Abstract
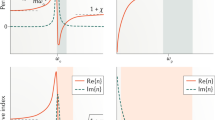
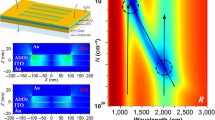
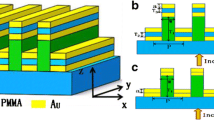
Electro-optic (EO) polymers offer a very attractive possibility of realizing low-cost microwave photonic components with a wide bandwidth and a low driving voltage, thanks to a low dispersion from microwave to optical frequency of polymeric materials on the one hand, and the progress in the synthesis of high hyperpolarizability chromophores on the other hand. This paper studies the influence of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticle loading on the microwave and optical properties of EO polymers. Thus, poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and disperse red 1 (DR1) are used as host polymer and guest EO chromophore, respectively. With 1–3% TiO2 nanoparticle homogeneously incorporated in the polymer, the dielectric constant varies from 2.73 to 3.40 over the 400 MHz–10 GHz range, and the refractive index increases from 1.483 to 1.488 at the wavelength of 1539.6 nm. It is shown that fine tuning of dielectric constant and refractive index could allow improvement of the microwave photonic component bandwidth. For example, with an EO interaction length L = 2 cm (typical length of EO modulators), the ultimate modulator bandwidth could be raised to 258 GHz by loading PMMA–DR1 EO polymer with 1% wt of TiO2 nanoparticles. It is also found that loading polymer with nanoparticles could improve the EO response of poled polymers, represented by the intensity of the second-harmonic-generation (SHG) signal. The latter presents more than a threefold increase by loading PMMA–DR1 EO polymer with 2% wt TiO2 nanoparticles.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Arizmendi, Phys. Status Solidi A 201, 253–283 (2004)
W.K. Burns, M.M. Howerton, R.P. Moeller, R. Krahenbuhl, R.W. McElhanon, A.S. Greenblatt, J. Light. Technol. 17, 2551–2555 (1999)
S. Huang, T.-D. Kim, J. Luo, S.K. Hau, Z. Shi, X.-H. Zhou, H.-L. Yip, A.K.-Y. Jen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 243311–243313 (2010)
D.M.Y. Enami, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 093505 (2007)
M. Hadjloum, M. El Gibari, H.W. Li, A.S. Daryoush, Opt. Commun. 373, 82–90 (2016)
B.M.A. Rahman, V. Haxha, S. Haxha, K.T.V. Grattan, J. Light. Technol. 24, 3506–3513 (2006)
S. Gross, D. Camozzo, V. Di Noto, L. Armelao, E. Tondello, Eur. Polym. J. 43, 673–696 (2007)
R.R. Prakash, S. Pandiarajan, P. Venkatesh, N. Kamaraj, in Emerging Trends in Electrical and Computer Technology, 2011 International Conference on, 46–49 (2011)
M.G. Kuzyk, C.W. Dirk, J.E. Sohn, JOSA B 7, 842–858 (1990)
B. Derkowska-Zielinska, O. Krupka, A. Wachowiak, V. Smokal, A. Grabowski, in Transparent Optical Networks, 2015 17th International Conference on, 1–3 (2015)
T. Pliska, W.-R. Cho, A.-C. Le Duff, V. Ricci, A. Otomo, M. Canva, P. Raimond, F. Kajzar, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17, 1554–1564 (2000)
A.H. Yuwono, J. Xue, J. Wang, H.I. Elim, W. Ji, Y. Li, T.J. White, J. Mater. Chem. 13, 1475–1479 (2003)
C.C. Evans, C. Liu, J. Suntivich, Opt. Express 23, 11160–11169 (2015)
Z. Ma, Andrew J. Becker, P. Polakos, H. Huggins, J. Pastalan, H. Wu, K. Watts, Y.H. Wong, P. Mankiewic, Electr. Dev. IEEE Trans. 45, 1811–1816 (1998)
T. Schneider, PhD Thesis, Université de Nantes, France, 2006
D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering, 4th edn. (Wiley, Hoboken, 2012)
K. R. Philippe-Auguste, PhD Thesis, Université de Nantes, France, 2012
J.G. Grote, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 8584–8591 (2004)
L. Liu, Z.H. Yang, L.B. Kong, W.Y. Yin, S. Wang, Appl. Phys. A 108, 843–848 (2012)
G. Wan, L. Yu, X. Peng, G. Wang, X. Huang, H. Zhao, Y. Qin, RSC Adv 5, 77443–77448 (2015)
K. Karkkainen, A. Sihvola, K. Nikoskinen, I.E.E.E. Trans, Geosci. Remote Sens. 39, 1013–1018 (2001)
A.V. Goncharenko, V.Z. Lozovski, E.F. Venger, Opt. Commun. 174, 19–32 (2000)
B.M. Suleiman, Appl. Phys. A 99, 223–228 (2010)
M. Yoshida, M. Lal, N.D. Kumar, P.N. Prasad, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4047–4051 (1997)
B. Guiffard, D. Guyomar, L. Seveyrat, Y. Chowanek, M. Bechelany, D. Comu, P. Miele, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 055503 (2009)
B. Guiffard, L. Seveyrat, G. Sebald, D. Guyomar, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 3053–3057 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Anthony Rousseau who is with Institut des Molécules et Matériaux du Mans (IMMM) for the TEM image. The financial support of region Pays de la Loire under the Project ADC PolyNano is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palessonga, D., El Gibari, M., Ginestar, S. et al. Bandwidth improvement of microwave photonic components based on electro-optic polymers loaded with TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 123, 542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1154-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1154-4