Abstract
Objective
To compare overall survival (OS) and local recurrence (LR) following radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and cryoablation (CA) for very early and early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
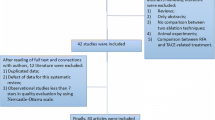
This systematic review was performed according to the PRISMA guidelines. MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies were included. OS and LR at 1 year and 3 years were assessed. OS was reported as hazard ratio (HR) with 95% credible intervals (CrI) and LR as relative risk (RR) with 95% CrI, to summarize effect of each comparison.
Results
Nineteen studies (3043 patients), including six RCTs and 13 observational studies, met inclusion criteria. For OS at 1 year, as compared to RFA, CA had HR of 0.81 (95% CrI: 0.43–1.51), and MWA had HR of 1.01 (95% CrI: 0.71–1.43). For OS at 3 years, as compared to RFA, CA had HR of 0.90 (95% CrI: 0.48–1.64) and MWA had HR of 1.07 (95% CrI: 0.73–1.50). For LR at 1 year, CA and MWA had RR of 0.75 (95% CrI: 0.45–1.24) and 0.93 (95% CrI: 0.78–1.14), respectively, as compared to RFA. For LR at 3 years, CA and MWA had RR of 0.96 (0.74–1.23) and 0.98 (0.87–1.09), respectively, as compared to RFA. Overall, none of the comparisons was statistically significant. Age of patients and tumor size did not influence treatment effect.
Conclusions
RFA, MWA, and CA are equally effective for locoregional treatment of very early and early HCC.
Key Points
• There is no significant difference in the OS and LR (at 1 year and 3 years) following ablation of very early and early HCC with RFA, MWA, and CA.
• There was no effect of tumor size on the treatment efficacy.
• More RCTs comparing CA with RFA and MWA should be performed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Cryoablation
- CrI:
-
Credible interval
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- LR:
-
Local recurrence
- LTP:
-
Local tumor progression
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- RR:
-
Relative risk
References
White DL, Thrift AP, Kanwal F, Davila J, El-Serag HB (2017) Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in all 50 United States, from 2000 through 2012. Gastroenterology 152(4):812–820. e5
Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M (2016) Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 150(4):835–853
Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS et al (2018) AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67(1):358–380
Shiina S, Sato K, Tateishi R et al (2018) Percutaneous ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of various ablation techniques and surgery. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018:4756147
Kalra N, Gupta P, Chawla Y, Khandelwal N (2015) Locoregional treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: the best is yet to come. World J Radiol 7(10):306–318
Kalra N, Gupta P, Gorsi U et al (2019) Irreversible electroporation for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: initial experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42(4):584–590
Vietti Violi N, Duran R, Guiu B et al (2018) Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: a randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(5):317–325
Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y et al (2002) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223(2):331–337
Kamal A, Elmoety AAA, Rostom YAM, Shater MS, Lashen SA (2019) Percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. J Gastrointest Oncol 10(3):562–571
Abdelaziz A, Elbaz T, Shousha HI et al (2014) Efficacy and survival analysis of percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an Egyptian multidisciplinary clinic experience. Surg Endosc 28(12):3429–3434
Yu J, Yu XL, Han ZY et al (2017) Percutaneous cooled-probe microwave versus radiofrequency ablation in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised controlled trial. Gut 66(6):1172–1173
Tait IS, Yong SM, Cuschieri SA (2002) Laparoscopic in situ ablation of liver cancer with cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation. Br J Surg 89(12):1613–1619
Bilchik AJ, Wood TF, Allegra D et al (2000) Cryosurgical ablation and radiofrequency ablation for unresectable hepatic malignant neoplasms: a proposed algorithm. Arch Surg 135(6):657–662
Adam R, Hagopian EJ, Linhares M et al (2002) A comparison of percutaneous cryosurgery and percutaneous radiofrequency for unresectable hepatic malignancies. Arch Surg 137(12):1332–1339
Kalra N, Gupta P, Jugpal T et al (2020) Percutaneous cryoablation of liver tumors: initial experience from a tertiary care center in India. J Clin Exp Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2020.10.005
Cha SY, Kang TW, Min JH et al (2020) RF ablation versus cryoablation for small perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: propensity score analyses of mid-term outcomes. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 43(3):434–444
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Wu Y et al (2020) Efficacy and safety of percutaneous argon-helium cryoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 31(3):393–400.e1
Hu J, Chen S, Wang X, Lin N, Yang J, Wu S (2019) Image-guided percutaneous microwave ablation versus cryoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in high-risk locations: intermediate-term results. Cancer Manag Res 11:9801–9811
