Abstract
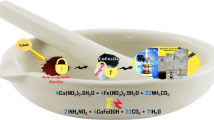
Combination of co-precipitation and hydrothermal methods is a promising route to synthesize various materials. Herein, we synthesized reduced graphene oxide/manganese ferrite (rGO/MnFe2O4) nanocomposites through combining a co-precipitation reaction of Mn2+ and Fe3+ ions in GO solution with subsequent hydrothermal treatment at different temperatures (80, 130, and 180 °C). The resulting rGO/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites were characterized using X-ray diffractometry, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and magnetic measurements at room temperature. The influence of hydrothermal temperature on structural, morphological, magnetic and As(III) adsorption properties of rGO/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites was studied. Increasing hydrothermal temperature leads to better crystallinity, magnetic properties, and As(III) adsorption capacity. At the hydrothermal temperature of 180 °C, the resulting rGO/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites exhibited a crystalline size of 37.2 nm, saturated magnetization of 22.7 emu/g, and As(III) removal efficiency of 83% at neutral pH (pH ≈ 7).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Wang, X. Wu, W. Zhang, S. Huang, One-pot synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Mater. Technol. 32, 32–37 (2017)
I. Kotutha, E. Swatsitang, W. Meewassana, S. Maensiri, One-pot hydrothermal synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical properties of rGO/MnFe2O4 nanocomposites. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 06FH10 (2015)
S.-F. Zhou, X.-J. Han, H.-L. Fan, J. Huang, Y.-Q. Liu, Enhanced electrochemical performance for sensing Pb (II) based on graphene oxide incorporated mesoporous MnFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 747, 447–454 (2018)
S. Chella, P. Kollu, E.V.P. Komarala, S. Doshi, M. Saranya, S. Felix, R. Ramachandran, P. Saravanan, V.L. Koneru, V. Venugopal, Solvothermal synthesis of MnFe2O4-graphene composite—investigation of its adsorption and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 327, 27–36 (2015)
H. Tang, P. Gao, A. Xing, S. Tian, Z. Bao, One-pot low-temperature synthesis of a MnFe2O4–graphene composite for lithium ion battery applications. RSC Adv. 4, 28421–28425 (2014)
K. Wu, G. Hu, Y. Cao, Z. Peng, K. Du, Facile and green synthesis of MnFe2O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 161, 178–180 (2015)
Z. Yang, Y. Huang, D. Ji, G. Xiong, H. Luo, Y. Wan, Hydrazine hydrate-induced hydrothermal synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles dispersed on graphene as high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 43, 10905–10912 (2017)
A.-T. Le, C.D. Giang, T.Q. Tuan, V.N. Phan, J. Alonso, J. Devkota, E. Garaio, J. García, R. Martín-Rodríguez, M.L. Fdez-Gubieda, Enhanced magnetic anisotropy and heating efficiency in multi-functional manganese ferrite/graphene oxide nanostructures. Nanotechnology 27, 155707 (2016)
Y. Yang, H. Shi, Y. Wang, B. Shi, L. Guo, D. Wu, S. Yang, H. Wu, Graphene oxide/manganese ferrite nanohybrids for magnetic resonance imaging, photothermal therapy and drug delivery. J. Biomater. Appl. 30, 810–822 (2016)
A.G. Tabrizi, N. Arsalani, A. Mohammadi, H. Namazi, L.S. Ghadimi, I. Ahadzadeh, Facile synthesis of a MnFe2O4/rGO nanocomposite for an ultra-stable symmetric supercapacitor. New J. Chem. 41, 4974–4984 (2017)
S. Kumar, R.R. Nair, P.B. Pillai, S.N. Gupta, M. Iyengar, A. Sood, Graphene oxide–MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 17426–17436 (2014)
S. Zhang, H. Niu, Y. Cai, X. Zhao, Y. Shi, Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on coprecipitated bimetal oxide magnetic nanomaterials: MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4. Chem. Eng. J. 158, 599–607 (2010)
S. Bai, X. Shen, X. Zhong, Y. Liu, G. Zhu, X. Xu, K. Chen, One-pot solvothermal preparation of magnetic reduced graphene oxide-ferrite hybrids for organic dye removal. Carbon 50, 2337–2346 (2012)
X. Peng, J. Qu, S. Tian, Y. Ding, X. Hai, B. Jiang, M. Wu, J. Qiu, Green fabrication of magnetic recoverable graphene/MnFe2O4 hybrids for efficient decomposition of methylene blue and the Mn/Fe redox synergetic mechanism. RSC Adv. 6, 104549–104555 (2016)
R. Rafiee, A. Eskandariyun, Comparative study on predicting Young’s modulus of graphene sheets using nano-scale continuum mechanics approach. Phys. E 90, 42–48 (2017)
N.U. Yamaguchi, R. Bergamasco, S. Hamoudi, Magnetic MnFe2O4–graphene hybrid composite for efficient removal of glyphosate from water. Chem. Eng. J. 295, 391–402 (2016)
