Abstract
Key message
Both bacterial and fungal endophytes exhibited one or more plant growth-promoting (PGP) traits. Among these strains, the Paenibacillus peoriae SYbr421 strain demonstrated the greatest activity in the direct biotransformation of tuber powder from D. nipponica into diosgenin.
Abstract
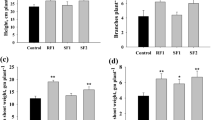
Endophytes play crucial roles in shaping active metabolites within plants, significantly influencing both the quality and yield of host plants. Dioscorea nipponica Makino accumulates abundant steroidal saponins, which can be hydrolyzed to produce diosgenin. However, our understanding of the associated endophytes and their contributions to plant growth and diosgenin production is limited. The present study aimed to assess the PGP ability and potential of diosgenin biotransformation by endophytes isolates associated with D. nipponica for the efficient improvement of plant growth and development of a clean and effective approach for producing the valuable drug diosgenin. Eighteen bacterial endophytes were classified into six genera through sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rDNA gene. Similarly, 12 fungal endophytes were categorized into 5 genera based on sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of the ITS rDNA gene. Pure culture experiments revealed that 30 isolated endophytic strains exhibited one or more PGP traits, such as nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, siderophore synthesis, and IAA production. One strain of endophytic bacteria, P. peoriae SYbr421, effectively directly biotransformed the saponin components in D. nipponica. Moreover, a high yield of diosgenin (3.50%) was obtained at an inoculum size of 4% after 6 days of fermentation. Thus, SYbr421 could be used for a cleaner and more eco-friendly diosgenin production process. In addition, based on the assessment of growth-promoting isolates and seed germination results, the strains SYbr421, SYfr1321, and SYfl221 were selected for greenhouse experiments. The results revealed that the inoculation of these promising isolates significantly increased the plant height and fresh weight of the leaves and roots compared to the control plants. These findings underscore the importance of preparing PGP bioinoculants from selected isolates as an additional option for sustainable diosgenin production.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information fles).
References
Aeron A, Dubey RC, Maheshwari DK (2020) Characterization of a plant-growth-promoting non-nodulating endophytic bacterium (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) from the root nodules of Mucuna utilis var. capitata L. (Safed Kaunch). Can J Microbiol 66(11):670–677. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2020-0196
Ahmad T, Farooq S, Mirza DN, Kumar A, Mir RA, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S (2022) Insights into the endophytic bacterial microbiome of crocus sativus: functional characterization leads to potential agents that enhance the plant growth, productivity, and key metabolite content. Microb Ecol 83(3):669–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01810-y
AlHabori M, Raman A, Lawrence MJ, Skett P (2001) In vitro effect of fenugreek extracts on intestinal sodium-dependent glucose uptake and hepatic glycogen phosphorylase A. Int J Exp Diab Res 2(2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1155/EDR.2001.91
ALKahtani MD, Fouda A, Attia KA, Al-Otaibi F, Eid AM, Ewais EE, Hijri M, St-Arnaud M, Hassan SE, Khan N (2020) Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting endophytic bacteria from desert plants and their application as bioinoculants for sustainable agriculture. Agronomy 10(9):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091325
Andriiuk KI (1967) Nitrogen-fixing activity of soil actinomycetes and associative cultures. Mikrobiol Z 29(2):91–95
Chen FQ, Yang F, Wang DL, Xiang G, Wang L (2007) The effect of plant growth regulators and sucrose on the micropropagation and microtuberization of Dioscorea nipponica Makino. J Plant Growth Regul 26(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-005-0147-2
Compant S, Cambon MC, Vacher C, Mitter B, Samad A, Sessitsch A (2021) The plant endosphere world—Bacterial life within plants. Environ Microbiol 23(4):1812–1829. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15240
Cueva-Yesquén LG, Goulart MC, Attili de Angelis D, Nopper Alves M, Fantinatti-Garboggini F (2021) Multiple plant growth-promotion traits in endophytic bacteria retrieved in the vegetative stage from passionflower. Front Plant Sci 11:621740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.621740
Dang SN, Gao RM, Zhang YQ, Feng YM (2022) In vitro regeneration and its histological characteristics of Dioscorea nipponica Makino. Sci Rep 12(1):18436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-22986-4
Delshadi S, Ebrahimi M, Shirmohammadi E (2017) Influence of plant-growth-promoting bacteria on germination, growth and nutrients’ uptake of Onobrychis sativa L. under drought stress. J Plant Interact 12:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2017.1316527
Dong JZ, Lei C, Lu DY, Wang Y (2015) Direct biotransformation of dioscin into diosgenin in rhizome of Dioscorea zingiberensis by Penicillium dioscin. Indian J Microbiol 55:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-014-0507-3
