Abstract
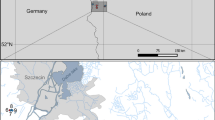
Studies on community structure of Antarctic benthos are mostly conducted on summer samplings, when ice-impacts and productivity blooms are intense. Few surveys performed during winter demonstrated that, despite temperatures and productivity stability, community structure is variable. In order to assess how polychaete community is influenced by seasonality and depth along a discontinuous year, six replicate samples were taken in nine surveys during winter and four in summer at two depths (12 and 25 m) in Admiralty Bay, King George Island. Spatial patchiness was more intense at 12 m presupposing ice-mediated and wave-induced disturbances, whereas 25-m patchiness among replicates was restricted to summer surveys. A pattern of temporal stability was partially confirmed in 12-m site. Deeper site was characterized by seasonality with dominant-species replacement reflecting shifts in organic matter availability. Diversity was higher in early and midwinter following both summer productivity blooms and macroalgal decomposition that extend the energy budget into the winter, analogous to microbial biomass supply of “food banks” that sustains the benthic ecosystem functions over winter in Antarctic Peninsula shelf deeper areas. Despite the opportunistic status of several nearshore polychaetes, it was possible to distinguish those that responded to organic enrichment (i.e., Capitella perarmata and Ophryotrocha notialis), from those associated with physical disturbances (i.e., Aphelochaeta cincinnatus and Levinsenia gracilis). Awareness of such patterns and their spatial and temporal variations will facilitate future studies on community assessment, especially those based on indicator species of benthic communities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46
Arnaud PM, Jażdżewski K, Presler P, Siciński J (1986) Preliminary survey of benthic invertebrates collected by Polish Antarctic expeditions in Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). Pol Polar Res 7:7–24
Arntz WE, Brey T, Gallardo VA (1994) Antarctic zoobenthos. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 32:241–304
Aronson RB, Moody RM, Ivany LC, Blake DB, Werner JE, Glass A (2009) Climate change and trophic response of the Antarctic bottom fauna. PLoS One 4:e4385
Aronson RB, Thatje S, McClintock JB, Hughes KA (2011) Anthropogenic impacts on marine ecosystems in Antarctica. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1223:82–107
Barbosa LS, Soares-Gomes A, Paiva PC (2010) Distribution of polychaetes in the shallow, sublittoral zone of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica in the early and late austral summer. Nat Sci 2:1155–1163
Barnes DKA (1999) The influence of ice on polar nearshore benthos. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 79:401–407
Barnes DKA, Conlan KE (2007) Disturbance, colonization and development of Antarctic benthic communities. Philos Trans R Soc B 362:11–38
Battershill CN (1990) Temporal changes in antarctic marine benthic community structure. NZ Antarct Rec 10:23–27
Bick A, Arlt G (2013) Description of intertidal macro- and meiobenthic assemblages in Maxwell Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Southern Ocean. Polar Biol 36:673–689
Bowden D (2005) Seasonality of recruitment in Antarctic sessile marine benthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 297:101–118
Bromberg S, Nonato EF, Corbisier TN, Petti MAV (2000) Polychaete distribution of the near shore zone of Martel Inlet, Admiralty Bay (King George Island, Antarctica). Bull Mar Sci 67:175–188
Brown KM, Fraser KPP, Barnes DKA, Peck LS (2004) Links between the structure of an Antarctic shallow-water community and ice-scour frequency. Oecologia 141:121–129
Clarke A (1996) Marine benthic populations in Antarctica: patterns and processes. In: Foundations for ecological research west of the Antarctic Peninsula. Antarct Res Ser 70:373–388
Clarke A, Johnson NM (2003) Antarctic marine benthic diversity. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 41:47–114
Colwell RK (2010) EstimateS: statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples. Version 8.2. User’s guide and application. http://purl.oclc.org/estimates. Accessed 29 Nov 2012
Colwell RK, Coddington JA (1994) Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 345:101–111
