Abstract
Objectives
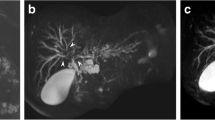
The current study evaluated the clinical usefulness of the gradient and spin-echo (GRASE) sequence with single breath-hold in 3.0 T magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). We compared the acquisition time and image quality between GRASE and breath navigator-triggered 3D turbo spin echo (3D TSE).
Methods
We examined 54 consecutive patients who underwent MRCP with GRASE and 3D TSE. We compared the image acquisition time and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) between the common bile duct (CBD) and liver. Overall image quality, blurring, motion artifacts and CBD visibility were scored on a 4-point scale by two radiologists. Paired t-tests were used to compare the variables.
Results
The mean image acquisition time was 95 % shorter with the GRASE than with 3D TSE (GRASE: 20 s; 3D TSE: 6 min 27 s). The CNR of GRASE was significantly higher than that of 3D TSE (GRASE: 25.4 ± 13.9 vs. 3D TSE: 18.2 ± 9.6, p < 0.01). All qualitative scores for GRASE were significantly better than those for 3D TSE.
Conclusions
3.0 T MRCP with GRASE sequence with single breath-hold significantly improved the CNR of CBD with a 95 % shorter acquisition time compared with conventional 3D MRCP with 3D TSE.
Key Points
• MRCP acquisition time was 95% shorter with GRASE than with 3D TSE.
• Overall image quality of GRASE was significantly better than 3D TSE.
• Pancreaticobiliary tree visibility with GRASE was better than that with 3D TSE.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBD:
-
Common bile duct
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise ratio
- EPI:
-
Echo-planar imaging
- GRASE:
-
Gradient and spin-echo
- MPD:
-
Main pancreatic duct
- SE:
-
Spin-echo
- TSE:
-
Turbo spin-echo
References
Mazziotti S, Costa C, Ascenti G, Gaeta M, Pandolfo A, Blandino A (2005) MR cholangiopancreatography diagnosis of juxtapapillary duodenal diverticulum simulating a cystic lesion of the pancreas: usefulness of an oral negative contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:432–435
Valls C, Alba E, Cruz M et al (2005) Biliary complications after liver transplantation: diagnosis with MR cholangiopancreatography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:812–820
Aube C, Delorme B, Yzet T et al (2005) MR cholangiopancreatography versus endoscopic sonography in suspected common bile duct lithiasis: a prospective, comparative study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:55–62
Asbach P, Klessen C, Kroencke TJ et al (2005) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using a free-breathing T2-weighted turbo spin-echo sequence with navigator-triggered prospective acquisition correction. Magn Reson Imaging 23:939–945
Kinner S, Dechene A, Ladd SC et al (2010) Comparison of different MRCP techniques for the depiction of biliary complications after liver transplantation. Eur Radiol 20:1749–1756
Morita S, Ueno E, Suzuki K et al (2008) Navigator-triggered prospective acquisition correction (PACE) technique vs. conventional respiratory-triggered technique for free-breathing 3D MRCP: an initial prospective comparative study using healthy volunteers. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:673–677
Zhang J, Israel GM, Hecht EM, Krinsky GA, Babb JS, Lee VS (2006) Isotropic 3D T2-weighted MR cholangiopancreatography with parallel imaging: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1564–1570
Schindera ST, Miller CM, Ho LM, DeLong DM, Merkle EM (2007) Magnetic resonance (MR) cholangiography: quantitative and qualitative comparison of 3.0 Tesla with 1.5 Tesla. Invest Radiol 42:399–405
Yokoyama K, Nakaura T, Iyama Y et al (2016) Usefulness of 3D hybrid profile order technique with 3T magnetic resonance cholangiography: comparison of image quality and acquisition time. J Magn Reson Imaging 44:1346–1353
Taylor AC, Little AF, Hennessy OF, Banting SW, Smith PJ, Desmond PV (2002) Prospective assessment of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography for noninvasive imaging of the biliary tree. Gastrointest Endosc 55:17–22
Nandalur KR, Hussain HK, Weadock WJ et al (2008) Possible biliary disease: diagnostic performance of high-spatial-resolution isotropic 3D T2-weighted MRCP. Radiology 249:883–890
