Abstract
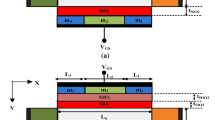
To overcome the problem of fabrication complexity and to reducei the cost of microelectronic devices, a new concept of dual-material control gate with dual-oxide tunnel field-effect transistor is investigated. A stack gate approach is applied to reduce the width of tunneling barrier at source–channel junction. Use of dual oxides at source–channel interface provides improved capacitive coupling, which enhances the on-state current. The entire gate segment has been partitioned into three parts, namely tunnel gate \((M_1)\), control gate \((M_2)\) and auxiliary gate \((M_3)\) with different work functions such as \(\phi _{1}\), \(\phi _{2}\) and \(\phi _{3}\). In this context, to keep dual-work functionality, the feasible combinations of these work functions are adopted. Technology computer- aided design (TCAD) simulations of these proposed combinations of work functions along with dual oxides provide better results for the combinations of \((\phi _1=\phi _3<\phi _2)\). In addition, comparison between these combinations on the basis of analog/RF performance is done in this work. This work shows improved analog/RF parameters such as \(g_\text {m}, C_\text {gs}, C_\text {gd}, f_\text {T}\) and TFP, and linearity parameters including \(g_\text {m3}, \text {VIP3, IIP3}\) and \(\text {IMD3}\) for the proposed device DMDODG-TFET (dual-material dual-oxide double-gate TFET). The use of this proposed device structure reduces the ambipolar behavior and subthreshold swing \((18.5\,\text {mV}/\text {deacde})\), and enhances the on-current [\(3.6\times 10^{-5}\,(A/\upmu \text {m})\)] significantly, making it suitable for analog/RF and linearity applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Pinczuk, E. Burstein, Raman scattering from InSb surfaces at photon energies near the \(E_{\rm 1}\) energy gap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 21, 1073–1075 (1968)
J.-P. Colinge, C.-W. Lee, A. Afzalian, Nanowire transistors without junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol 5, 225229 (2010)
S.O. Koswatta, M.S. Lundstrom, D.E. Nikonov, Performance comparison between p-i-n tunneling transistors and conventional MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Device 56, 456465 (2007)
A.C. Seabaugh, Q. Zhang, Low-voltage tunnel transistors for beyond CMOS logic. Proc. IEEE 98(12), 20952110 (2010)
W.Y. Choi, B.G. Park, J.D. Lee, Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) with subthreshold swing (SS) less than 60 mV/dec. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28(8), 743745 (2007)
P.F. Wang, K. Hilsenbeck, T. Nirschl, Complementary tunneling transistor for low power application. Solid-State Electron. 48(12), 22812286 (2004)
A.M. Ionescu, H. Riel, Tunnel field-effect transistors as energy efficient electronic switches. Nature 479(7373), 329337 (2011)
A.M. Ionescu, L.D. Michielis, N. Dagtekin, Ultra low power emerging devices and their benefits for integrated circuits. Proc. IEEE IEDM, 16.1.116.1.4 (2011)
The international technology roadmap for semiconductors. http://www.itrs.net
M.R. William, A.J. Gehan, Silicon surface tunnel transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 494496 (1995)
Q. Zhang, W. Zhao, A. Seabaugh, Low subthreshold swing tunnel transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Device Lett. 27, 297300 (2006)
K. Boucart, A.M. Ionescu, Double gate tunnel FET with high-k gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54, 17251733 (2007)
R.M.I. Abadi, M. Saremi, A resonant tunneling nanowire field effect transistor with physical contractions: a negative differential resistance device for low power very large scale integration applications. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 10911098 (2018)
K. Nigam, S. Pandey, P.N. Kondekar, A barrier controlled charge plasma based TFET with gate engineering for ambipolar suppression and RF/linearity performance improvement. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 27512757 (2017)
A.M. Ionescu, H. Riel, Tunnel field-effect transistors as energy efficient electronic switches. Nature/em 479, 329337 (2010)
W.Y. Choi, B.-G. Park, J.D. Lee, Tunneling field effect transistor with subthreshold swing (SS) less than 60 mV/Dec. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28, 743745 (2007)
R.M. Imenabadi, Mehdi Saremi, W.G. Vandenberghe, A novel PNPN like Z-shaped tunnel field-effect transistor with improved ambipolar behavior and RF performance. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 47524758 (2017)
A. Lahgere, C. Sahu, J. Singh, Electrically doped dynamically configurable field-effect transistor for low power and high-performance applications. Electron. Lett. 51, 12841286 (2015)
K. Nigam, P.N. Kondekar, D. Sharma, A new approach for design and investigation of junctionless tunnel FET using electrically doped mechanism. Superlattices Microstruct. 98, 1–7 (2016)
P.N. Kondekar, K. Nigam, S. Pandey, D. Sharma, Design and analysis of polarity controlled electrically doped tunnel FET with bandgap engineering for analog/RF applications. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64(2), 412–418 (2017)
K. Nigam, P. kondekar, D. Sharma, Approach for ambipolar behaviour suppression in tunnel FET by workfunction engineering. Micro Nano Lett. 11(8), 460–464 (2016)
A. Sarkar, A.K. Das, S. De, C.K. Sarkar, Effect of gate engineering in double-gate MOSFETs for analog/RF applications. Microelectron. J. 43(11), 873882 (2012)
J. Madan, R. Chaujar, Interfacial charge analysis of heterogeneous gate dielectric-gate all around-tunnel FET for improved device reliability. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 16, 227234 (2016)
J.H. Huang, Z.H. Liu, M.C. Jeng, A physical model for MOSFET output resistance. Int. Electron Devices Meet. 13, 569–572 (1992)
R. Nagar, M. Saxena, R.S. Gupta, M. Gupta, Linearity and analog performance analysis of double gate tunnel FET: effect of temperature and gate stack. Int. J. VLSI Design Commun. Syst. 2(3), 186–200 (2011)
A. Bansal, B.C. Paul, K. Roy, An analytical fringe capacitance model for interconnects using conformal mapping. IEEE Trans. CAD 25(12), 2765–2774 (2006)
K.M.H. Badami, S. Karmalkar, Quasi-static compact model for coupling between aligned contacts on lnite substrates with insulating or conducting backplanes. IEEE Trans. CAD 31(06), 858–8674 (2012)
S. Ahish, D. Sharma, Y.B.N. Kumar, M.H. Vasantha, Performance enhancement of novel InAs/Si hetero double-gate tunnel FET using Gaussian doping. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63(1), 288–295 (2016)
T.C. Lim, Bernard, O. Rozeau, T. Ernst, B. Guillaurnot, N. Vulliet, C.B. Dufournet, M. Paccaud, S. Lepilliet, G. Dambrine, F. Dan- neville, A charge oriented model for MOS transistor capacitances. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56(7), 1473–1482 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Singh, K.S., Nigam, K. et al. Dual-material dual-oxide double-gate TFET for improvement in DC characteristics, analog/RF and linearity performance. Appl. Phys. A 125, 353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2650-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2650-5