Abstract
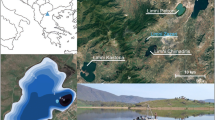
The Lindu plain, located in the northern mountainous region of the Lore Lindu National Park in Sulawesi, Indonesia, provides many ecosystem services for the population inhabiting the area and harbours a unique biodiversity. Palynological, charcoal and diatom analyses of a lake sediment core from Lake Lindu (Danau Lindu) reveal that during the last 1,000 years the Lindu plain has been modified by human activities. Evidence of frequent burning and possible shifting cultivation from an earlier phase from ca. ad 1000 to 1200 might be related to the metal age population which erected the megaliths in the province of Central Sulawesi. From ca. ad 1200–1700 there followed 500 years of wetter climate conditions, corresponding to the southward movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone. At the same time, decreases of macro-charcoal concentrations and pioneer vegetation indicators show that the use of the landscape of Lindu plain had become more permanent. Following a phase of forest recovery from ca. ad 1730 to 1910, the most recent part of the Lake Lindu record shows a trend towards deforestation that started in the late 20th century, lasting until now. The lake level started to fall at the beginning of the 20th century, as shown by the increase of sedimentation rate and supported by low pollen concentration and palaeomagnetic data. Such a change was unprecedented for the last 1,000 years covered by the record, and it has no link to the climate variability as reconstructed for the last hundred years. If deforestation increases and a larger amount of water is channelled away from the lake for irrigation purposes, the lake level will continue to fall. This suggests that there is a need for better management of the forests surrounding the plain and of the irrigation systems in the area open for cultivation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acciaioli GL (1989) Searching for good fortune: the making of a Bugis shore community at Lake Lindu, Central Sulawesi. Unpublished dissertation, Australian National University, Canberra
Acciaioli GL (2000) Kinship and debt: the social organization of Bugis migration and fish marketing at Lake Lindu, Central Sulawesi. Bijdraden tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde 156:589–617
Acciaioli GL (2001) Grounds of conflict, idioms of harmony: custom, religion, and nationalism in violence avoidance at the Lindu Plain, Central Sulawesi. Indonesia (Cornell Southeast Asia Program) 72:81–112
Adriani N, Kruyt AC (1898) Van Posso naar Parigi, Sigi en Lindoe. Mededeelingen van wege het Nederlandsche Zendelinggenootschap 42:369–535
Ali M, Oda H, Hayashida A, Takemura K, Torii M (1999) Holocene palaeomagnetic secular variation at Lake Biwa, central Japan. Geophys J Int 136:218–228
Barletta F, Channell JET, Rochon A (2010) Dating of Holocene western Canadian Arctic sediments by matching paleomagnetic secular variation to a geomagnetic field model. Quat Sci Rev 29:2,315–2,324
Bellwood P (1979) Man’s conquest of the Pacific. The prehistory of Southeast Asia and Oceania. Oxford University Press, New York
Biagioni S, Wündsch M, Haberzettl T, Behling H (2015) Assessing resilience/sensitivity of tropical mountain rainforests towards climate variability of the last 1500 years: the long-term perspective at Lake Kalimpaa (Sulawesi, Indonesia). Rev Palaeobot Palynol 213:42–53
Cane MA (2005) The evolution of El Niño, past and future. Earth Planet Sci Lett 230:227–240
Cannon CH, Summers M, Harting JR, Kessler PJA (2007) Developing conservation priorities based on forest type, condition, and threats in a poorly known ecoregion: sulawesi, Indonesia. Biotropica 39:747–759
Carris LM, Castlebury LA (2006) Nonsystemic bunt fungi—Tilletia indica and T. horrida: a review of history, systematics, and biology. Ann Rev Phytopathol 44:113–133
Chaturvedi M, Datta K, Nair KK (1998) Pollen morphology of Oryza (Poaceae). Grana 37:79–86
Clarke MD, Carney WP, Cross JH, Hadidjaja P, Oemijati S, Joesoef A (1974) Schistosomiasis and other human parasitoses of Lake Lindu in Central Sulawesi (Celebes) Indonesia. Am J Trop Med Hyg 23:385–392
Culmsee H, Pitopang R (2009) Tree diversity in sub-montane and lower montane primary rain forests in Central Sulawesi. Blumea 54:119–123