Wang F, Ma J, Wu L et al (2020) Percutaneous cryoablation of subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 57 cases. Diagn Interv Radiol 26(1):34–39
Wang C, Wang H, Yang W et al (2015) Multicenter randomized controlled trial of percutaneous cryoablation versus radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 61(5):1579–1590
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM et al (2015) The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med 162(11):777–784
Woods BS, Hawkins N, Scott DS (2010) Network meta-analysis on the log-hazard scale, combining count and hazard ratio statistics accounting for multi-arm trials. A tutorial. BMC Med Res Methodol 10:54
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355:i4919
R Core Team (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 14 May 2020
Valkenhoef G, Kuiper J (2016) gemtc: Network meta-analysis using Bayesian methods. R package version 0.8–2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gemtc. Accessed 14 May 2020
Plummer M (2019) rjags: Bayesian graphical models using MCMC. R package version 4–10. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rjags. Accessed 14 May 2020
Plummer M (2003) JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international workshop on distributed statistical computing
Ghweil A, Osman H (2019) Percutaneous microwave and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study. Hepatol Int 13(1):1–266
Liu W, Zheng Y, He W et al (2018) Microwave vs radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a propensity score analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 48(6):671–681
Zhang L, Wang N, Shen Q, Cheng W, Qian GJ (2013) Therapeutic efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 8(10):e76119
Xu J, Noda C, Erickson A et al (2018) Radiofrequency ablation vs. cryoablation for localized hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-matched population study. Anticancer Res 38(11):6381–6386
Vogl TJ, Farshid P, Naguib NN et al (2015) Ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study between radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Abdom Imaging 40(6):1829–1837
Potretzke TA, Ziemlewicz TJ, Hinshaw JL et al (2016) Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison of efficacy at a single center. J Vasc Interv Radiol 27(5):631–638
Sever IH, Suku M, Biyikli E (2018) Radiofrequency and microwave ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Iran J Radiol 15(3):e62396
Lu MD, Xu HX, Xie XY et al (2005) Percutaneous microwave and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective comparative study. J Gastroenterol 40(11):1054–1060
Ding J, Jing X, Liu J et al (2013) Comparison of two different thermal techniques for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 82(9):1379–1384
Xu Y, Shen Q, Wang N et al (2017) Microwave ablation is as effective as radiofrequency ablation for very-early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Cancer 36(1):14
Zhang NN, Cheng XJ, Liu JY (2014) Comparison of high-powered MWA and RFA in treating larger hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pract Oncol 4:349–356
Shum JK, Fung TP, Wong SW (2016) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. RCSEd/CSHK Conjoint Scientific Congress, Making Wise Choices in Surgery, 17–18 September 2016, Aberdeen, Hong Kong. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-1633.12208
Facciorusso A, Di Maso M, Muscatiello N (2016) Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperthermia 32:339–344
Tan W, Deng Q, Lin S, Wang Y, Xu G (2019) Comparison of microwave ablation and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperthermia 36(1):264–272
Wu S, Hou J, Ding Y et al (2015) Cryoablation versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies: a systematic review and literature-based analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(49):e2252
Huang YZ, Zhou SC, Zhou H, Tong M (2013) Radiofrequency ablation versus cryosurgery ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatogastroenterology 60(125):1131–1135
Rong G, Bai W, Dong Z et al (2015) Long-term outcomes of percutaneous cryoablation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. PLoS One 10(4):e0123065
Lin Y, Wen Q, Guo L, Wang H, Sui G, Sun Z (2018) A network meta-analysis on the efficacy and prognosis of different interventional therapies for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Hyperthermia 35(1):450–462
Lan T, Chang L, Rahmathullah MN, Wu L, Yuan YF (2016) Comparative efficacy of interventional therapies for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(15):e3185
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Pankaj Gupta (pankajgupta959@gmail.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors (Dr. Praveen Kumar-M) has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was not required because this is a systematic review.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was not required because this is a systematic review.
Methodology
• Systematic review and meta-analysis
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 10687 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, P., Maralakunte, M., Kumar-M, P. et al. Overall survival and local recurrence following RFA, MWA, and cryoablation of very early and early HCC: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 31, 5400–5408 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07610-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07610-1