Feinberg DA, Oshio K (1991) GRASE (gradient- and spin-echo) MR imaging: a new fast clinical imaging technique. Radiology 181:597–602
Ba-Ssalamaha A, Schick S, Heimberger K et al (2000) Ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Magn Reson Imaging 18:237–243
Fernandez-Jimenez R, Sanchez-Gonzalez J, Aguero J et al (2015) Fast T2 gradient-spin-echo (T2-GraSE) mapping for myocardial edema quantification: first in vivo validation in a porcine model of ischemia/reperfusion. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17:92
Patel MR, Klufas RA, Shapiro AW (1995) MR imaging of diseases of the brain: comparison of GRASE and conventional spin-echo T2-weighted pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:963–966
Rockwell DT, Melhem ER, Bhatia RG (1997) GRASE (gradient- and spin-echo) MR of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1923–1928
Sprinkart AM, Luetkens JA, Traber F et al (2015) Gradient Spin Echo (GraSE) imaging for fast myocardial T2 mapping. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17:12
Yoshikawa T, Mitchell DG, Hirota S et al (2006) Gradient- and spin-echo T2-weighted imaging for SPIO-enhanced detection and characterization of focal liver lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:712–719
Yoshikawa T, Mitchell DG, Hirota S et al (2006) Focal liver lesions: breathhold gradient- and spin-echo T2-weighted imaging for detection and characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:520–528
Baessler B, Schaarschmidt F, Stehning C, Schnackenburg B, Maintz D, Bunck AC (2015) Cardiac T2-mapping using a fast gradient echo spin echo sequence - first in vitro and in vivo experience. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17:67
Itatani R, Namimoto T, Kusunoki S, Mizuguchi T, Ohtsuka S, Yamashita Y (2016) Usefulness of the short-echo time cube sequence at 3-T magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: prospective comparison with the conventional 3-dimensional fast spin-echo sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr 40:551–556
Hardy PA, Yue G (1997) Measurement of magnetic resonance T2 for physiological experiments. J Appl Physiol (1985) 83:904–911
Irie H, Honda H, Kuroiwa T et al (2001) Pitfalls in MR cholangiopancreatographic interpretation. Radiographics 21:23–37
Oshio K, Feinberg DA (1992) Single-shot GRASE imaging without fast gradients. Magn Reson Med 26:355–360
Isoda H, Maetani Y, Kataoka M et al (2008) Contrast behavior and image quality of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography imaging using variable echo times at 3.0 T. Clin Imaging 32:362–366
Jung G, Krahe T, Kugel H et al (1997) Prospective comparison of fast SE and GRASE sequences and echo planar imaging with conventional SE sequences in the detection of focal liver lesions at 1.0 T. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:341–347
Lee VS, Krinsky GA, Nazzaro CA et al (2004) Defining intrahepatic biliary anatomy in living liver transplant donor candidates at mangafodipir trisodium-enhanced MR cholangiography versus conventional T2-weighted MR cholangiography. Radiology 233:659–666
Kim JH, Hong SS, Eun HW, Han JK, Choi BI (2012) Clinical usefulness of free-breathing navigator-triggered 3D MRCP in non-cooperative patients: comparison with conventional breath-hold 2D MRCP. Eur J Radiol 81:e513–e518
Liu K, Xie P, Peng W, Zhou Z (2015) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: comparison of two- and three-dimensional sequences for the assessment of pancreatic cystic lesions. Oncol Lett 9:1917–1921
Acknowledgements
We thank Kazunori Shigemi of Philips Electronics Japan for the technical support.
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Yasuyuki Yamashita
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: We were received MR technical supports from Kazuki Shigemi of Philips Electronics Japan, Ltd.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• prospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• performed at one institution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, M., Nakaura, T., Inoue, T. et al. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with GRASE sequence at 3.0T: does it improve image quality and acquisition time as compared with 3D TSE?. Eur Radiol 28, 2436–2443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5240-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5240-y