Abstract
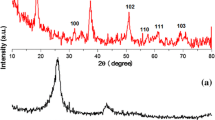
Nanoporous/cracked structures of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) electrodes were successfully fabricated by electroplating of zinc–cobalt onto previously formed TiO2 nanotubes by anodizing of titanium, leaching of zinc in a concentrated alkaline solution and followed by drying and annealing at 400 °C. The structure and morphology of the obtained Co3O4 electrodes were characterized by X-ray diffraction, EDX analysis and scanning electron microscopy. The results showed that the obtained Co3O4 electrodes were composed of the nanoporous/cracked structures with an average pore size of about 100 nm. The electrochemical capacitive behaviors of the nanoporous Co3O4 electrodes were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge–discharge studies and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in 1 M NaOH solution. The electrochemical data demonstrated that the electrodes display good capacitive behavior with a specific capacitance of 430 F g−1 at a current density of 1.0 A g−1 and specific capacitance retention of ca. 80 % after 10 days of being used in electrochemical experiments, indicating to be promising electroactive materials for supercapacitors. Furthermore, in comparison with electrodes prepared by simple cathodic deposition of cobalt onto TiO2 nanotubes(without dealloying procedure), the impedance studies showed improved performances likely due to nanoporous/cracked structures of electrodes fabricated by dealloying of zinc, which provide fast ion and electron transfer routes and large reaction surface area with the ensued fast reaction kinetics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Markoulidis, C. Lei, C. Lekakou, Appl. Phys. A doi:10.1007/s00339-012-7471-8
S.G. Kandalkar, J.L. Gunjakar, C.D. Lokhande, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 5540 (2008)
T. Cottineau, M. Toupin, T. Delahaye, T. Brousse, D. Belanger, Appl. Phys. A 82, 599 (2006)
Y. Gao, S. Chen, D. Cao, G. Wang, J. Yin, J. Power Sources 195, 1757 (2010)
W.C. Li, G.Z. Nong, A.H. Lu, H.Q. Hu, J. Porous Mater. 18, 23 (2011)
W. Kim, M.Y. Kang, J.B. Joo, N.D. Kim, I.K. Song, P. Kim, J.R. Yoon, J. Yi, J. Power Sources 195, 2125 (2010)
F. Gobal, M. Faraji, J. Electroanal. Chem. 691, 51 (2013)
Y. Xie, D. Fu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 122, 23 (2010)
Y. Wang, H. Wang, X. Wang, Electrochim. Acta 92, 298 (2013)
R. Tummala, R.K. Guduru, P.S. Mohanty, J. Power Sources 209, 44 (2012)
R.P. Antony, T. Mathews, S. Dash, A.K. Tyagi, B. Raj, Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 957 (2012)
I. Herraiz-Cardona, E. Ortega, V. Pérez-Herranz, Electrochim. Acta 56, 1308 (2011)
D.K. Pawar, J.S. Shaikh, B.S. Pawar, S.M. Pawar, P.S. Patil, S.S. Kolekar, J. Porous Mater. 19, 649 (2012)
Y. Li, K. Huang, S. Liu, Z. Yao, S. Zhuang, J. Solid State Electrochem. 15, 587 (2011)
Y.Q. Zhang, X.H. Xia, J. Kang, J.P. Tu, Chin. Sci. Bull. 57, 32 (2012)
D. Kalpana, K.S. Omkumar, S. Suresh Kumar, N.G. Renganathan, Electrochim. Acta 52, 1309 (2006)
M. Selvakumar, D. Krishna Bhat, A. Manish Aggarwal, S. PrahladhIyer, G. Sravani, Phys. B 405, 2286 (2010)
N. Padmanathan, S. Selladurai, Ionics 20, 409 (2014)
N. Padmanathan, S. Selladurai, Ionics 20, 479 (2014)
X. Wang, S. Liu, H. Wang, F. Tu, D. Fang, Y. Li, J. Solid State Electrochem. 16, 3593 (2012)
K.S. Kim, S.J. Park, J. Solid State Electrochem. 16, 2751 (2012)
Y.F. Li, Y.Z. Liu, Y.G. Yang, M.Z. Wang, Y.F. Wen, Appl. Phys. A 108, 701 (2012)
C. Xia, Y. Xie, Y. Wang, W. Wang, H. Du, F. Tian, J. Appl. Electrochem. 43, 1225 (2013)
T.C. Girija, M.V. Sangaranarayanan, J. Power Sources 156, 705 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express thanks to the office of vice chancellor of research of Sharif University of Technology for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobal, F., Faraji, M. Preparation and electrochemical performances of nanoporous/cracked cobalt oxide layer for supercapacitors. Appl. Phys. A 117, 2087–2094 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8623-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8623-9