Abstract
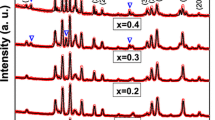
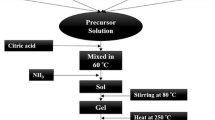
(xCo)-BaFe12O19 nanoparticles, with 0 \(\le x \le\) 0.1 wt%, have been prepared using a chemical co-precipitation method and different calcination temperatures (850 °C, 900 °C and 950 °C). The samples were subjected to structural, optical and magnetic studies. X-ray powder diffraction showed the hexagonal crystal structure of (xCo)-BaFe12O19, and the more convenient temperature for the formation of this phase was 950 °C. Transmission electron microscope was used for investigating the morphology as well as the average particle size of the samples. It was found that the average size of all samples ranges between 65 and 90 nm. The energy band gap Eg was determined using UV–Vis spectroscopy. It was noticed that the values of Eg decreased with the addition of cobalt and the increase in the calcination temperature. The M–H curve obtained from vibrating sample magnetometer has been used to study the magnetic behavior. The anisotropy field (Ha), the saturation magnetization (σs), the effective crystalline anisotropy constant (Keff), the remanent magnetization (σr) and squareness ratio (S) for each sample were calculated. The maximum value of coercivity (5087Oe) was found for x = 0 wt% at T = 950 °C which is suitable for magnetic applications, such as the recording equipment and permanent magnets.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Bhattacharya, S. Dhibar, G. Hatui, A. Mandal, T. Das, C.K. Das, Graphene decorated with hexagonal shaped M-type ferrite and polyaniline wrapper: a potential candidate for electromagnetic wave absorbing and energy storage device applications. RSC Adv. 4, 17039–17053 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA00448E
C. Navau, J. Prat-Camps, O. Romero-Isart, J.I. Cirac, A. Sanchez, Long-distance transfer and routing of static magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 253901 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.253901
T. Kaur, S. Kumar, B.H. Bhat, A.K. Srivastava, Enhancement in physical properties of barium hexaferrite with substitution. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2753–2762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.244
M. Anbarasu, M. Anandan, E. Chinnasamy, V. Gopinath, K. Balamurugan, Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol (PEG) coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by chemical co-precipitation method for biomedical applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 135, 536–539 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.07.059
H.A. Patel, J. Byun, C.T. Yavuz, Arsenic removal by magnetic nanocrystalline barium hexaferrite, in Nanotechnology for Sustainable Development, ed. by M.S. Diallo, N.A. Fromer, M.S. Jhon (Springer, Cham, 2014), pp. 163–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05041-6_13
D. Lisjak, K. Bobzin, K. Richardt, M. Bégard, G. Bolelli, L. Lusvarghi, A. Hujanen, P. Lintunen, M. Pasquale, E. Olivetti, M. Drofenik, T. Schläfer, Preparation of barium hexaferrite coatings using atmospheric plasma spraying. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 2333–2341 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2009.01.028
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Effect of annealing temperature on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 5, 7279–7284 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.068
H. Li, J. Huang, Q. Li, X. Su, Preparation of barium ferrite films with high Fe/Ba ratio by sol–gel method. J. Sol–Gel. Sci. Technol. 52, 309 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-2052-9
V.K. Sankaranarayanan, D.C. Khan, Mechanism of the formation of nanoscale M-type barium hexaferrite in the citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 153, 337–346 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(95)00537-4
X. Liu, J. Wang, L.-M. Gan, S.-C. Ng, J. Ding, An ultrafine barium ferrite powder of high coercivity from water-in-oil microemulsion. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 184, 344–354 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(97)01141-4
G. Mendoza-Suárez, K.K. Johal, H. Mancha-Molinar, J.I. Escalante-Garcı́a, M.M. Cisneros-Guerrero, Magnetic properties of Zn-Sn-substituted Ba-ferrite powders prepared by ball milling. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2597–2603 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00751-6
A. González-Angeles, G. Mendoza-Suárez, A. Grusková, I. Tóth, V. Jančárik, M. Papánová, J.I. Escalante-Garcı́a, Magnetic studies of NiSn-substituted barium hexaferrites processed by attrition milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 270, 77–83 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.08.001
J. Kreisel, H. Vincent, F. Tasset, M. Paté, J.P. Ganne, An investigation of the magnetic anisotropy change in BaFe12 − 2xTixCoxO19 single crystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 224, 17–29 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01355-X
G.B. Teh, S. Nagalingam, D.A. Jefferson, Preparation and studies of Co(II) and Co(III)-substituted barium ferrite prepared by sol–gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 101, 158–162 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2006.03.008
