Abstract
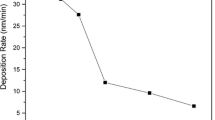
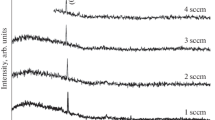
Zinc oxide thin films were deposited on glass substrates at different oxygen flow rates by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. The oxygen flow rate was found to be one of the crucial parameters which influence structural, optical and electrical properties of grown films. The structural and optical characterization of the deposited films was carried out using X-ray diffraction and UV–visible spectroscopy, respectively. Swanepoel envelope and Drude–Lorentz (DL) models were applied to extract the optoelectronic parameters such as refractive index, dispersion energy and plasma frequency. Structurally, grain size was found to decrease with increase in oxygen flow rate during deposition. Moreover, all the films exhibited preferred (002) orientation confirming c-axis orientation of the films perpendicular to the substrate. For a particular range of oxygen flow rates, columnar growth was achieved. Marginal increase in the optical band gap from 3.14 to 3.22 eV was observed as the oxygen flow rate increased from 3 to 10 sccm. Calculated plasma frequency from the DL model was found to be in the infrared region. It has decreased as oxygen flow rate increased with the value from 1.625 × 1014 rad/s (862 cm−1) to 1.072 × 1014 rad/s (568 cm−1).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Garcia-Mendez, A. Bedora-Calle, R.R. Segura, V. Coello, Investigation of the annealing effects on the structural and optoelectronic properties of RF-sputtered ZnO films studied by the Drude–Lorentz model. Appl. Phys. A 120, 1375 (2015)
D.C. Look, Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 80, 383 (2001)
J.-L. Tian, H.-Y. Zhang, G.-G. Wang, X.-Z. Wang, R. Sun, L. Jin, J.-C. Han, Influence of film thickness and annealing temperature on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films on Si (100) substrates grown by atomic layer deposition. Superlattices Microstruct. 83, 719 (2015)
Y. Nishi, T. Miyata, T. Minami, The impact of heterojunction formation temperature on obtainable conversion efficiency in n-ZnO/p-Cu2O solar cells. Thin Solid Films 528, 72 (2013)
S.S. Wilson, J.P. Bosco, Y. Tolstova, D.O. Scanlon, G.W. Watson, H.A. Atwater, Interface stoichiometry control to improve device voltage and modify band alignment in ZnO/Cu2O heterojunction solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3606 (2014)
S. Ilican, M. Caglar, Y. Calgar, Preparation and characterization of ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel spin coating method. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 10, 2578 (2008)
M. Benhaliliba, C.E. Benouis, M.S. Aida, A. Sanchez Juarez, F. Yakuphanoglud, A. Tiburcio Silver, A comparative study on structural, optical, photoconductivity properties of In and Al doped ZnO thin films grown onto glass and FTO substrates grown by spray pyrolysis process. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 548 (2010)
S.S. Jeong, A. Mittiga, E. Salza, A. Masci, S. Passerini, Electrodeposited ZnO/Cu2O heterojunction solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 53, 2226 (2008)
W.T. Yen, Y.C. Lin, J.H. Ke, Surface textured ZnO: Al thin films by pulsed DC magnetron sputtering for solar cell applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 960 (2010)
G. Kiriakidis, M. Suchea, S. Christoulakis, P. Horvath, T. Kitsopoulos, J. Stoemenos, Structural characterization of ZnO thin films by dc magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 515, 8577 (2007)
E. Sachet, M.D. Losego, J. Guske, S. Franzen, J.P. Maria, Mid infrared surface plasmon resonance in zinc oxide semiconductor thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 0511111 (2013)
Dongping Zhang, Ping Fan, Xingmin Cai, Jianjun Huang, Lili Ru, zhuanghao Zheng, Guangxing Liang, Yukun Huang, Properties of ZnO thin films deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering under different plasma power. Appl. Phys. A. 97, 437–441 (2009)
S. Uthanna, T.K. Subramanyam, B.S. Naidu, G.M. Rao, Structure-composition-property dependence in reactive magnetron sputtered ZnO thin films. Opt. Mater. 19, 461 (2002)
R. Swanepoel, Determination of the thickness and optical constants of amorphous silicon. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 16, 1214 (1983)
K.J. Saji, M.K. Jayaraj, Effect of oxygen partial pressure on optical and electrical properties of co-sputtered amorphous zinc indium tin oxide thin films. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 205, 1625 (2008)
M. Fox, Optical properties of solids, 2nd edn. (Oxford University Press, New York, 2011). ISBN 978-0-19-957337-0
C.R. Aita, A.J. Purdes, K.L. Lad, P.D. Funkenbusch, The effect of O2 on reactively sputtered zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 5533 (1980)
E.M. Alkoy, P.J. Kelly, Structure and properties of copper oxide and copper aluminum oxide coatings prepared by pulsed magnetron sputtering of power targets. Vacuum 79, 221 (2005)
A. Frolich, M. Wegener, Spectroscopic characterization of highly doped ZnO films grown by atomic-layer deposition for three-dimensional infrared metamaterials. Opt. Mater. Express 1–5, 883 (2011)
S.H. Wemple, M. DiDomenico Jr, Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys. Rev. B 3–4, 1338 (1971)
R.N. Gayen, K. Sarkar, S. Hussain, R. Bhar, A.K. Pal, ZnO films prepared by modified sol gel technique. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 49, 470 (2011)
D.K. Madhup, D.P. Subedi, A. Huczko, Optoelectron. Influence of doping on optical properties of ZnO nano films. Adv. Mater. 4–10, 1582 (2010)
B.L. Zhu, J. Wang, S.J. Zhu, J. Wu, R. Wu, D.W. Zeng, C.S. Xie, Influence of hydrogen introduction on structure and properties of ZnO thin films during sputtering and post-annealing. Thin Solid Films 519, 3809 (2011)
Z.H. Zhang, M. He, Q. Li, Obtaining the effective electron mass from valence electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Solid State Commun. 149, 1856 (2009)
Y. Imanaka, M. Oshikiri, K. Takehana, T. Takamasu, G. Kido, Strong Coulomb correlation effects in ZnO. Phys. B 298, 211 (2001)
M. Oshikiri, Y. Imanaka, F. Aryasetiawan, G. Kido, Comparison of the electron effective mass of the n-type ZnO in the wurtzite structure measured by cyclotron resonance and calculated from first principle theory. Phys. B 298, 472 (2001)
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Manipal University for the financial support to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobbiner, C.R., Ali Avanee Veedu, M. & Kekuda, D. Influence of oxygen flow rate on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO films grown by DC magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. A 122, 272 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9806-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9806-3