Du XW, Liu YP, Meng FJ, Wu JK, Yu D (2017) Isolation of endophytic fungi from Dioscorea nipponica Makino and analysis of its secondary metabolites. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol 5:004. https://doi.org/10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392
Gao YG, Mo QQ, Zhao Y (2019) Microbial mediated accumulation of plant secondary metabolites and its action mechanism in medicinal plants: a review. J Southern Agric 50(10):2234–2240
Gouda S, Das G, Sen SK, Shin HS, Patra JK (2016) Endophytes: a treasure house of bioactive compounds of medicinal importance. Front Microbiol 7:1538. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01538
Gupta R, Elkabetz D, Leibman-Markus M, Sayas T, Schneider A, Jami E, Kleiman M, Bar M (2022) Cytokinin drives assembly of the phyllosphere microbiome and promotes disease resistance through structural and chemical cues. ISME J 16(1):122–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01060-3
Hardoim PR, van Overbeek LS, Berg G, Pirttilä AM, Compant S, Campisano A, Döring M, Sessitsch A (2015) The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 79:293–320. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00050-14
Hazarika SN, Saikia K, Borah A, Thakur D (2021) Prospecting endophytic bacteria endowed with plant growth promoting potential isolated from Camellia sinensis. Front Microbiol 12:738058. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.738058
Higdon K, Scott A, Tucci M, Benghuzzi H, Tsao A, Puckett A, Cason Z, Hughes J (2001) The use of estrogen, DHEA, and diosgenin in a sustained delivery setting as a novel treatment approach for osteoporosis in the ovariectomized adult rat model. Biomed Sci Instrum 37:281–286
Hu Z, Wang C, Pan L, Han SY, Jin M, Xiang YS, Zheng LF, Li ZH, Gao R, Qin BF (2021) Identification and a phased pH control strategy of diosgenin bio-synthesized by an endogenous Bacillus licheniformis Syt1 derived from Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H Wright Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:9333–9342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11679-z
Huang N, Yu D, Huo J, Wu J, Chen Y, Du X, Wang X (2022) Study of saponin components after biotransformation of Dioscorea nipponica by endophytic fungi C39. J Anal Methods Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2943177
Jain A, Chatterjee A, Das S (2020) Synergistic consortium of beneficial microorganisms in rice rhizosphere promotes host defense to blight-causing Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Planta 252(6):106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03515-x
Kumari P, Shanker K, Singh A (2023) Insight into Andrographis paniculata associated bacterial endomicrobiome and assessment of culturable bacterial endophytes for enhancement of industrially important andrographolide content. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116840
Laczeski ME, Onetto AL, Cortese IJ (2020) Isolation and selection of endophytic spore-forming bacteria with plant growth promoting properties isolated from Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil. (yerba mate). Anais Da Academia Brasileira De Ciencias 92(1):e20181381. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202020181381
Li P, Mao Z, Lou J, Li Y, Mou Y, Lu S, Peng Y, Zhou L (2011) Enhancement of diosgenin production in Dioscorea zingiberensis cell cultures by oligosaccharides from its endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum Dzf17. Molecules (basel, Switzerland) 16(12):10631–10644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210631
Li J, Mosongo I, Li H, Wu Y, Li C, Yang S, Zhang Y (2021) Identification and characterization of a trillin rhamnosyltransferase from Dioscorea zingiberensis. Front Plant Sci 12:713036. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.713036
Liu T, Yu H, Liu C, Bao Y, Hu X, Wang Y, Liu B, Fu Y, Tang S, Jin F (2013) Preparation of progenin III from total steroidal saponins of Dioscorea nipponica Makino using a crude enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae strain. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40(5):427–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1246-x
Liu H, Carvalhais LC, Crawford MH, Singh E, Dennis PG, Pieterse CM, Schenk PM (2017) Inner plant values: diversity, colonization and benefits from endophytic bacteria. Front Microbiol 8:2552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02552
Liu X, Zhou ZY, Cui JL, Wang ML, Wang JH (2021) Biotransformation ability of endophytic fungi: from species evolution to industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(19):7095–7113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11554-x
Liu LH, Yuan T, Zhang JY, Tang GX, Lü H, Zhao HM, Li H, Li YW, Mo CH, Tan ZY, Cai QY (2022) Diversity of endophytic bacteria in wild rice (Oryza meridionalis) and potential for promoting plant growth and degrading phthalates. Sci Total Environ 806(Pt1):150310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150310
Luo SL, Dang LZ, Li JF, Zou CG, Zhang KQ, Li GH (2013) Biotransformation of saponins by endophytes isolated from Panax notoginseng. Chem Biodivers 10(11):2021–2031. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201300005
Maciá-Vicente JG, Jansson HB, Abdullah SK, Descals E, Salinas J, Lopez-Llorca LV (2008) Fungal root endophytes from natural vegetation in Mediterranean environments with special reference to Fusarium spp. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64(1):90–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00443.x