A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako, Static and high frequency magnetic properties of Mn–Co–Zr substituted Ba-ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 456, 485–491 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.101
S. Singhal, K. Kaur, S. Jauhar, S. Bhukal, S. Bansal, Structural and magnetic properties of BaCoxFe12-xO19 (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, &1. 0) nanoferrites synthesized via citrate sol–gel method. World J. Condens. Matter Phys 1, 101–104 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/wjcmp.2011.13016
S. Kumar, S. Supriya, L.K. Pradhan, R. Pandey, M. Kar, Grain size effect on magnetic and dielectric properties of barium hexaferrite (BHF). Phys. B 1(2019), 411908 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411908
S. Anand, S. Pauline, V. Maria Vinosel, M. Asisi Janifer, Structural rietveld refinement and vibrational study of M-type BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 8(2019), 476–483 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.02.141
S. Ashima, A. Sanghi, Agarwal, Reetu, Rietveld refinement, electrical properties and magnetic characteristics of Ca–Sr substituted barium hexaferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 513, 436–444 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.10.071
S.B. Waje, M. Hashim, W.D. Wan Yusoff, Z. Abbas, Sintering temperature dependence of room temperature magnetic and dielectric properties of Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared using mechanically alloyed nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 686–691 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.10.041
D.A. Vinnik, D.A. Zherebtsov, L.S. Mashkovtseva, S. Nemrava, A.S. Semisalova, D.M. Galimov, S.A. Gudkova, I.V. Chumanov, L.I. Isaenko, R. Niewa, Growth, structural and magnetic characterization of Co- and Ni-substituted barium hexaferrite single crystals. J. Alloy. Compd. 628, 480–484 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.124
R. Topkaya, I. Auwal, A. Baykal, Effect of temperature on magnetic properties of BaYxFe12 − xO19 hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 16296–16302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.178
S.S.S. Afghahi, M. Jafarian, Y. Atassi, Microstructural and magnetic studies on BaMgxZnxX2xFe12 − 4xO19 (x = Zr, Ce, Sn) prepared via mechanical activation method to act as a microwave absorber in X-band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 184–191 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.01.020
V.V. Soman, V.M. Nanoti, D.K. Kulkarni, Dielectric and magnetic properties of Mg–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 39, 5713–5723 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.12.089
S.M. El-Sayed, T.M. Meaz, M.A. Amer, H.A. El Shersaby, Magnetic behavior and dielectric properties of aluminum substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. Phys. B 426, 137–143 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.06.026
N.I. Sulaiman, M.A. Bakar, N.H.H.A. Bakar, M.H. Hussin, Sol-gel synthesis of barium hexaferrite and their catalytic application in methyl ester synthesis. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 509, 012103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/509/1/012103
H. Cui, Y. Liu, W. Ren, Structure switch between α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 during the large scale and low temperature sol–gel synthesis of nearly monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 93–97 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2012.03.001
A. Lassoued, B. Dkhil, A. Gadri, S. Ammar, Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys. 7, 3007–3015 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.066
A. Zielińska-Jurek, Z. Bielan, S. Dudziak, I. Wolak, Z. Sobczak, T. Klimczuk, G. Nowaczyk, J. Hupka, Design and application of magnetic photocatalysts for water treatment. The effect of particle charge on surface functionality. Catalysts 7, 360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120360
M. Hafeez, R. Shaheen, B. Akram, Z. Abdin, S. Haq, S. Mahsud, S. Ali, R.T. Khan, Green Synthesis of cobalt oxide nanoparticles for potential biological applications. Mater. Res. Express. 1, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab70dd
K. Pradeev Raj, K. Sadaiyandi, A. Kennedy, S. Sagadevan, Z.Z. Chowdhury, M.R.B. Johan, F.A. Aziz, R.F. Rafique, R. Thamiz Selvi, R. Rathina Bala, Influence of Mg doping on ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic evaluation and antibacterial analysis. Nanosc. Res. Lett. 13, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2643-x
S. Anjum, A. Seher, Z. Mustafa, Effect of La3 + ions substituted M-type barium hexa-ferrite on magnetic, optical, and dielectric properties. Appl. Phys. A 125, 664 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2937-6
B.S. Rema Devi, R. Raveendran, A.V. Vaidyan, Synthesis and characterization of Mn2 + -doped ZnS nanoparticles. Pramana J. Phys. 68, 679–687 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-007-0068-7
T. Kaur, S. Kumar, B.H. Bhat, B. Want, A.K. Srivastava, Effect on dielectric, magnetic, optical and structural properties of Nd–Co substituted barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 119, 1531–1540 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9134-z