Culmsee H, Leuschner C, Moser G, Pitopang R (2010) Forest above ground biomass along an elevational transect in Sulawesi, Indonesia, and the role of Fagaceae in tropical montane rain forests. J Biogeogr 37:960–974
Culmsee H, Ramadhanil P, Mangopo H, Sabir S (2011) Tree diversity and phytogeographical patterns of tropical high mountain rain forests in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Biodivers Conserv 20:1,103–1,123
Dam RAC, Fluin J, Suparan P, Van der Kaars S (2001) Palaeoenvironmental developments in the Lake Tondano area (N. Sulawesi, Indonesia) since 33,000 years bp. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 171:147–183
Davis GJ (1976) Parigi: a social history of the Balinese movement to Central Sulawesi, 1907–1974. PhD dissertation, Stanford University, Stanford
Duran R, Fischer GW (1961) The genus Tilletia. Washington State University, Pullman
Fægri K, Iversen J (1989) Textbook of pollen analysis, 4th edn. (by Fægri K, Kaland PE and Krzywinski K) Wiley, Chichester
Finsinger W, Tinner W (2005) Minimum count sums for charcoal concentration estimates in pollen slides: accuracy and potential errors. Holocene 15:293–297
Flenley JR (1967) Highland Papua New Guinea pollen flora I. In: Flenley JR (eds) The present and former vegetation of the Wabag region of New Guinea. Dissertation, Australian National University Canberra (extract at http://palaeoworks.anu.edu.au/databases.html)
Garrett-Jones SE (1979) Pollen flora: lowland Papua New Guinea. In: Garrett-Jones SE (ed) Evidence for changes in Holocene vegetation and lake sedimentation in the Markham Valley, Papua New Guinea. Dissertation, Australian National University, Canberra (extract at http://palaeoworks.anu.edu.au/databases.html)
Gomez N, Riera J, Sabater S (1995) Ecology and morphological variability of Aulacoseira granulata (Bacillariophyceae) in Spanish reservoirs. J Plankton Res 17:1–16
Grimm E (1987) CONISS: a FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput Geosci 13:13–35
Grimm E (1993) TILIA v20 (computer software). Illinois State Museum Research and Collections Center, Springfield
Gunawan D (2006) Atmospheric variability in Sulawesi, Indonesia, regional atmospheric model results and observations. Doctoral dissertation, University of Göttingen, Göttingen
Guy-Ohlson D (1992) Botryococcus as an aid in the interpretation of palaeoenvironment and depositional processes. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 71:1–15
Haberzettl T, St-Onge G, Behling H, Kirleis W (2013) Evaluating Late Holocene radiocarbon-based chronologies by matching palaeomagnetic secular variations to geomagnetic field models: an example from Lake Kalimpaa (Sulawesi, Indonesia). Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 373:245–259
Haug GH, Hughen KA, Sigman DM, Peterson LC, Röhl U (2001) Southward migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone through the Holocene. Science 29:1,304–1,308
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1,965–1,978
Horner RR, Welch EB, Seeley MR, Jacoby JM (1990) Responses of periphyton to changes in current velocity, suspended sediment and phosphorus concentration. Freshwater Biol 24:215–232
Huang TC (1972) Pollen flora of Taiwan. Ching-Hwa Press, Taipei
Jantz N, Homeier J, Behling H (2013) Representativeness of tree diversity in the modern pollen rain of Andean montane forests. J Veget Sci 25:317–613
Juggins S (2007) C2 Version 15 User guide software for ecological and palaeoecological data analysis and visualisation. Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne
Kaudern W (1925) Migrations of the Toradja in central Celebes. Ethnographical studies in Celebes 2: Results of the author’s expedition to Celebes 1917-1920. Elanders Boktryckeri Aktiebolag II, Göteborg
Kaudern W (1938) Megalithic finds in Central Celebes. Ethnographical studies in Celebes 5: Results of the author’s expedition to Celebes 1917-1920. Elanders Boktryckeri Aktiebolag V, Göteborg
Kessler PJA, Bos MM, Sierra Daza SEC, Kop A, Willemse LPM, Pitopang R, Gradstein SR (2002) Checklist of woody plants of Sulawesi, Indonesia. (Blumea, Journal of Plant taxonomy and plant geography, Supplement 14) Nationaal Herbarium Nederland, Universiteit Leiden Branch, Leiden
Kirilova EP, Van Hardenbroek M, Heiri O, Cremer H, Lotter AF (2010) 500 years of trophic-state history of a hypertrophic Dutch dike-breach lake. J Paleolimnol 43:829–842
