricated by magnetron sputtering. Infrared Phys. Technol. 86, 181–186 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2017.09.008
G.A.M. Amin, A.F. Maged, Compositional dependence of the physical properties of Ge1Se9-xTex amorphous system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 97, 420–424 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.08.037
R. Svoboda, D. Brandova, Crystallization behavior of (GeTe4)x(GaTe3)100–x glasses for far-infrared optics applications. J. Alloys Compd. 770, 564–571 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.150
A. Lecomte, V. Nazabal, D. Le Coq, L. Calvez, Ge-free chalcogenide glasses based on Ga-Sb-Se and their stabilization by iodine incorporation. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 481, 543–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.11.046
N. Sharma, S. Sharda, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Far-infrared investigation of ternary Ge-Se-Sb and quaternary Ge-Se-Sb-Te chalcogenide glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 375, 114–118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.04.065
R. Pumlianmunga, N. Venkatesh, A. Naresh, E.S.R. Sankhla, K. Gopal, Ramesh, Influence of connectivity on the rigidity of the covalently bonded (GeTe4)100–x(As2Se3)x glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 447, 178–182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.06.014
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to JIIT Noida for providing the XRD facility and SAIF, IIT Bombay, for FTIR facility. PS gratefully acknowledges SERB-DST, India, for “project file no. EMR/2014/001108, Dated 11/09/2015”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, E., Barman, P.B. & Sharma, P. Structural correlation of GeTeSeGa system by XRD and far-infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. A 127, 345 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04493-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04493-x