Abstract
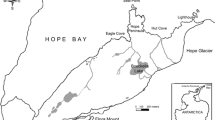
The Southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina) is a major consumer from the Southern Ocean. This species is highly sexually dimorphic and frequently exhibits resource partitioning according to sex and/or age classes. This study analysed the feeding habits of the M. leonina population from Isla 25 de mayo (King George Island) in the spring/summer seasons of 1995/1996–2002/2003. A total of 232 individuals from different sex-age groups were stomach lavaged. The analysis of stomach samples showed that cephalopods were the main prey followed by fish, their frequency of occurrence being 98.1 and 17.9 % respectively. Cephalopods were dominated by the Antarctic glacial squid, Psychroteuthis glacialis, which occurred in 83 % of samples, constituting 57.2 % in numbers and 61.3 % in mass. Octopods were of lesser relevance, occurring in 18 % of samples, but became more important in the diet of male individuals. Juvenile seals fed on a lower variety of cephalopod prey than older ones. This would coincide with the diving pattern characteristic of the different sex-age categories of seals. The predominance of P. glacialis might be associated with the more southerly location of the foraging areas of this population compared to others. Fish were largely represented by the myctophid Gymnoscopelus nicholsi, which occurred in 81.3 % of samples containing otoliths and constituted 76.4 % in numbers and 66.4 % in mass. However, while myctophids may be the dominant fish prey of elephant seals in areas close to the South Shetlands, they would be probably replaced by P. antarcticum as seals migrate towards higher latitudes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allcock AL (2005) On the confusion surrounding Pareledone charcoti (Joubin 1905) (Cephalopoda: Octopodidae): endemic radiation in the Southern Ocean. Zool J Linn Soc 143:75–108
Allcock AL, Strugnell JM, Prodöhl P, Piatkowski U, Vecchione M (2007) A new species of Pareledone (Cephalopoda: Octopodidae) from Antarctic Peninsula waters. Polar Biol 30:883–893
Allcock AL, Barrat I, Eléaume M, Linse K, Norman MD, Smith PJ, Steinke D, Stevens DW, Strugnell JM (2011) Cryptic speciation and the circumpolarity debate: a case study on endemic Southern Ocean octopuses using the COI barcode of life. Deep-Sea Res 58:242–249
Arnbom TA, Lunn NJ, Boyd IL, Barton T (1992) Aging live Antarctic fur seals and southern elephant seals. Mar Mamm Sci 8:37–43
Authier M, Delord K, Guinet C (2011) Population trends of female Elephant Seals breeding on the Courbet Peninsula, Îles Kerguelen. Polar Biol 34:319–328
Barrera-Oro E (2002) The role of fish in the Antarctic marine food web: differences between inshore and offshore waters in the southern Scotia Arc and west Antarctic Peninsula. Antarct Sci 14:293–309
Bester MN (1988) Marking and monitoring studies of the Kerguelen stock of southern elephant seals Mirounga leonina and their bearing on biological research in the Vestfold Hills. Hydrobiologia 165:269–277
Bigg MA, Fawcett I (1985) Two biases in diet determination of northern fur seal (Callorhinus ursinus). In: Beddington JR, Beverton RJH, Lavigne DM (eds) Marine mammals and fisheries. Allen & Unwin, London, pp 284–291
Biuw M, Boehme L, Guinet C, Hindell MA, Costa DP, Charrassin J-B, Roquet F, Bailleul F, Meredith M, Thorpe S, Tremblay Y, McDonald BI, Park Y-H, Rintoul SR, Bindoff N, Goebel ME, Crocker DE, Lovell P, Nicholson J, Monks F, Fedak M (2007) Variations in behavior and condition of a Southern Ocean top predator in relation to in situ oceanographic conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13705–13710
Bornemann H, Kreyscher S, Ramdohr S, Martin T, Carlini A, Sellmann L, Plotz J (2000) Southern elephant seal movements and Antarctic sea ice. Antarct Sci 12:3–15
Boyd IL, Walker TR, Poncet J (1996) Status of southern elephant seals in South Georgia. Antarct Sci 8:237–244
Bradshaw CJA, Hindell MA, Best NJ, Phillips KL, Wilson G, Nichols PD (2003) You are what you eat: describing the foraging ecology of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) using blubber fatty acids. Proc R Soc Lond B 270:1283–1292
Brown DJ, Boyd IL, Cripps GC, Butler PJ (1999) Fatty acid signature analysis from the milk of Antarctic fur seals and Southern elephant seals from South Georgia: implications for diet determination. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 187:251–263
Burns JM (1999) The development of diving behavior in juvenile Weddell seals: pushing physiological limits in order to survive. Can J Zool 66:446–458
