Abstract
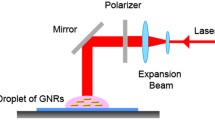
Light-driven self-assembly and coalescence of two nearby hetero-shaped gold nanorods (GNRs) with different lengths are studied theoretically. The optical forces and torques, in terms of Maxwell’s stress tensor, upon these GNRs provided by a linearly polarized (LP) plane wave are analyzed using the multiple multipole (MMP) method. Numerical results show that the optical torque dominates their alignments and the optical force their attraction. The most likely outcome of the plasmon-mediated light–matter interaction is wavelength dependent. Three different coalescences of the two GNRs could be induced by a LP light in three different wavelength regimes, respectively. For example, the side-by-side coalescence of two GNRs with radius of 15 nm and different lengths (120 and 240 nm) is induced in water as irradiated by a LP light at 633 nm, the T-shaped one at 1064 nm, and the end-to-end one at 1700 nm. The plasmonic attractive force and heating power densities inside GNRs with different gaps are also studied; the smaller the gap, the larger the attractive force and heating power. The results imply that the plasmonic coalescence and heating of two discrete GNRs may cause the local fusion at the junction of the assembly and the subsequent annealing (even recrystallization). Because the heating makes the two discrete GNRs fused to become a new nanostructure, the plasmonic coalescence of optical manipulation is irreversible.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.L. Juan, M. Righini, R. Quidant, Plasmon nano-optical tweezers. Nat. Photonics 5, 349–356 (2011)
C. Min, Z. Shen, J. Shen, Y. Zhang, H. Fang, G. Yuan, L. Du, S. Zhu, T. Lei, X. Yuan, Focused plasmonic trapping of metallic particles. Nat. Commun. 4, 2891 (2013)
T.V. Raziman, R.J. Wolke, O.J.F. Martin, Optical forces in nanoplasmonic systems: how do they work, what can they be useful for? Faraday Discuss 178, 421–434 (2015)
A. Serkov et al., Self-assembly of nanoparticles into nanowires under laser exposure in liquids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 623, 93–97 (2015)
R.A. Nome, M.J. Guffey, N.F. Scherer, S.K. Gray, Plasmonic interactions and optical forces between Au bipyramidal nanoparticle dimers. J. Phys. Chem. A 113(16), 4408–4415 (2009)
M. Fujii, Finite-difference analysis of plasmon-induced forces of metal nano-clusters by the Lorentz force formulation. Opt. Express 18(26), 27731–27747 (2010)
J.W. Liaw, H.Y. Wu, C.C. Huang, M.K. Kuo, Metal enhanced fluorescence of silver island associated with silver nanoparticle. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 26 (2016)
S.V. Perminov, V.P. Drachev, S.G. Rautian, Optical bistability driven by the light-induced forces between metal nanoparticles. Opt. Lett. 33(24), 2998–3000 (2008)
R. Zhao, P. Tassin, T. Koschny, C.M. Soukoulis, Optical forces in nanowire pairs and metamaterials. Opt. Express 18(25), 25665–25676 (2010)
Q. Zhang et al., Reversal of optical binding force by Fano resonance in plasmonic nanorod heterodimer. Opt. Express 21(5), 6601–6608 (2013)
Y.Q. Wang, W.S. Liang, C.Y. Geng, Coalescence behavior of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 4, 684–688 (2009)
G. González-Rubio, J. González-Izquierdo, L. Bañares, G. Tardajos, A. Rivera, T. Altantzis, S. Bals, O. Peña-Rodríguez, A. Guerrero-Martínez, L.M. Liz-Marzán, Femtosecond laser-controlled tip-to-tip assembly and welding of gold nanorods. Nano Lett. 15(12), 8282–8288 (2015)