Kirleis W, Pillar VD, Behling H (2011) Human-environment interactions in mountain rainforests: archaeobotanical evidence from central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Veget Hist Archaeobot 20:165–179
Kirleis W, Müller J, Kortemeier C, Behling H, Soegondho S (2012) Chapter 16: The megalithic landscape of central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Combining archaeological and palynological investigations. In: Bonatz D, Reinecke A, Tjoa-Bonatz ML (eds) Crossing borders in Southeast Asian archaeology. NUS Press, Singapore, pp 199–220
Kirschvink JL (1980) The least-squares line and plane and the analysis of palaeomagnetic data. Geophys J Roy Astr Soc 62:699–718
Korte M, Constable C (2011) Improving geomagnetic field reconstructions for 0–3 ka. Phys Earth Planet In 188:247–259
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1986) Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2, Teil 2: Bacillariophyceae. Fischer, Jena
Kreisel W, Weber R, Faust H (2004) Historical impacts on use and management of natural resources in the rainforest margins of Central Sulawesi. In: Gerold G, Fremerey M, Guhardja E (eds) Land use, nature conservation and the stability of rainforest margins in Southeast Asia. Springer, Berlin, pp 39–65
Leemhuis C, Gerold G (2006) The impact of the warm phase of ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation) events on water resource availability of tropical catchments in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Adv Geosci 6:217–220
Lehmusluoto P (1997) National inventory of the major lakes and reservoirs in Indonesia: general limnology. University of Helsinki, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Helsinki
Mazaud A (2005) User-friendly software for vector analysis of the magnetization of long sediment cores. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 6:1,525–2,027
Moss SJ, Wilson MEJ (1998) Biogeographic implications from the Tertiary palaeogeographic evolution of Sulawesi and Borneo. In: Hall R, Holloway JD (eds) Biogeography and geological evolution of SE Asia. Backhuys, Leiden, pp 133–163
Ólafsdóttir S, Geirsdóttir A, Miller GH, Stoner JS, Channell JET (2013) Synchronizing Holocene lacustrine and marine sediment records using paleomagnetic secular variation. Geology 41:535–538
Philander SGH (1990) El Niño, La Niña, and the southern oscillation. Academic Press, San Diego
Powell JM (1970) Highland Papua New Guinea pollen flora II. In: Powell JM (ed) The impact of man on the vegetation of the Mt. Hagen region, New Guinea. Dissertation, Australian National University, Canberra (extract at http://palaeoworks.anu.edu.au/databases.html)
Renberg I (1991) The HON-Kajak sediment corer. J Paleolimnol 6:167–170
Rhodes AN (1998) A method for the preparation and quantification of microscopic charcoal from terrestrial and lacustrine sediment cores. Holocene 8:113–117
Sarasin P, Sarasin F (1905) Reisen in Celebes: ausgeführt in den Jahren 1893–1896 and 1902–1903. Kreidel, Wiesbaden
Scott Anderson R, Homola RL, Davis RB, Jacobson GL Jr (1984) Fossil remains of the mycorrhizal fungal Glomus fasciculatum complex in postglacial lake sediments from Maine Canadian. Can J Bot 62:2,325–2,328
Stevenson J (1998) New Caledonia pollen flora. In: Stevenson J (ed) Late Quaternary environmental change and the impact of Melanesian colonization in New Caledonia. Unpublished doctoral thesis, University of New South Wales, Kensington (extract at http://palaeoworks.anu.edu.au/databases.html)
Stevenson J, Haberle SG (2005) Macro charcoal analysis: A modified technique used by the Department of Archaeology and Natural History. (PalaeoWorks Technical Report 5) Australian National University, Canberra
Stoner JS, St-Onge G (2007) Magnetic stratigraphy in paleoceanography: Reversals, excursions, paleointensity, and secular variation. In: Hillaire-Marcel C, De Vernal A (eds) Proxies in Late Cenozoic: paleoceanography. (Developments in Marine Geology 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 99–138
St-Onge G, Stoner JS (2011) Paleomagnetism near the north magnetic pole: a unique vantage point for understanding the dynamics of the geomagnetic field and its secular variations. Oceanography 24:42–50
