Abstract
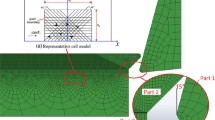
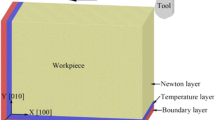
During the nanofabrication process of polycrystalline materials, the interactions of dislocations in material determine the evolution of subsurface defects. In this paper, the molecular dynamics simulation models of nanocutting polycrystalline copper, which is used to study the relationship between the crystal structure and the cutting force during the cutting process, were established, and the transformation process between grain boundaries and dislocations was studied to get the effects of grain boundary on dislocation slip and stress conduction. The results show that there are obvious rules between cutting force and cutting process and grain boundaries can prevent dislocation slip and shielding stress conduction. The influence of different cutting parameters on the evolution of subsurface defects of workpiece was further analyzed. Finally, the nanoindentation simulations and experiments were carried out to study the influence of cutting parameters on surface mechanical properties of workpiece. It is found that to some extent, the surface hardening effect of the workpiece is remarkable with the cutting depth increase.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.S. Pande, K.P. Cooper, Nanomechanics of Hall–Petch relationship in nanocrystalline materials[J]. Prog. Mater Sci. 54(6), 689–706 (2009)
T. Chookajorn, C.A. Schuh, Design of stable nanocrystalline alloys[J]. Science 337(6097), 951 (2012)
P.R. Cantwell, M. Tang, J.D. Shen et al., Grain boundary complexions[J]. Acta Mater. 62(1), 1–48 (2014)
R.A. Andrievskii, Thermal stability of nanomaterials[J]. J. Mater. Sci. 49(4), 1449–1460 (2014)
I.J. Beyerlein, M.J. Demkowicz, A. Misra, et al., Defect–interface interactions[J]. Prog. Mater Sci. 74, 125–210 (2015)
R. Barretta, M.D.S. Francesco, A nonlocal model for carbon nanotubes under axial loads[J]. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 1–6 (2013)
R. Barretta, M. Čanađija, F.M. Sciarra et al. A higher-order Eringen model for Bernoulli–Euler nanobeams[J]. Arch. Appl. Mech. 86, 483 (2016)
R. Barretta, M. Čanađija, R. Luciano, et al., Stress-driven modeling of nonlocal thermoelastic behavior of nanobeams[J]. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 126, 53–67 (2018)
M. Čanađija, R. Barretta, M.D.S. Francesco, A gradient elasticity model of Bernoulli–Euler nanobeams in non-isothermal environments[J]. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2015, S0997753815001291 (2015)
V. Yamakov, D. Wolf, S.R. Phillpot, et al., Deformation twinning in nanocrystalline Al by molecular-dynamics simulation[J]. Acta Mater. 50(20), 5005–5020 (2002)
V. Yamakov, D. Wolf, S.R. Phillpot, et al., Dislocation processes in the deformation of nanocrystalline aluminium by molecular-dynamics simulation[J]. Nat. Mater. 1(1), 45–49 (2002)
T. Zhu, H. Gao, Plastic deformation mechanism in nanotwinned metals: an insight from molecular dynamics and mechanistic modeling[J]. Scripta Mater. 66(11), 843–848 (2012)
A. Moitra, Grain size effect on microstructural properties of 3D nanocrystalline magnesium under tensile deformation[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 79(Complete), 247–251 (2013)
Z.S. You, X.Y. Li, L.J. Gui et al., Plastic anisotropy and associated deformation mechanisms in nanotwinned metals[J]. Acta Mater. 61(1), 217–227 (2013)
Y. Zhao, X. Wei, Y. Zhang et al., Crystallization of amorphous materials and deformation mechanism of nanocrystalline materials under cutting loads: a molecular dynamics simulation approach[J]. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 439, 21–29 (2016)
Influence of cutting parameters on the depth of, subsurface deformed layer in nano-cutting process of single crystal copper[J]. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10(1), 396 (2015)
T. Kadoyoshi, H. Kaburaki, F. Shimizu et al., Molecular dynamics study on the formation of stacking fault tetrahedra and unfaulting of Frank loops in FCC metals[J]. Acta Mater. 55(9), 3073–3080 (2007)
R.G. Hoagland, Molecular dynamics studies of the interaction of /6 <112> Shockley dislocations with stacking fault tetrahedra in copper. Part I: intersection of SFT by an isolated Shockley[J]. Philos. Mag. 89(7), 623–640 (2009)