Manganyi MC, Ateba CN (2020) Untapped potentials of endophytic fungi: a review of novel bioactive compounds with biological applications. Microorganisms 8(12):1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121934
Miller KI, Qing C, Sze DMY, Roufogalis BD, Neilan BA (2012) Culturable endophytes of medicinal plants and the genetic basis for their bioactivity. Microb Ecol 64:431–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0044-8
Moalic S, Liagre B, Corbière C, Bianchi A, Dauça M, Bordji K, Beneytout JL (2001) A plant steroid, diosgenin, induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and COX activity in osteosarcoma cells. FEBS Lett 506(3):225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02924-6
Ouyabe M, Tanaka N, Shiwa Y, Fujita N, Kikuno H, Babil P, Shiwachi H (2020) Rhizobium dioscoreae sp. nov., a plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from yam (Dioscorea species). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70(9):5054–5062. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004381
Özçakmak S, Dervişoğlu M, Yilmaz A (2012) Effects of polysaccharides and oligosaccharides from endophytic fungus Berkleasmium sp. Dzf12 on diosgenin accumulation in Dioscorea zingiberensis cell and seedling cultures. Afr J Microbiol Res 6:3079–3084. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR12.599
Özçinar Ö, Tağ Ö, Yusufoglu H, Kivçak B, Bedir E (2018) Biotransformation of ruscogenins by Cunninghamella blakesleeana NRRL 1369 and neoruscogenin by endophytic fungus Neosartorya hiratsukae. Phytochemistry 152:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.04.002
Pan CX, Zhao Y, Liu GH, Dou GY, Ru ZG, Zhu K (2014) Development and demonstration of a cleaner process to produce diosgenin from Dioscorea zingiberensis based on physical separation. J Clean Prod 76:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.074
Pan XY, Sun HJ, Yuan ZL (2018) Toxin accumulation of three Leymus mollis-associated endophytic Fusarium isolates and their effects on growth and salt tolerance of Liquidambar styraciflua seedlings. Forest Res 31(5):64–73. https://doi.org/10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2018.05.009
Pandey DK, Nazir A, Dey A (2017) Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere of Dioscorea alata stimulating growth and diosgenin production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect B Biol 87:1143–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0670-2
Passari AK, Mishra VK, Leo VV, Gupta VK, Singh BP (2016) Phytohormone production endowed with antagonistic potential and plant growth promoting abilities of culturable endophytic bacteria isolated from Clerodendrum colebrookianum Walp. Microbiol Res 193:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2016.09.006
Qi SS, Dong YS, Zhao YK, Xiu ZL (2009) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of microbial transformation of steroidal saponins in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Chroma 69:865–870. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-0978-2
Qin HL, Dong CM, Zhang AH, Zhao Y, Tang H, Ruan YZ (2015) Screening and identification of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere soil in banana orchards in Hainan and its influence on growth of banana seedlings. South China Fruits 44(2):18–22. https://doi.org/10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20140644
Shade A, Handelsman J (2012) Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environ Microbiol 14(1):4–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x
Sharma P, Kumar S (2021) Bioremediation of heavy metals from industrial effluents by endophytes and their metabolic activity: Recent advances. Biores Technol 339:125589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125589
Sharma S, Dhar MK, Kaul S (2023) Antagonistic, plant growth promoting and extracellular hydrolytic enzyme activity of fungal endophytes of Dioscorea bulbifera L. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 50:1878–8181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102694
Shukla N, Singh D, Tripathi A, Kumari P, Gupta RK, Singh S, Shanker K, Singh A (2022) Synergism of endophytic Bacillus subtilis and Klebsiella aerogenes modulates plant growth and bacoside biosynthesis in Bacopa monnieri. Front Plant Sci 13:896856. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.896856
Skiada V, Faccio A, Kavroulakis N, Genre A, Bonfante P, Papadopoulou KK (2019) Colonization of legumes by an endophytic Fusarium solani strain FsK reveals common features to symbionts or pathogens. Fungal Genet Biol 127:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2019.03.003
Stierle A, Strobel G, Stierle D (1993) Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew. Science (new York) 260(5105):214–216. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8097061
Vendan RT, Yu YJ, Lee SH, Rhee YH (2010) Diversity of endophytic bacteria in ginseng and their potential for plant growth promotion. J Microbiol (seoul, Korea) 48(5):559–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0082-1
Vinayarani G, Prakash HS (2018) Growth promoting rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria from Curcuma longa L. as biocontrol agents against rhizome rot and leaf blight diseases. Plant Pathol J 34(3):218–235. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.OA.11.2017.0225
