Abstract
Key message
Inoculation of wheat seedling with Bacillus sp. wp-6 changed amino acid metabolism and flavonoid synthesis and promoted plant growth.
Abstract
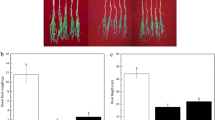
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), which can reduce the use of agrochemicals, is vital for the development of sustainable agriculture. In this study, proteomics and metabolomics analyses were performed to investigate the effects of inoculation with a PGPR, Bacillus sp. wp-6, on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedling growth. The results showed that inoculation with Bacillus sp. wp-6 increased shoot and root fresh weights by 19% and 18%, respectively, after 40 days. The expression levels of alpha-linolenic acid metabolism-related proteins and metabolites (lipoxygenase 2, allene oxide synthase 2, jasmonic acid, 17-hydroxylinolenic acid) and flavonoid biosynthesis-related proteins and metabolites (chalcone synthase 2 and PHC 4′-O-glucoside) were up-regulated. In addition, the expression levels of amino acid metabolism-related proteins (NADH-dependent glutamate synthase, bifunctional aspartokinase/homoserine, anthranilate synthase alpha subunit 1, and 3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase) and metabolites (l-aspartate, l-arginine, and S-glutathionyl-l-cysteine) were also significantly up-regulated. Among them, NADH-dependent glutamate synthase and bifunctional aspartokinase/homoserine could act as regulators of nitrogen metabolism. Overall, inoculation of wheat with Bacillus sp. wp-6 altered alpha-linolenic acid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and flavonoid synthesis and promoted wheat seedling growth. This study will deepen our understanding of the mechanism by which Bacillus sp. wp-6 promotes wheat growth using proteomics and metabolomics.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abdelaziz AM, El-Wakil DA, Attia MS, Ali OM, AbdElgawad H, Hashem AH (2022) Inhibition of Aspergillus flavus growth and aflatoxin production in Zea mays L. using endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus. J Fungi 8:482. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050482
Ahmadi J, Asgharzadeh A, Bakhtiari S (2013) The effect of microbial inoculants on physiological responses of two wheat cultivars under salt stress. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 4:364–371
Ahmed T, Noman M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Ijaz U, Nazir MM, ALHaithloul HAZ, Alghanem SM, Li B, (2022) Green molybdenum nanoparticles-mediated bio-stimulation of Bacillus sp. strain ZH16 improved the wheat growth by managing in planta nutrients supply, ionic homeostasis and arsenic accumulation. J Hazard Mater 423:127024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127024
Ajilogba C, Babalola O, Adebola P, Adeleke R (2016) Evaluation of PGPR and biocontrol activities of bacteria isolated from Bambara groundnut rhizosphere. New Biotechnol 2016:S128–S129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2016.06.1169
Almuhayawi MS, Abdel-Mawgoud M, Al Jaouni SK, Almuhayawi SM, Alruhaili MH, Selim S, AbdElgawad H (2021) Bacterial endophytes as a promising approach to enhance the growth and accumulation of bioactive metabolites of three species of Chenopodium sprouts. Plants 10:2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122745
Balasubramanian VK, Dampanaboina L, Cobos CJ, Yuan N, Xin Z, Mendu V (2021) Induced secretion system mutation alters rhizosphere bacterial composition in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Planta 253:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03569-5
Begum N, Wang L, Ahmad H, Akhtar K, Roy R, Khan MI, Zhao T (2022) Co-inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improve growth and photosynthesis in tobacco under drought stress by up-regulating antioxidant and mineral nutrition metabolism. Microb Ecol 83:971–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01815-7
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cao Y, Pi HL, Chandrangsu P, Li YT, Wang YQ, Zhou H, Xiong HQ, Helmann JD, Cai YF (2018) Antagonism of two plant-growth promoting Bacillus velezensis isolates against Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum. Sci Rep 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22782-z
Chu TN, Bui LV, Hoang MTT (2020) Pseudomonas PS01 isolated from maize rhizosphere alters root system architecture and promotes plant growth. Microorganisms 8:471