T. Iida, Control of plasmonic superradiance in metallic nanoparticle assembly by light-induced force and fluctuations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 332–336 (2012)
L. Tong, V.D. Miljković, M. Käll, Alignment, rotation, and spinning of single plasmonic nanoparticles and nanowires using polarization dependent optical forces. Nano Lett. 10, 268–273 (2010)
J.W. Liaw, W.J. Lo, M.K. Kuo, Wavelength-dependent longitudinal polarizability of gold nanorod on optical torque. Opt. Express 22(9), 10858–10867 (2014)
J.W. Liaw, W.J. Lo, W.C. Lin, M.K. Kuo, Theoretical study of optical torques for alignments of Ag nanorod and nanowire. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 162, 133–142 (2015)
J.W. Liaw, Y.S. Chen, M.K. Kuo, Maxwell stress induced optical torque upon gold prolate nanospheroid. Appl. Phys. A 122(3), 182 (2016)
M. Moocarme, B. Kusin, L.T. Vuong, Plasmon-induced Lorentz forces of nanowire chiral hybrid modes. Opt. Mater. Express 4(11), 2355–2367 (2014)
A. Babynina, M. Fedoruk, P. Kühler, A. Meledin, M. Döblinger, T. Lohmüller, Bending gold nanorods with light. Nano Lett. 16, 6485–6490 (2016)
J.W. Liaw, W.C. Lin, M.K. Kuo, Wavelength-dependent plasmon-mediated coalescence of two gold nanorods. Sci. Rep. 7, 46095 (2017)
S. Ito, H. Yamauchi, M. Tamura, S. Hidaka, H. Hattori, T. Hamada, K. Nishida, S. Tokonami, T. Itoh, H. Miyasaka, T. Iida, Selective optical assembly of highly uniform nanoparticles by doughnut-shaped beams. Sci. Rep. 3, 3047 (2013)
S.Y. Yu, H. Gunawan, S.W. Tsai, Y.J. Chen, T.C. Yen, J.W. Liaw, Single-crystalline gold nanowires synthesized from light-driven oriented attachment and plasmon-mediated self-assembly of gold nanorods or nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 7, 44680 (2017)
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370–4379 (1972)
J. Aizpurua, G.W. Bryant, L.J. Richter, F.J. García de Abajo, B.K. Kelley, T. Mallouk, Optical properties of coupled metallic nanorods for field-enhanced spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 71, 235420 (2005)
L. Ling, H.L. Guo, X.L. Zhong, L. Huang, J.F. Li, L. Gan, Z.Y. Li, Manipulation of gold nanorods with dual-optical tweezers for surface plasmon resonance control. Nanotechnology 23, 215302 (2012)
M. Gordel, K. Piela, R. Kołkowski, T. Kozlecki, M. Buckle, M. Samoc, End-to-end self-assembly of gold nanorods in isopropanol solution: experimental and theoretical studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 17, 477 (2015)
B. Ingham, T.H. Lim, C.J. Dotzler, A. Henning, M.F. Toney, R.D. Tilley, How nanoparticles coalesce: an in situ study of Au nanoparticle aggregation and grain growth. Chem. Mater. 23, 3312–3317 (2011)
J. Wang, S. Chen, K. Cui, D. Li, D. Chen, Approach and coalescence of gold nanoparticles driven by surface thermodynamic fluctuations and atomic interaction forces. ACS Nano 10, 2893–2902 (2016)
S. Raza, S.M. Esfandyarpour, A.L. Koh, N.A. Mortensen, M.L. Brongersma, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, Electron energy-loss spectroscopy of branched gap plasmon resonators. Nat. Commun. 7, 13790 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 103-2221-E-182-033-MY2, 103-2112-M-019-003-MY3, 104-2221-E-182-053, 105-2221-E-182-031, 105-2221-E-002-079) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CIRPD2E0032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liaw, JW., Chao, HY., Huang, CW. et al. Light-driven self-assembly of hetero-shaped gold nanorods. Appl. Phys. A 124, 16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1432-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1432-1