Abstract
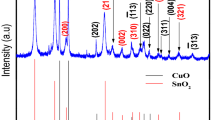
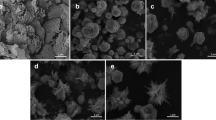
The development of low cost, long-term stable and highly efficient electrocatalyst is one of the major current research activities towards electrochemical water oxidation process for the clean-energy hydrogen production. The transition metal oxides (CuO, TiO2, NiO, Co2O3, etc.,) have been desirable for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in alkaline electrolyte. Among these transition metal oxides, the CuO based composites are most promising constituents for the water oxidation process due to their good electronic properties and the anticipated synergistic effect to alter the surface properties of the materials dramatically to favor the electrocatalysis. Here, we have reported the synthesis of CuO-SnO2 nanoparticles network by a facile chemical method as the electrocatalyst for an efficient OER. The physiochemical properties of CuO-SnO2 nanoparticles network electrocatalyst were characterized by using various techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies (XPS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for their structural, absorption/presence of functional groups, elemental composition and morphology, respectively. Further, the electrochemical properties of the catalysts were investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV), chronopotentiometry and Tafel curve measurements in alkaline electrolyte. The electrocatalysts showed a low onset potential of 1.39 V vs reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) and high stability for 6 h in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte, which demonstrated their better performance than the benchmark Ni electrocatalyst.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.R. Stamenkovic, D. Strmcnik, P.P. Lopes, N.M. Markovic, Energy and fuels from electrochemical interfaces. Nat. Mater. 16, 57–69 (2017)
L. Peng, Z. Wei, Catalyst engineering for electrochemical energy conversion from water to water: water electrolysis and the hydrogen fuel cell. Engineering 6, 653–679 (2020)
R.D.L. Smith, M.S. Prévot, R.D. Fagan, Z. Zhang, P.A. Sedach, M.K.J. Siu, S. Trudel, C.P. Berlinguette, Photochemical route for accessing amorphous metal oxide materials for water oxidation catalysis. Science 340, 60–63 (2013)
T.R. Cook, D.K. Dogutan, S.Y. Reece, Y. Surendranath, T.S. Teets, D.G. Nocera, Solar energy supply and storage for the legacy and nonlegacy worlds. Chem. Rev. 110, 6474–6502 (2010)
L. Trotochaud, S.L. Young, J.K. Ranney, S.W. Boettcher, Nickel–iron oxyhydroxide oxygen-evolution electrocatalysts: the role of intentional and incidental iron incorporation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6744–6753 (2014)
J.A. Koza, Z. He, A.S. Miller, J.A. Switze, Electrodeposition of crystalline Co3O4-A catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 24, 3567–3573 (2012)
J. Tian, Q. Liu, A.M. Asiri, X. Sun, Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: an efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 7587–7590 (2014)
H.W. Park, D.U. Lee, P. Zamani, M.H. Seo, L.F. Nazar, Z. Chen, Electrospun porous nanorod perovskite oxide/nitrogen-doped graphene composite as a bi-functional catalyst for metal air batteries. Nano Energy 10, 192–200 (2014)
J.A. Haber, Y. Cai, S. Jung, C. Xiang, S. Mitrovic, J. Jin, A.T. Bellbd, J.M. Gregoire, Discovering Ce-rich oxygen evolution catalysts, from high throughput screening to water electrolysis. Energy. Environ. Sci. 7, 682–688 (2014)
J.A. Haber, E. Anzenburg, J. Yano, C. Kisielowski, J.M. Gregoire, Multiphase nanostructure of a quinary metal oxide electrocatalyst reveals a new direction for OER electrocatalyst design. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1402307–1402317 (2015)
Kumar MP, Murugadoss G, Kumar MR (2020) Synthesis and characterization of CuO–NiO nanocomposite: highly active electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction application.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. In Electronics 31:11286–11294
L. Trotochaud, J.K. Ranney, K.N. Williams, S.W. Boettcher, Solution-cast metal oxide thin film electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 17253–17261 (2012)
R. Subbaraman, D. Tripkovic, K.C. Chang, D. Strmcnik, A.P. Paulikas, P. Hirunsit, M. Chan, J. Greeley, V. Stamenkovic, N.M. Markovic, Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3 d M (Ni Co, Fe, Mn) hydr (oxy) oxide catalysts. Nat. Mater. 11, 550–557 (2012)
W. Zhou, X. Wu, X. Cao, X. Huang, C. Tan, J. Tian, H. Liu, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Ni3S2nanorods/Ni foam composite electrode with low overpotential for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 2921–2924 (2013)