Conesa MR, Conejero W, Vera J, Ruiz-Sánchez M (2022) Root reserves ascertain postharvest sensitivity to water deficit of nectarine trees. Agronomy 12:1805. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081805
Cox J, Michalski A, Mann M (2011) Software lock mass by two-dimensional minimization of peptide mass errors. J Am Soc Mass Spectr 22:1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-011-0142-8
Di YN, Kui L, Singh P, Liu LF, Xie LY, He LL, Li FS (2022) Identification and characterization of Bacillus subtilis B9: a diazotrophic plant growth-promoting endophytic bacterium isolated from sugarcane root. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10653-x
Dong XM, Lian QG, Chen J, Jia RM, Zong ZF, Ma Q, Wang Y (2022) The improved biocontrol agent, F1–35, protects watermelon against Fusarium Wilt by triggering jasmonic acid and ethylene pathways. Microorganisms 10:1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091710
El-Gendi H, Al-Askar AA, Király L, Samy MA, Moawad H, Abdelkhalek A (2022) Foliar Applications of Bacillus subtilis HA1 culture filtrate enhance tomato growth and induce systemic resistance against tobacco mosaic virus infection. Horticulturae 8:301. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040301
Elías JM, Guerrero-Molina MF, Martínez-Zamora MG, Díaz-Ricci JC, Pedraza RO (2018) Role of ethylene and related gene expression in the interaction between strawberry plants and the plant growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum brasilense. Plant Biol 20:490–496. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12697
Essalimi B, Esserti S, Rifai LA, Koussa T, Makroum K, Belfaiza M, Rifai S, Venisse JS, Faize L, Alburquerque N, Burgos L, Jadoumi SE, Faize M (2022) Enhancement of plant growth, acclimatization, salt stress tolerance and verticillium wilt disease resistance using plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) associated with plum trees (Prunus domestica). Sci Hortic 291:110621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110621
Fernandes LB, Ghag SB (2022) Molecular insights into the jasmonate signaling and associated defense responses against wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Physiol Biochem 174:22–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.032
Fu J, Ren R, Jin S, Fang R, Wen Z, Yang M, Wang X, Liu B, Yin T, Lu G, Yang Y, Qi J (2022) Overexpression of a putative 12-oxophytodienoate reductase gene, EpOPR1, enhances acetylshikonin production in Echium plantagineum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 58:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-022-10259-8
Gorina S, Ogorodnikova A, Mukhtarova L, Toporkova Y (2022) Gene expression analysis of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) lipoxygenase cascade and oxylipin signature under abiotic stress. Plants 11:683. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050683
Han H, Zhang H, Qin S, Zhang J, Yao L, Chen Z, Yang J (2021) Mechanisms of Enterobacter bugandensis TJ6 immobilization of heavy metals and inhibition of Cd and Pb uptake by wheat based on metabolomics and proteomics. Chemosphere 276:130157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130157
Hu P, Meng Y, Wise RP (2009) Functional contribution of chorismate synthase, anthranilate synthase, and chorismate mutase to penetration resistance in barley–powdery mildew interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-22-3-0311
Huang S, Lim SY, Lau H, Ni W, Li SFY (2022a) Effect of glycinebetaine on metabolite profiles of cold-stored strawberry revealed by 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Food Chem 393:133452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133452
Huang XJ, Jian SF, Chen DL, Zhong C, Miao JH (2022b) Concentration-dependent dual effects of exogenous sucrose on nitrogen metabolism in Andrographis paniculata. Sci Rep 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08971-x
Kang X, Wang L, Guo Y, ul Arifeen MZ, Cai X, Xue Y, Bu Y, Wang G, Liu C (2019) A comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of hexaploid wheat’s responses to colonization by Bacillus velezensis and Gaeumannomyces graminis, both separately and combined. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32:1336–1347. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-03-19-0066-R