Conlan KE, Kim SL, Leninhan HS, Oliver JS (2004) Benthic changes during 10 years of organic enrichment by McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Mar Poll Bull 49:43–60
Conlan KE, Kim SL, Thurber AR, Hendrycks E (2010) Benthic changes at McMurdo Station, Antarctica following local sewage treatment and regional iceberg-mediated productivity decline. Mar Poll Bull 60:419–432
Corbisier TN, Petti MVA, Skowronski RSP, Brito TAS (2004) Trophic relationships in the nearshore zone of Martel Inlet (King George Island, Antarctica): δ13 C stable-isotope analysis. Polar Biol 27:75–82
Dayton PK (1989) Interdecadal variation in an Antarctic sponge and its predators from oceanographic climate shifts. Science 245:1484–1486
Echeverría CA, Paiva PC (2006) Macrofaunal shallow benthic communities along a discontinuous annual cycle at Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol 29:263–269
Echeverría CA, Paiva PC, Alves VC (2005) Composition and biomass of shallow benthic megafauna during an annual cycle in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 17:312–318
Fauchald K, Jumars PA (1979) The diet of worms: a study of polychaete feeding guilds. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 17:193–284
Gotelli NJ, Colwell RK (2010) Estimating species richness. In: Magurran AE, McGill BJ (eds) Frontiers in measuring biodiversity. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 39–54
Gutt J (2001) On the direct impact of ice on marine benthic communities, a review. Polar Biol 24:553–564
Gutt J (2007) Antarctic macro-zoobenthic communities: a review and an ecological classification. Antarct Sci 19:165–182
Gutt J, Piepenburg D (2003) Scale-dependent impact on diversity of Antarctic benthos caused by grounding of icebergs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 253:77–83
Hall SJ (1994) Physical disturbance and marine benthic communities: life in unconsolidated sediments. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 32:179–239
Hilbig B, Gerdes D, Montiel A (2006) Distribution patterns and biodiversity in polychaete communities of the Weddell Sea and Antarctic Peninsula area (Southern Ocean). J Mar Biol Ass UK 86:711–725
Jassby AD, Powell TM (1990) Detecting changes in ecological time series. Ecology 71:2044–2052
Jażdżewski K, Jurasz W, Kittel W, Presler E, Presler P, Siciński J (1986) Abundance and biomass estimates of the benthic fauna in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 6:5–16
Jażdżewski K, Teodorczyk W, Sicinski J, Kontek B (1991) Amphipod crustaceans as an important component of zoobenthos of the shallow Antarctic sublittoral. Hydrobiologia 223:105–117
Jażdżewski K, DeBroyer C, Pudlarz M, Zielinski D (2001) Seasonal fluctuations of vagile benthos in the uppermost sublittoral of a maritime Antarctic fjord. Polar Biol 24:910–917
Kim S, Hammerstom KK, Conlan KE, Thurber AR (2010) Polar ecosystem dynamics: recovery of communities from organic enrichment in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Integr Comp Biol 50:1031–1040
Leinster T, Cobbold CA (2012) Measuring diversity: the importance of species similarity. Ecology 93:477–489
Levin LA, Gage JD (1998) Relationships between oxygen, organic matter and the diversity of bathyal macrofauna. Deep-Sea Res Pt II 45:129–163
Maurer BA, McGill BJ (2011) Measurement of species diversity. In: Magurran A, McGill BJ (eds) Biological diversity—frontiers in measurement and assessment. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 55–65
Meulman JJ (1992) The integration of multidimensional scaling and multivariate analysis with optimal transformations. Psychometrika 57:539–565
Nedwell D, Walker T, Ellis-Evans J, Clarke A (1993) Measurements of seasonal rates and annual budgets of organic carbon fluxes in an Antarctic coastal environment at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, suggest a broad balance between production and decomposition. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3989–3995
Nonato EF, Brito TAS, Paiva PC, Petti MAV, Corbisier TN (2000) Benthic megafauna of the nearshore zone of Martel Inlet (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica): depth zonation and underwater observations. Polar Biol 23:580–588
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2011) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0-1. http://cran.r-project.org