F. Song, X. Hu, Ultrathin cobalt–manganese layered double hydroxide is an efficient oxygen evolution catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 16481–16484 (2014)
X. Long, J. Li, S. Xiao, K. Yan, Z. Wang, H. Chen, S. Yang, A strongly coupled graphene and FeNi double hydroxide hybrid as an excellent electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 53, 7584–7588 (2014)
T. Ma, S. Dai, M. Jaroniec, S. Qiao, Metal-organic framework derived hybrid Co3O4-carbon porous nanowire arrays as reversible oxygen evolution electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 13925–13931 (2014)
H. Wang, H.W. Lee, Y. Deng, Z. Lu, P.C. Hsu, Y. Liu, D. Lin, Y. Cui, Bifunctional non-noble metal oxide nanoparticle electrocatalysts through lithium-induced conversion for overall water splitting. Nat. Comm. 6, 7261–7268 (2015)
J. Kundu, S. Khilari, K. Bhunia, D. Pradhan, Ni-doped CuS as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 9, 406–417 (2019)
R. Hutchings, K. Müller, S. Stucki, A structural investigation of stabilized oxygen evolution catalysts. J. Mater. Sci. 19, 3987–3994 (1984)
M.S. Park, Y.M. Kang, G.X. Wang, S.X. Dou, H.K. Liu, The effect of morphological modification on the electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 455–461 (2008)
F. Han, W.C. Li, M.R. Li, A.H. Lu, Fabrication of superior-performance SnO2@C composites for lithium-ion anodes using tubular mesoporous carbon with thin carbon walls and high pore volume. J Mater Chem. 22, 9645–9651 (2012)
J. Deng, C. Yan, L. Yang, S. Baunack, S. Oswald, H. Wendrock, Sandwich-stacked SnO2/Cu hybrid nanosheets as multichannel anodes for lithium ion batteries. ACS Nano 7, 6948–6954 (2013)
X. Wang, Z. Li, Q. Li, C. Wang, A. Chen, Z. Zhang, R.L. FanYin, Ordered mesoporous SnO2 with a highly crystalline state as an anode material for lithium ion batteries with enhanced electrochemical performance. CrystEngComm 15, 3696–3704 (2013)
Joshi S, Satyanarayana L, Manjula P, Sunkara MV, Ippolito SJ (2015) Chemo-Resistive CO2 gas sensor based on CuO-SnO2 heterojunction nanocomposite material. ISPTS 2015 - 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors: Dive Deep into Sensors, Proceedings, art. no. 7220079:43–48.
G.Z. Xing, Y. Wang, J.I. Wong, Y.M. Shi, Z.X. Huang, S. Li, H.Y. Yang, Hybrid CuO/SnO2 nanocomposites: Towards cost-effective and high performance binder free lithium ion batteries anode materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 143905–143910 (2014)
S. Singh, N. Verma, A. Singh, B.C. Yadav, Synthesis and characterization of CuO-SnO2 nanocomposite and its application as liquefied petroleum gas sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 18, 88–96 (2014)
S.W. Choi, A. Katoch, J. Zhang, S.S. Kim, Electrospun nanofibers of CuO-SnO2 nanocomposite as semiconductor gas sensors for H2S detection. Sens. Actuators, B: Chem. 176, 585–591 (2013)
X. Hl, H.S. Zhuang, T. Zhang, D.C. Xiao, Photocatalytic degradation of Acid Blue 62 over CuO-SnO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst under simulated sunlight. J. Environ. Sci. 19, 1141–1145 (2007)
S. Sundar, G. Venkatachalam, S.J. Kwon, Biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanowires and their use for the electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Nanomaterials 8, 823–839 (2018)
A. Majid, J. Tunney, S. Argue, D. Kingston, M. Post, J. Margeson, G.J. Gardner, Characterization of CuO phase in SnO2–CuO prepared by the modified Pechini method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 53, 390–398 (2010)
V. Maruthapandian, T. Pandiarajan, V. Saraswathy, S. Muralidharan, Oxygen evolution catalytic behaviour of Ni doped Mn3O4 in alkaline medium. RSC Adv. 6, 48995–49002 (2016)
R.P. Putra, H. Horino, I.I. Rzeznicka, An efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline solutions derived from a copper chelate polymer via in situ electrochemical transformation. Catalysts 10, 233–243 (2020)
J.K. Wu, C.T. He, G.R. Li, J.P. Zhang, Inorganic-MOF-inorganic approach to ultrathin CuO decorated Cu-C hybrid nanorod arrays for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6, 19176–19181 (2018)
B. Zhang, C. Li, G. Yang, K. Huang, J. Wu, Z. Li, X. Cao, D. Peng, S. Hao, Y. Huang, nanostructured CuO/C hollow shell@3D copper dendrites as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 23807–23812 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M.P., Murugadoss, G., Mangalaraja, R.V. et al. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of CuO-SnO2 nanocomposite in alkaline medium. Appl. Phys. A 127, 66 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04228-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04228-4