Campagna C, Lewis M (1992) Growth and distribution of a southern elephant seal colony. Mar Mamm Sci 8:387–396
Carlini AR, Marquez MEI, Daneri GA, Poljak S (1999) Mass changes during their annual cycle in females of southern elephant seals at King George Island. Polar Biol 21:234–239
Carlini AR, Daneri GA, Marquez MEI, Bornemann H, Panarello H, Casaux R, Ramdohr S, Plotz J (2005) Food consumption estimates of southern elephant seal females during their post-breeding aquatic phase at King George Island. Polar Biol 28:769–775
Carlini AR, Poljak S, Daneri GA, Márquez MEI, Negrete J (2006) The dynamics of male harem dominance in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) at the South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 29:796–805
CCAMLR (2008) Statistical bulletin, vol 20 (1998–2007). CCAMLR, Hobart
Chaigne A, Authier M, Richard P, Cherel Y, Guinet C (2013) Shift in foraging grounds and diet broadening during ontogeny in southern elephant seals from Kerguelen Islands. Mar Biol 160:977–986
Cherel Y, Ducatez S, Fontaine C, Richard P, Guinet C (2008) Stable isotopes reveal the trophic position and mesopelagic fish diet of female southern elephant seals breeding on Kerguelen Islands. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 370:239–247
Clarke MR (1986) A handbook for the identification of cephalopod beaks. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Clarke MR, MacLeod N (1982) Cephalopods in the diet of elephant seals at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Br Antarct Surv Bull 57:27–31
Collins MA, Rodhouse PGK (2006) Southern ocean cephalopods. Adv Mar Biol 50:191–265
Cortés E (1997) A critical review of methods of studying fish feeding based on analysis of stomach contents: application to elasmobranch fishes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:726–738
Croxall JP, Prince PA, Ricketts C (1985) Relationships between prey life-cycles and the extent, nature and timing of seal and seabird predation in the Scotia Sea. In: Siegfried WR, Condy P, Laws RM (eds) Antarctic nutrient cycles and food webs. Springer, Berlin, pp 516–533
Daneri GA, Carlini AR (2002) Fish prey of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, at King George Island. Polar Biol 25:739–743
Daneri GA, Carlini AR, Rodhouse PGK (2000) Cephalopod diet of the southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina, at King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Antarct Sci 12:16–19
Daneri GA, Carlini AR, Harrington A (2005) The feeding habits of male southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, at King George Island, South Shetland Islands. In: Proceedings of the IX SCAR international biology symposium, Curitiba
Daneri GA, Carlini AR, Negri A, Allcock AL, Corbalán A (2012) Predation on cephalopods by Weddell seals, Leptonychotes weddellii, at Hope Bay, Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 35:585–592
Dragon AC, Bar-Hen A, Monestiez P, Guinet C (2012) Horizontal and vertical movements as predictors of foraging success in a marine predator. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 447:243–257
Ducatez S, Dalloyau S, Richard P, Guinet C, Cherel Y (2008) Stable isotopes document winter trophic ecology and maternal investment of adult female southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) breeding at the Kerguelen Islands. Mar Biol 155:413–420
Field I, Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Michael KJ (2001) Foraging strategies of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) in relation to frontal zones and water masses. Antarct Sci 13:371–379
Field IC, Bradshaw CJA, Burton HR, Sumner MD, Hindell MA (2005) Resource partitioning through oceanic segregation of foraging juvenile southern elephant seals. Oecologia 142:127–135
Field IA, Bradshaw CJA, van den Hoff J, Burton HR, Hindell MA (2007) Age-related shifts in the diet composition of southern elephant seals expand overall trophic niche. Mar Biol 150:1441–1452
Filippova JA, Pakhomov EA (1994) Young squid in the plankton of Prydz Bay, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 6:171–173
Fischer W, Hureau JC (1988) FAO species identification sheets for fisheries purposes. Southern Ocean (Fishing areas 48, 58 and 88 CCAMLR convention area), vol 1-2. CCAMLR, Rome
Gon O, Heemstra PC (1990) Fishes of the Southern Ocean, 1st edn. JLB Smith Institute, Grahamstown
Green K, Burton HR (1993) Comparison of the stomach contents of the Southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina, at Macquarie and Heard Islands. Mar Mamm Sci 9:10–22