Pabis K, Siciński J (2010) Distribution and diversity of polychaetes collected by trawling in Admiralty Bay—an Antarctic glacial fiord. Polar Biol 33:141–151
Pabis K, Siciński J, Krymarys M (2011) Distribution patterns in the biomass of macrozoobenthic communities in Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetlands, Antarctic). Polar Biol 34:489–500
Peck LS, Brockington S, Vanhove S, Beghyn M (1999) Community recovery following catastrophic iceberg impacts in a soft-sediment shallow-water site at Signy Island, Antarctica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 186:1–8
Peck LS, Convey P, Barnes DKA (2006) Environmental constraints on life histories in Antarctic ecosystems: tempos, timings and predictability. Biol Rev 81:75–109
Quinn G, Keough M (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists, 1st edn. Cambridge University, Cambridge
R Development Core Team (2011) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for statistical computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 29 Nov 2012
Ricklefs RE, Schluter D (1993) Species diversity in ecological communities: historical and geographical perspectives. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London
Siciński J (1986) Benthic assemblages of polychaeta in chosen regions of the Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands). Pol Polar Res 7:63–78
Siciński J (2000) Polychaeta (Annelida) of Admiralty Bay: species richness, diversity, and abundance. Pol Polar Res 21:153–169
Siciński J (2004) Polychaetes of Antarctic sublittoral in the proglacial zone (King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Pol Polar Res 25:67–96
Siciński J, Janowska E (1993) Polychaetes of the shallow sublittoral of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Antarct Sci 5:161–167
Siciński J, Jażdżewski K, De Broyer C, Presler P, Ligowski R, Nonato EF, Corbisier TN, Petti MAV, Brito TAS, Lavrado HP, Błażewicz-Paszkowycz M, Pabis K, Jażdżewska J, Campos LS (2011) Admiralty Bay Benthos diversity—A census of a complex polar ecosystem. Deep Sea Res II 58:30–48
Smale DA (2007) Ice disturbance intensity structures benthic communities in nearshore Antarctic waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 349:89–102
Smith CR, DeMaster DJ (2008) Preface and brief synthesis for the FOODBANCS volume. Deep Sea Res II 55:2399–2403
Smith CR, DeMaster DJ, Thomas C, Sršen P, Grange L, Evrard V, DeLeo F (2012) Pelagic-benthic coupling, food banks, and climate change on the West Antarctic Peninsula Shelf. Oceanography 25:188–201
Stark JS (2000) The distribution and abundance of soft sediment macrobenthos around Casey Station, East Antarctica. Polar Biol 23:840–850
Stark JS, Riddle MJ, Simpson RD (2003) Human impacts in soft-sediment assemblages at Casey Station, East Antarctica: spatial variation, taxonomic resolution and data transformation. Austral Ecol 28:287–304
Thursh SF, Hewitt JE, Cummings VJ, Norkko A, Chiantore M (2010) β-Diversity and species accumulation in Antarctic coastal benthos: influence of habitat, distance and productivity on ecological connectivity. PLoS One 5:e11899
Tóthmérész B (1995) Comparison of different methods for diversity ordering. J Veg Sci 6:283–290
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank the CNPq-PROANTAR (Brazilian Antarctic Program), SECIRM (Brazilian Secretariat of the Inter-ministerial Commission for Marine Resources) and specially to the crew of the Brazilian Antarctic Station “Comandante Ferraz” for their crucial help in field work. We also wish to thank three anonymous reviewers for comments and criticism and to Ramon Clark and Joana Zanol for language revision. This work was supported by grants and fellowships from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We dedicate this paper to Edmundo Ferraz Nonato who passed away on April 14, 2014. He was a Brazilian expert in marine benthic studies, taxonomy and biology of polychaetes and a pioneer of Brazilian Antarctic research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paiva, P.C., Seixas, V.C. & Echeverría, C.A. Variation of a polychaete community in nearshore soft bottoms of Admiralty Bay, Antarctica, along austral winter (1999) and summer (2000–2001). Polar Biol 38, 1345–1356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1698-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1698-8