Kazerooni EA, Maharachchikumbura SS, Al-Sadi AM, Rashid U, Kim ID, Kang SM, Lee IJ (2022) Effects of the rhizosphere fungus Cunninghamella bertholletiae on the Solanum lycopersicum response to diverse abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 23:8909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168909
Kołton A, Długosz-Grochowska O, Wojciechowska R, Czaja M (2022) Biosynthesis regulation of folates and phenols in plants. Sci Hortic 291:110561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110561
Kwon YS, Lee DY, Rakwal R, Baek SB, Lee JH, Kwak YS, Seo JS, Chung WS, Bae DW, Kim SG (2016) Proteomic analyses of the interaction between the plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 and Arabidopsis thaliana. Proteomics 16:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201500196
Li Y, Qiu L, Liu X, Zhang Q, Zhuansun X, Fahima T, Sun Q, Krugman T, Xie C (2020) Glycerol-induced powdery mildew resistance in wheat by regulating plant fatty acid metabolism, plant hormones cross-talk, and pathogenesis-related genes. Int J Mol Sci 21:673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020673
Li YH, Yang YY, Wang ZG, Chen Z (2022) Emerging function of ecotype-specific splicing in the recruitment of commensal microbiome. Int J Mol Sci 23:4860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094860
Liang X, Deng H, Bai Y, Fan TP, Zheng X, Cai Y (2022) Characterization of a novel type homoserine dehydrogenase with high oxidation activity from Arthrobacter nicotinovorans. Process Biochem 114:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.01.019
Liu Y, Gao S, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Xu Y, Wei J (2022) Transcriptomics and metabolomics analyses reveal defensive responses and flavonoid biosynthesis of Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S. C. Chen under wound stress in natural conditions. Molecules 27:4514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144514
Lou H, Yang Y, Zheng S, Ma Z, Chen W, Yu C, Song L, Wu J (2022) Identification of key genes contributing to amino acid biosynthesis in Torreya grandis using transcriptome and metabolome analysis. Food Chem 379:132078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132078
Miljaković D, Marinković J, Tamindžić G, Đorđević V, Tintor B, Milošević D, Ignjatov M, Nikolić Z (2022) Bio-priming of soybean with Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Bacillus megaterium: strategy to improve seed germination and the initial seedling growth. Plants 11:1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11151927
Mushtaq Z, Asghar HN, Zahir ZA, Maqsood M (2022) The interactive approach of rhizobacteria and l-tryptophan on growth, physiology, tuber characteristics, and iron concentration of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J Plant Growth Regul 41:1359–1366
Olanrewaju OS, Babalola OO (2022) The rhizosphere microbial complex in plant health: a review of interaction dynamics. J Integr Agric 21:2168–2182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63817-0
Parvandi M, Rezadoost H, Farzaneh M (2021) Introducing Alternaria tenuissima SBUp1, as an endophytic fungus of Ferula assa-foetida from Iran, which is a rich source of rosmarinic acid. Lett Appl Microbiol 73:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13542
Qian R, Hu Q, Ma X, Zhang X, Ye Y, Liu H, Gao H, Zheng J (2022) Comparative transcriptome analysis of heat stress responses of Clematis lanuginosa and Clematis crassifolia. BMC Plant Biol 22:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03497-w
Rane NR, Tapase S, Kanojia A, Watharkar A, Salama ES, Jang M, Yadav KK, Amin MA, Cabral-Pinto MMS, Jadhav JP, Jeon BH (2022) Molecular insights into plant–microbe interactions for sustainable remediation of contaminated environment. Bioresour Technol 344:126246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126246
Recep K, Fikrettin S, Erkol D, Cafer E (2009) Biological control of the potato dry rot caused by Fusarium species using PGPR strains. Biol Control 50:194–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.04.004
Reddy DP, Pal A, Reddy MD (2022) Effect of nitrogen levels on yield of rice varieties during kharif in South Odisha. Crop Res 57:108–112. https://doi.org/10.31830/2454-1761.2022.015
Ren J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li C, Bian Z, Zhang X, Liu H, Xu J, Jiang C (2022) Deletion of all three MAP kinase genes results in severe defects in stress responses and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum. Stress Biol 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44154-021-00025-y