Sudomo M, Patrick Carney W, Kurniawan L (1990) 20 years of progress in schistosomiasis research. Bul Penelit Kesehat 18:18–23
Sukendar H (1976) Obyek kepurbakalaan di Palu Sulawesi Tengah [Archaeological objects in Palu, central Sulawesi, in Indonesian]. Kalpataru 3:61–104
Sukendar H (1980a) Mencari peninggalan nenek moyang, pendukung tradisi megalitik di Tanah Bada (Sulteng) [Looking for ancestors, supporting megalithic tradition in the Land Bada (Sulawesi), in Indonesian]. Kalpataru 5:1–63
Sukendar H (1980b) Tinjauan tentang peninggalan tradisi megalitik di daerah Sulawesi Tengah [Overview of the relics of megalithic tradition in Central Sulawesi, in Indonesian]. Pertemuan Ilmiah Arkeologi 1977
Ter Braak C, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO Reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (version 45). Microcomputer Power, Ithaka
Tierney JE, Russell JM (2007) Abrupt climate change in southeast tropical Africa influenced by Indian monsoon variability and ITCZ migration. Geophys Res Lett 34:1–6
Tierney JE, Oppo DW, Rosenthal Y, Russell JM, Linsley BK (2010) Coordinated hydrological regimes in the Indo-Pacific region during the past two millennia. Paleoceanogr 25:1–7
Valentyn F (1724–1726) Oud en Nieuwe Oost-Indiën, Vervattende een Naaukerige en uitvoerige Verhandelinge van Nederlands Mogentheyd in die Gewesten, benevens eene wydlustige Beschryvinge der Moluccos, Ambonia, Banda, Timor, en Solor, Java, en alle de Eylanden onder de zelve Landbestieringen behoorende; het Comptoir op Suratte, en de Levens der Groote Mogols, 5 vols 5. Dordrecht
Van Dam H, Mertens A, Sinkeldam J (1994) A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from The Netherlands. Aquat Ecol 28:117–133
Wang LC, Lee TQ, Chen SH, Wu JT (2010) Diatoms in Liyu Lake, Eastern Taiwan. Taiwania 55:228–242
Wang LC, Behling H, Lee TQ, Li HC, Huh CA, Shiau LJ, Chen SH, Wu JT (2013) Increased precipitation during the Little Ice Age in northern Taiwan inferred from diatoms and geochemistry in a sediment core from a subalpine lake. J Paleolimnol 49:619–631
Weber R, Kreisel W, Faust H (2003) Colonial interventions on the cultural landscape of central Sulawesi by “Ethical Policy”: the impact of the Dutch rule in Palu and Kulawi valley, 1905–1942. Asian J Soc Sci 31:398–434
WorldClim (2006) WorldClim version 14, Bioclim ESRI grids 30 arc-seconds (1 km) resolution. Available at: http://www.worldclim.org
Wündsch M, Biagioni S, Behling H, Reinwarth B, Franz S, Bierbaß P, Daut G, Mäusbacher R, Haberzettl T (2014) ENSO and monsoon variability during the past 1.5 kyr as reflected in sediments from Lake Kalimpaa, Central Sulawesi (Indonesia). Holocene 24:1,743–1,756
Yang X, Heller F, Yang J, Su Z (2009) Paleosecular variations since ~ 9000 yr bp as recorded by sediments from maar lake Shuangchiling, Hainan, South China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 288:1–9
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out as part of the project “Environmental and land-use change in Sulawesi, Indonesia (ELUC)” at Göttingen University, Germany, and was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) BE 2116/22-1. We appreciate the financial support provided by a grant from the National Science Council (NSC 102-2917-I-564-058) and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (KERDC201301). Torsten Haberzettl was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship scholarship from Fonds de recherche du Québec - Nature et technologies (FQRNT). We gratefully acknowledge Wiebke Kirleis for support in field work and thank for the logistic support the ELUC coordination team and the Indonesian partner universities in Bogor and Palu, Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB) and Universitas Tadulako (UNTAD), the Ministry of Education in Jakarta (DIKTI), the Indonesian Institute of Sciences (LIPI) and the authorities of Lore Lindu National Park. Finally, the authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Yasuda.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biagioni, S., Haberzettl, T., Wang, LC. et al. Unravelling the past 1,000 years of history of human–climate–landscape interactions at the Lindu plain, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Veget Hist Archaeobot 25, 1–17 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-015-0523-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-015-0523-1