Green K, Williams R (1986) Observations on food remains in faeces of elephant, leopard and crabeater seals. Polar Biol 6:43–45
Groger J, Piatkowski U, Heinemann H (2000) Beak length analysis of the Southern Ocean squid Psychroteuthis glacialis (Cephalopoda: Psychroteuthidae) and its use for size and biomass estimation. Polar Biol 23:70–74
Harvey JT, Antonelis GA (1994) Biases associated with non-lethal methods of determining the diet of northern elephant seals. Mar Mamm Sci 10:178–187
Hecht T (1987) A guide to the otoliths of Southern Ocean fishes. S Afr J Antarct Res 17:1–87
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1991) The diving behavior of adult male and female southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina (Pinnipedia: Phocidae). Aust J Zool 39:595–619
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1994) Possible causes of the decline of southern elephant seal populations in the southern Pacific and southern Indian Oceans. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 66–84
Hubold G (1984) Spatial distribution of Pleuragramma antarcticum (Pisces: Nototheniidae) near the Filchner and Larson Ice Shelves (Weddell Sea/Antarctica). Polar Biol 3:231–236
Hubold G, Ekau W (1987) Midwater fish fauna of the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. In: Kullander SO, Fernholm B (eds) Proceedings of the fifth congress of European ichthyologists. Swedish Museum of Natural History, Stockholm, pp 391–396
Irvine LG, Hindell MA, Van den Hoff J, Burton HR (2000) The influence of body size on dive duration of underyearling southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). J Zool (Lond) 251:463–471
Jonker FC, Bester MN (1998) Seasonal movements and foraging areas adult southern female elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, from Marion Island. Antarct Sci 10:21–30
Kooyman GL, Castellini MA, Davis RW, Maue RA (1983) Aerobic dive limits in immature Weddell seals. J Comp Physiol 151:171–174
Kozlov AN (1995) A review of the trophic role of mesopelagic fish of the family Myctophidae in the Southern Ocean ecosystem. CCAMLR Sci 2:71–77
Laws RM (1956) The elephant seal (Mirounga leonina Linn). II. General, social and reproductive behaviour. Sci Rep Falkl Isl Depend Surv 13:1–88
Laws RM (1994) History and present status of the southern elephant seal populations. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behaviour and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 49–65
Le Boeuf BJ, Morris PA, Blackwell SB, Crocker DE, Costa DP (1996) Diving behavior of juvenile northern elephant seals. Can J Zool 74:1632–1644
Lu CC, Williams R (1994) Contribution to the biology of squid in the Prydz Bay region, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 6:223–229
McConnell BJ, Fedak MA (1996) Movements of southern elephant seals. Can J Zool 74:1485–1496
McIntyre T, Ansorge I, Bornemann H, Plötz J, Tosh C, Bester M (2011) Elephant seal dive behaviour is influenced by ocean temperature: implications for climate change impacts on an ocean predator. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 441:257–272
McMahon CR, Bester MN, Burton HR, Hindell MA, Bradshaw CJA (2005) Population status and trends of a wide-ranging marine mammal predator, the southern elephant seal: reexamining hypotheses to explain the decline. Mamm Rev 35:82–100
Mennucci JA, Negrete J, Juáres MA, Santos MM, Coria NR, Márquez ME (2012) Seasonal variation in the number of breeding females of Southern Elephant Seal, at 25 de Mayo/King George Island. XXXII SCAR and Open Science Conference. Portland, Oregón
Moore JK, Abbott MR, Richman JG (1999) Location and dynamics of the Antarctic Polar Front from satellite sea surface temperature data. J Geophys Res 104:3059–3073
Newland CB, Field IC, Nichols PD, Bradshaw CJA, Hindell MA (2009) Blubber fatty acid profiles indicate dietary resource partitioning between adult and juvenile southern elephant seals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 384:303–312
Newland CB, Field IC, Cherel Y, Guinet C, Bradshaw CJA, McMahon CR, Hindell MA (2011) Diet of juvenile southern elephant seals reappraised by stable isotopes in whiskers. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 424:247–258
North AW (1996) Fish in the diet of Antarctic fur seals (Arctocephalus gazella) at South Georgia during winter and spring. Antarct Sci 8:155–160
Okutani T, Clarke M (1985) Identification key and species description for Antarctic squids. BIOMASS Handbook no 21