P.T.L. Huong, N. Tu, H. Lan, N. Van Quy, P.A. Tuan, N.X. Dinh, V.N. Phan, A.-T. Le, Functional manganese ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites: effects of graphene oxide on the adsorption mechanisms of organic MB dye and inorganic As (v) ions from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 8, 12376–12389 (2018)
C. Liu, Z.J. Zhang, Size-dependent superparamagnetic properties of Mn spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized from reverse micelles. Chem. Mater. 13, 2092–2096 (2001)
R. Upadhyay, K. Davies, S. Wells, S. Charles, Preparation and characterization of ultra-fine MnFe2O4 and MnxFe1–xFe2O4 spinel systems: I. particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 132, 249–257 (1994)
P.T.L. Huong, V.N. Phan, T.Q. Huy, M.H. Nam, V.D. Lam, A.-T. Le, Application of graphene oxide-MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids as magnetically separable adsorbent for highly efficient removal of arsenic from water. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 2372–2380 (2016)
T.V. Thu, P.J. Ko, T.V. Nguyen, N.T. Vinh, D.M. Khai, L.T. Lu, Green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/Ag ternary nanohybrid and its application as magnetically recoverable catalyst in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol, Appl. Organomet. Chem. 31 (2017)
K.V. Sankar, R.K. Selvan, The preparation of MnFe2O4 decorated flexible graphene wrapped with PANI and its electrochemical performances for hybrid supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 4, 17555–17566 (2014)
T.V. Thu, P.J. Ko, N.H.H. Phuc, A. Sandhu, Room-temperature synthesis and enhanced catalytic performance of silver-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids. J. Nanoparticle Res. 15, 1–13 (2013)
Y. Sang, H. Liu, X. Sun, X. Zhang, H. Qin, Y. Lv, D. Huo, D. Liu, J. Wang, R.I. Boughton, Formation and calcination temperature-dependent sintering activity of YAG precursor synthesized via reverse titration method. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 2407–2413 (2011)
Y. Sang, Y. Lv, H. Qin, X. Zhang, H. Liu, J. Wang, X. Sun, R.I. Boughton, Chemical composition evolution of YAG co-precipitate determined by pH during aging period and its effect on precursor properties. Ceram. Int. 38, 1635–1641 (2012)
A. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56, 978 (1939)
H. Cui, Y. Liu, W. Ren, Structure switch between α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 during the large scale and low temperature sol–gel synthesis of nearly monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 93–97 (2013)
Y. Jiang, C. Hu, H. Cheng, C. Li, T. Xu, Y. Zhao, H. Shao, L. Qu, Spontaneous, straightforward fabrication of partially reduced graphene oxide–polypyrrole composite films for versatile actuators. ACS Nano 10, 4735–4741 (2016)
G. Titelman, V. Gelman, S. Bron, R. Khalfin, Y. Cohen, H. Bianco-Peled, Characteristics and microstructure of aqueous colloidal dispersions of graphite oxide. Carbon 43, 641–649 (2005)
K.N. Kudin, B. Ozbas, H.C. Schniepp, R.K. Prud’Homme, I.A. Aksay, R. Car, Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 8, 36–41 (2008)
C. Liu, B. Zou, A.J. Rondinone, Z.J. Zhang, Reverse micelle synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 1141–1145 (2000)
V. Chandra, J. Park, Y. Chun, J.W. Lee, I.-C. Hwang, K.S. Kim, Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 4, 3979–3986 (2010)
Y. Yoon, W.K. Park, T.-M. Hwang, D.H. Yoon, W.S. Yang, J.-W. Kang, Comparative evaluation of magnetite–graphene oxide and magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composite for As (III) and As (V) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 304, 196–204 (2016)
G. Zhao, J. Li, X. Ren, C. Chen, X. Wang, Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 10454–10462 (2011)
X. Luo, C. Wang, L. Wang, F. Deng, S. Luo, X. Tu, C. Au, Nanocomposites of graphene oxide-hydrated zirconium oxide for simultaneous removal of As (III) and As (V) from water. Chem. Eng. J. 220, 98–106 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under Grant number 103.02-2015.100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thu, T.V., Thao, V.D. Influence of temperature on structure, morphology, and magnetic property of graphene–MnFe2O4 nanocomposites synthesized by a combined hydrothermal/co-precipitation method. Appl. Phys. A 124, 675 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2092-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2092-5