H.C. Fang, Z. Yang, C.K. Ong, Y. Li, C.S. Wang, Preparation and magnetic properties of (Zn–Sn) substituted barium hexaferrite nanoparticles for magnetic recording. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 187, 129–135 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00139-5
A. Demir, S. Güner, Y. Bakis, S. Esir, A. Baykal, Magnetic and optical properties of Mn1 − xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 24, 729–736 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-014-0032-1
H. Kojima, Chapter 5 Fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite structure, in Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials. Elsevier, 1982, pp. 305–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1574-9304(05)80091-4
T. Kaur, B. Kaur, B.H. Bhat, S. Kumar, A.K. Srivastava, Effect of calcination temperature on microstructure, dielectric, magnetic and optical properties of Ba0.7La0.3Fe11.7Co0.3O19 hexaferrites. Phys. B 456, 206–212 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.09.003
R.C. Alange, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, A.V. Humbe, K.M. Jadhav, Structural, magnetic and dielectrical properties of Al–Cr Co-substituted M-type barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1106, 460–467 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.11.004
M.G. Shalini, S.C. Sahoo, Magnetic studies of cobalt doped barium hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared by modified sol-gel method. AIP Conf. Proc. 1728, 020445 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4946496
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001
G. Mendoza-Suárez, M.C. Cisneros-Morales, M.M. Cisneros-Guerrero, K.K. Johal, H. Mancha-Molinar, O.E. Ayala-Valenzuela, J.I. Escalante-Garcı́a, Influence of stoichiometry and heat treatment conditions on the magnetic properties and phase constitution of Ba-ferrite powders prepared by sol–gel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 796–801 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00141-4
R. Safi, A. Ghasemi, R. Shoja-Razavi, A novel approach for enhancement of coercivity in magnetic cobalt ferrite nanocrystal without applying post annealing. Ceram. Int. 42, 17357–17365 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.033
H.-F. Yu, K.-C. Huang, Effects of pH and citric acid contents on characteristics of ester-derived BaFe12O19 powder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260, 455–461 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)01389-6
M.G. Naseri, E.B. Saion, H.A. Ahangar, A.H. Shaari, M. Hashim, Simple synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by a thermal treatment method. J. Nanomater. 2010, 75:1–75:8 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/907686
B.D. Cullity, C.D. Graham, Introduction to magnetic materials (Wiley, New York, 2011)
M. Kishimoto, S. Kitahata, M. Amemiya, Effect of magnetic anisotropy of Ba-ferrite particles on squareness of perpendicular recording media. J. Appl. Phys. 61, 3875–3877 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.338626
E.A. Setiadi, M. Yunus, N. Nababan, S. Simbolon, C. Kurniawan, S. Humaidi, P. Sebayang, M. Ginting, The effect of temperature on synthesis of MgFe2O4based on natural iron sand by Co-precipitation method as adsorbent Pb ion. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 985, 012046 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/985/1/012046
I.A. Auwal, H. Güngüneş, S. Güner, S.E. Shirsath, M. Sertkol, A. Baykal, Structural, magneto-optical properties and cation distribution of SrBixLaxYxFe12 − 3xO19 (0.0 ≤ x≤0.33) hexaferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 80, 263–272 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.03.028
H. Luo, B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, V.V. Nguyen, J.P. Liu, Physical and magnetic properties of highly aluminum doped strontium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by auto-combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2602–2608 (2012)
S. Anjum, M. Shahid Rafique, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, K. Siraj, A. Usman, S.I. Hussain, S. Naseem, Investigation of induced parallel magnetic anisotropy at low deposition temperature in Ba-hexaferrites thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 711–716 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.08.059
I.A. Auwal, A. Baykal, H. Güngüneş, S.E. Shirsath, Structural investigation and hyperfine interactions of BaBixLaxFe12 − 2xO19 (00 ≤ x≤05) hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 3380–3387 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.132
Acknowledgements
This research was accomplished in the Specialized Materials Science Lab and Advanced Nanomaterials Research Lab, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Beirut Arab University, Lebanon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habanjar, K., Shehabi, H., Abdallah, A.M. et al. Effect of calcination temperature and cobalt addition on structural, optical and magnetic properties of barium hexaferrite BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 126, 402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03497-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03497-3