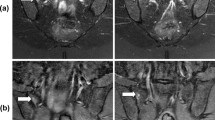
Abstract
Objective
To compare the diagnostic performance of two different sets of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the detection of subchondral erosions in the sacroiliac joints regarding the application of fat-water separation techniques when acquiring T1-weighted (T1w) images, using multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) as the reference standard.
Methods
We retrospectively included 31 consecutive patients having or being suspected for axial spondyloarthritis (SpA) assessed using both MRI and MDCT. Three sets of images were independently assessed for the presence of erosions by two musculoskeletal radiologists (R1, R2): (1) MRI with standard T1w without fat suppression, (2) MRI with both T1w with and without fat suppression, and (3) MDCT. The diagnostic performance of both sets of MRIs was assessed using MDCT as the referent.
Results
The assessment of T1w images with fat suppression substantially increased sensitivity (76% vs. 63% R1; 70% vs. 60% R2), specificity (97% vs. 84% R1; 96% vs. 81% R2), positive predictive value (85% vs. 45% R1; 81% vs. 40% R2), and overall accuracy (94% vs. 80% R1; 92% vs. 77% R2) in the detection of erosions when compared to the assessment using T1w images without fat suppression.
Conclusion
The assessment of T1w images with fat suppression substantially improves the diagnostic performance of MRI in the detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints.
Key Points
• The presence of erosions in the sacroiliac joints may influence the decision on the diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis.
• T1w fat-suppressed MR imaging relatively increases the contrast between the joint space (high signal) and the adjacent subchondral bone (low signal), potentially improving the detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints.
• T1w fat-suppressed images improve the diagnostic performance of MRI in the detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints compared to T1w without fat suppression, using MDCT as the reference.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASAS:
-
Assessment in SpondyloArthritis International Society
- IDEAL:
-
Iterative Decomposition of water and fat Echo Asymmetry and Least squares estimation
- MDCT:
-
Multi-detector computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SpA:
-
Spondyloarthritis
- STIR:
-
Short tau inversion recovery
References
Lambert RGW, Bakker PAC, van der Heijde D et al (2016) Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1958–1963
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–783
Bakker PAC, van den Berg R, Lenczner G et al (2017) Can we use structural lesions seen on MRI of the sacroiliac joints reliably for the classification of patients according to the ASAS axial spondyloarthritis criteria? Data from the DESIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 76:392–398
Diekhoff T, Hermann KA, Greese J et al (2017) Comparison of MRI with radiography for detecting structural lesions of the sacroiliac joint using CT as standard of reference: results from the SIMACT study. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1502–1508
Diekhoff T, Greese J, Sieper J, Poddubnyy D, Hamm B, Hermann KA (2018) Improved detection of erosions in the sacroiliac joints on MRI with volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (VIBE): results from the SIMACT study. Ann Rheum Dis 77:1585–1589
Melchior J, Azraq Y, Chary-Valckenaere I et al (2017) Radiography, abdominal CT and MRI compared with sacroiliac joint CT in diagnosis of structural sacroiliitis. Eur J Radiol 95:169–176
Hu L, Huang Z, Zhang X et al (2014) The performance of MRI in detecting subarticular bone erosion of sacroiliac joint in patients with spondyloarthropathy: a comparison with x-ray and CT. Eur J Radiol 83:2058–2064
Madsen KB, Jurik AG (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging grading system for active and chronic spondylarthritis changes in the sacroiliac joint. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 62:11–18
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Michel D. Crema, MD.
Conflict of interest
Professor Yves Menu is the Editor-in-Chief of European Radiology and has therefore not taken part in the review or selection process of this article. One of the authors (Ling Li) is employed by Pfizer Inc. The remaining authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors (Ling Li) has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• cross sectional study/diagnostic study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crema, M.D., Miquel, A., Gouvion, A. et al. Improved detection of subchondral erosions in the sacroiliac joints with T1-weighted fat-suppressed MRI. Eur Radiol 31, 6810–6815 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07785-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07785-1