X. Zhao, C. Lu, A.K. Tieu et al., Deformation twinning and dislocation processes in nanotwinned copper by molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 142, 59–71 (2018)
J. Li, J. Guo, H. Luo et al., Study of nanoindentation mechanical response of nanocrystalline structures using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 364(3), 190–200 (2016)
J. Li, B. Liu, H. Luo et al., A molecular dynamics investigation into plastic deformation mechanism of nanocrystalline copper for different nanoscratching rates[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 118, 66–76 (2016)
Y.B. Guo, T. Xu, M. Li, Hierarchical dislocation nucleation controlled by internal stress in nanocrystalline copper[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(24), 241910–241910 (2013)
Y.B. Guo, T. Xu, M. Li, Generalized type III internal stress from interfaces, triple junctions and other microstructural components in nanocrystalline materials[J]. Acta Mater. 61(13), 4974–4983 (2013)
Liu. Research on Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polycrystalline Materials[D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin (2009)
F. Liu, Y.C. Liang, Q.S. Bai, Y.B. Guo, Molecular dynamics simulation of nanometric cutting of polycrystalline copper[J]. Tool Eng. 44(2), 31–34 (2010)
S. Goel, A. Kovalchenko, A. Stukowski et al., Influence of microstructure on the cutting behaviour of silicon[J]. Acta Mater. 105, 464–478 (2016)
J. Shi, Y. Wang, X. Yang, Nano-scale machining of polycrystalline coppers—effects of grain size and machining parameters[J]. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 1–18 (2013)
C. Ji, J. Shi, Y. Wang et al., Tool/chip interfacial stress distributions in atomistic machining of polycrystalline coppers[C]. ASME 2014 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference Collocated with the Jsme 2014 International Conference on Materials and Processing and the, North American Manufacturing Research Conference. V001T03A019 (2014)
S.Z. Chavoshi, S. Goel, X. Luo, Molecular dynamics simulation investigation on the plastic flow behaviour of silicon during nanometric cutting[J]. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 24(1), 015002 (2016)
J. Li, J. Guo, H. Luo et al., Study of nanoindentation mechanical response of nanocrystalline structures using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 364(3), 190–200 (2015)
H.T. Liu, X.F. Zhu, Y.Z. Sun et al., Evolution of stacking fault tetrahedral and work hardening effect in copper single crystals[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 422, 413–419 (2017)
Q. Liu, L. Deng, X. Wang et al., Formation of stacking fault tetrahedron in single-crystal Cu during nanoindentation investigated by molecular dynamics[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 131, 44–47 (2017)
S. Mojumder, T. Rakib, D. Datta, Hardening mechanism of polycrystalline Al–Cu alloy nanowire through tensile loading[J]. 2017
M. Chamani, G.H. Farrahi, M.R. Movahhedy, Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoindentation of nanocrystalline Al/Ni multilayers[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 112, 175–184 (2016)
P.Z. Zhu, C. Qiu, F.Z. Fang et al., Molecular dynamics simulations of nanometric cutting mechanisms of amorphous alloy[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 432–442 (2014)
T. Xu, M. Li, Topological and statistical properties of a constrained Voronoi tessellation[J]. Philos. Mag. 89(4), 349–374 (2009)
S. Plimpton, J. Comp. Phys. 117, 1–19 (1995). http://lammps.sandia.gov/
M. Stukowski, Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2009)
S.M. Foiles, M.I. Baskes, M.S. Daw, Phys. Rev. B Cond. Matt. 33, 7983 (1986)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments[J]. J. Mater. Res. 7(06), 1564–1583 (1992)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51475108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Hao, M., Tao, M. et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of dislocation evolution and surface mechanical properties on polycrystalline copper. Appl. Phys. A 125, 214 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2508-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2508-x