Piatkowski U, Vergani DF, Stanganelli ZB (2002) Changes in the cephalopod diet of southern elephant seal females at King George Island, during El Niño-La Niña events. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 82:913–916
Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson ILK (1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. California Department of Fish and Game, Fish Bull 152:1–105
Pusch C, Hulley PA, Kock KH (2004) Community structure and feeding ecology of mesopelagic fishes in the slope waters of King George Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). Deep-Sea Res I 51:1685–1708
Reeves RR, Stewart BS, Leatherwood S (1992) The Sierra Club handbook of seals and sirenians. Sierra Club Books, San Francisco
Reid K (1995) The diet of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, during winter at South Georgia. Antarct Sci 7:241–249
Reid K (1996) A guide to the use of otoliths in the study of predators at South Georgia. British Antarctic Survey
Rodhouse PGK, Prince PA, Clarke MR, Murray AWA (1990) Cephalopod prey of the grey-headed albatross Diomedea chrysostoma. Mar Biol 104:353–362
Rodhouse PG, Arnbom TR, Fedak MA, Yeatman J, Murray AWA (1992) Cephalopod prey of the southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina L. Can J Zool 70:1007–1015
SCAR (2006) Report of the 29th meeting of the SCAR Group of Specialists on seals. Hobart, Tasmania
Slip DJ (1995) The diet of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) from Heard Island. Can J Zool 73:1519–1528
Slip DJ, Hindell MA, Burton HR (1994) Diving behavior of southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island: an overview. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 253–270
Tollit DJ, Steward M, Thompson PM, Pierce GJ, Santos MB, Hughes S (1997) Species and size differences in the digestion of otoliths and beaks; implications for estimates of pinniped diet composition. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:105–119
Tosh CA, Bornemann H, Ramdohr S, Schroder M, Martin T, Carlini AR, Plotz J, Bester MN (2009) Adult male southern elephant seals from King George Island utilize the Weddell Sea. Antarct Sci 21:113–121
Vacquié-Garcia J, Royer F, Dragon AC, Viviant M, Bailleul F, Guinet C (2012) Foraging in the darkness of the Southern Ocean: influence of Bioluminescence on a deep diving predator. PLoS ONE 7:e43565
Van den Hoff J (2004) A comparative study of the cephalopod prey of Patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides) and southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) near Macquarie Island. Polar Biol 27:604–612
Van Den Hoff J, Burton H, Davies R (2003) Diet of male southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina L.) hauled out at Vincennes Bay, East Antarctica. Polar Biol 26:27–31
Vergani DF, Spairani HJ (1980) Elefante marino I. Estudio del crecimiento durante la lactancia del elefante marino del sur, Mirounga leonina. Contribución del Instituto Antártico Argentino 270:93–118
Walters A, Lea MA, van den Hoff J, Field IC, Virtue P, Sokolov S, Pinkerton MH, Hindell MA (2014) Spatially explicit estimates of prey consumption reveal a new krill predator in the Southern Ocean. PLoS ONE 9:e86452
Williams R, McEldowney A (1990) A guide to the fish otoliths from waters off the Australian Antarctic Territory, Heard and Macquarie Island. ANARE Res 75:1–173
Xavier JC, Cherel Y (2009) Cephalopod beak guide for the Southern Ocean. British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Marthan Bester and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the manuscript. We are also grateful to Mr. Campbell McMillan for improvement of the English language in text. This work was funded by the Dirección Nacional del Antártico and the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (Grants: Picto No. 11559-36054). Our procedures conform with the Code of Ethics of Animal Experimentation in Antarctica. The permit for this work was granted by the Dirección Nacional del Antártico (Environmental Office), Argentina. This work is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Alejandro Carlini (“Alex”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. R. Carlini: Deceased on 20 December 2010.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daneri, G.A., Carlini, A.R., Marschoff, E.R. et al. The feeding habits of the Southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina, at Isla 25 de Mayo/King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 38, 665–676 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1629-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1629-0