Wang X, Meng JF, Ma R, He SW, Guo HB, Isolation ZXX (2022) Isolation, identification of an endophytic Paraburkholderia kururiensis in rice and evaluation of its plant growth promotion. Soil Fertil Sci China 4:218–228. https://doi.org/10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20709
Xiang HB, Zhang T, Pang X, Wei YZ, Liu HY, Zhang YQ, Ma BP, Yu LY (2018) Isolation of endophytic fungi from Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H. Wright and application for diosgenin production by solid-state fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:5519–5532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9030-5
Xu L, Wang J, Zhao J, Li P, Shan T, Wang J, Li X, Zhou L (2010) Beauvericin from the endophytic fungus, Fusarium redolens, isolated from Dioscorea zingiberensis and its antibacterial activity. Nat Prod Commun 5(5):811–814. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1000500527
Xu Z, Tian J, Gan L, Tian Y (2020) Discovery of the endophytic fungi from Polygonum cuspidatum and biotransformation of resveratrol to pterostillbene by the endophyte Penicillium sp. F5. Appl Biochem Microbiol 56:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820030163
Yang H, Yin H, Shen YP, Xia GH, Zhang B, Wu XY, Cai B, Tam JP (2016) A more ecological and efficient approach for producing diosgenin from Dioscorea zingiberensis tubers via pressurized biphase acid hydrolysis. J Clean Prod 131:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.030
Yu H, Yu M, Liu B, Zhao ZY, Wu RZ (2018) Rapid propagation of Discorea nipponica Makino via axillary bud proliferation. Agric Biotechnol 7(5):6–9
Zhang YZ, Chen WF, Li M, Sui XH, Liu HC, Zhang XX, Chen WX (2012) Bacillus endoradicis sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from soybean root. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(2):359–363. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.028936-0
Zhang T, Xiang HB, Zhang YQ, Liu HY, Wei YZ, Zhao LX, Yu LY (2013) Molecular analysis of fungal diversity associated with three bryophyte species in the Fildes Region, King George Island, maritime Antarctica. Extremophiles 17(5):757–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0558-0
Zhang H, Liu MM, Liu XN, Li ZY, Zhao LL, Yang QX (2022) Impact of endophytic microorganisms on pharmaco-active compounds production in medicinal plants: a review. Biotechnol Bull 38(8):41–51. https://doi.org/10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1487
Zhao J, Shan T, Mou Y, Zhou L (2011) Plant-derived bioactive compounds produced by endophytic fungi. Mini Rev Med Chem 11(2):159–168. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955711794519492
Zhao L, Xu Y, Lai XH, Shan C, Deng Z, Ji Y (2015) Screening and characterization of endophytic Bacillus and Paenibacillus strains from medicinal plant Lonicera japonica for use as potential plant growth promoters. Braz J Microbiol 46(4):977–989. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246420140024
Zhu YL, Huang W, Ni JR, Liu W, Li H (2010) Production of diosgenin from Dioscorea zingiberensis tubers through enzymatic saccharification and microbial transformation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2200-8
Zhu YH, Shao YY, Li L, Zhao L, Zhang MJ, Dong CM (2022) The plant growth-promoting endophytic Fusarium oxysporum GG22 enhances Rehmannia glutinosa secondary metabolites accumulation. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114881
Zou K, Liu X, Hu Q, Zhang D, Fu S, Zhang S, Huang H, Lei F, Zhang G, Miao B, Meng D, Jiang L, Liu H, Yin H, Liang Y (2021) Root endophytes and Ginkgo biloba are likely to share and compensate secondary metabolic processes, and potentially exchange genetic information by LTR-RTs. Front Plant Sci 12:704985. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.704985
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Forestry College of Shanxi Agricultural University for invaluable instrumental support. In addition, the authors acknowledge the Science and Technology Department of Shanxi Province for their financial assistance. We appreciate Dr. Shabir A. Rather (Center for Integrative Conservation & Yunnan Key Laboratory for Conservation of Tropical Rainforests and Asian Elephants, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yunnan, China) for their assistance in revising the manuscript and enhancing its English language quality.
Funding
We acknowledge the funding provided by the Science and Technology Department of Shanxi Province (Shanxi Province Basic Research Project number 20210302123391) and the grant received from the Shanxi Provincial Education Department (Shanxi Province Postgraduate Innovation Project number J202282027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SND performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. JG facilitated the experiment by providing essential experimental equipment. RW and YMF contributed to the data analysis and manuscript refinement. RMG and YZH designed the study and provided advice. All the authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Prakash Lakshmanan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, S., Geng, J., Wang, R. et al. Isolation of endophytes from Dioscorea nipponica Makino for stimulating diosgenin production and plant growth. Plant Cell Rep 43, 95 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-024-03164-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-024-03164-4