Abstract
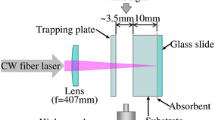
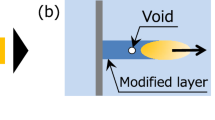
Pulsed-laser-induced glass fiber generation has been reported. We demonstrate a novel glass fiber generation technique by continuous-wave laser illumination and reveal the generation mechanism. In this technique, borosilicate glass, metal foil, and a heat insulator are stacked and clamped by a jig as the sample. Glass fibers are ejected from the side surface of the borosilicate glass by laser illumination of the sample from the borosilicate glass side. SEM observation shows that nanoparticles are attached on the glass fibers. High-speed imaging reveals that small bubbles are formed at the side surface of the borosilicate glass and the bursting of the bubble ejects the fibers. The temperature at the fiber ejection point is estimated to be ~1220 K. The mechanism of the fiber ejection includes the following steps: the metal thin foil heated by the laser increases the temperature of the surrounding glass by heat conduction. Since the absorption coefficient of the glass is increased by increasing the temperature, the glass starts to absorb the laser irradiation. The heated glass softens and bubbles form. When the bubble bursts, molten glass and gas inside the bubble scatter into the air to generate the glass fibers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Herszberg, H.C.H. Li, F. Dharmawan, A.P. Mouritz, M. Nguyen, J. Bayandor, Compos. Struct. 67, 205 (2005)
J. Paz, J. Díaz, L. Romera, M. Costas, Compos. Struct. 133, 499 (2015)
S. Hamid, M.R. Ehsani, J. Struct. Eng. 117, 3417 (1991)
M. Kupke, H.P. Wentzel, K. Schulte, Mat. Res. Innov. 2, 164 (1998)
Y. Takahashi, T. Mohri, Earozoru Kenkyu 6, 4 (1991) (in Japanase)
B. Tan, K. Venkatakrishnan, Opt. Express 17, 1064 (2009)
V.N. Tokarev, S. Lazare, C. Belin, D. Debarre, Appl. Phys. A 79, 717 (2004)
S. Itoh, M. Sakakura, Y. Shimotsuma, K. Miura, Appl. Phys. B 119, 519 (2015)
M. Sivakumar, K. Venkatakrishnan, B. Tan, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 4, 1263 (2009)
K. Venkatakrishnan, D. Vipparty, B. Tan, Opt. Express 19, 15770 (2011)
G.A.J. Markillie, H.J. Baker, F.J. Villarreal, D.R. Hall, Appl. Opt. 41, 5660 (2002)
M. Yamane, I. Yasui, M. Wada, Y. Kokubu, R. Terai, K. Kondo, S. Ogawa, Handbook of glass engineering, 1st edn. (Asakura Publishing Co., Ltd, Japan, 1999), pp. 356–377 (in Japanase)
H. Hidai, M. Yoshioka, K. Hiromastu, H. Tokura, Appl. Phys. A 94, 869 (2009)
H. Hidai, N. Saito, S. Matsusaka, A. Chiba, N. Morita, Appl. Phys. A 122, 4 (2016)
S. Itoh, H. Hidai, H. Tokura, Appl. Phys. A 112, 4 (2013)
H. Hidai, M. Yoshioka, K. Hiromatsu, H. Tokura, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 6 (2010)
A. Goldsmith, T.E. Waterman, J.J. Hirschhorn, Handbook of thermophysical properties of solid materials, vol. 3 (Pergamon Press, New York, 1961), p. 871
D. Bäuerle, Laser processing and chemistry, 4th edn. (Springer, New York, 2011), p. 21
S. Todoroki, Fiber fuse: light-induced continuous breakdown of silica glass optical fiber (Springer Japan, Tokyo, 2014), pp. 51–52
Acknowledgements
Support by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science under a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B, 20360065) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishioka, N., Hidai, H., Matsusaka, S. et al. Continuous-wave laser-induced glass fiber generation. Appl. Phys. A 123, 600 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1210-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1210-0