Safdarian M, Askari H, Shariati V, Nematzadeh G (2019) Transcriptional responses of wheat roots inoculated with Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus to salt stress. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38398-2
Samain E, Ernenwein C, Aussenac T, Selim S (2022) Effective and durable systemic wheat-induced resistance by a plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria consortium of Paenibacillus sp. strain B2 and Arthrobacter spp. strain AA against Zymoseptoria tritici and drought stress. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 119:101830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101830
Shen N, Li S, Li S, Zhang H, Jiang M (2022) The siderophore-producing bacterium, Bacillus siamensis Gxun-6, has an antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum and promotes the growth of banana. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 32:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-022-00533-7
Singh RP, Runthala A, Khan S, Jha PN (2017) Quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the tolerance of wheat to salt stress in response to Enterobacter cloacae SBP-8. PLoS One 12:e0183513. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183513
Tirry N, Kouchou A, El Omari B, Ferioun M, El Ghachtouli N (2021) Improved chromium tolerance of Medicago sativa by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00254-8
Trinh CS, Lee H, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Chung N, Han J, Kim J, Hong S, Lee H et al (2018) Evaluation of the plant growth-promoting activity of Pseudomonas nitroreducens in Arabidopsis thaliana and Lactuca sativa. Plant Cell Rep 37:873–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2275-8
Tu C, Jin Z, Che F, Cao X, Song X, Lu C, Huang W (2022) Characterization of phosphorus sorption and microbial community in lake sediments during overwinter and recruitment periods of cyanobacteria. Chemosphere 307:135777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135777
Vega A, Canessa P, Hoppe G, Retamal I, Moyano TC, Canales J, Gutiérrez RA, Rubilar J (2015) Transcriptome analysis reveals regulatory networks underlying differential susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea in response to nitrogen availability in Solanum lycopersicum. Front Plant Sci 6:911. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00911
Veselova SV, Sorokan AV, Burkhanova GF, Rumyantsev SD, Cherepanova EA, Alekseev VY, Sarvarova ER, Kasimova AR, Maksimov IV (2022) By modulating the hormonal balance and ribonuclease activity of tomato plants Bacillus subtilis induces defense response against potato virus X and potato virus Y. Biomolecules 12:288. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020288
Wang W, Scali M, Vignani R, Spadafora A, Sensi E, Mazzuca S, Cresti M (2003) Protein extraction for two-dimensional electrophoresis from olive leaf, a plant tissue containing high levels of interfering compounds. Electrophoresis 24:2369–2375. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200305500
Wang J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang X, Nan W, Hu Y, Zhang H, Zhao C, Wang F, Li P, Shi H, Bi Y (2015) Endophytic microbes Bacillus sp. LZR216-regulated root development is dependent on polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell Rep 34:1075–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1766-0
Wang A, Hua J, Wang Y, Zhang G, Luo S (2020) Stereoisomers of nonvolatile acetylbutanediol metabolites produced by Bacillus velezensis WRN031 improved root elongation of maize and rice. J Agr Food Chem 68:6308–6315. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01352
Wang C, Zhang M, Zhou J, Gao X, Zhu S, Yuan L, Hou X, Liu T, Chen G, Tang X, Shan G, Hou J (2022a) Transcriptome analysis and differential gene expression profiling of wucai (Brassica campestris L.) in response to cold stress. BMC Genom 23:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08311-3
Wang J, Qu F, Liang J, Yang M, Hu X (2022b) Bacillus velezensis SX13 promoted cucumber growth and production by accelerating the absorption of nutrients and increasing plant photosynthetic metabolism. Sci Hortic 301:111151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111151
Weckwerth W, Loureiro ME, Wenzel K, Fiehn O (2004) Differential metabolic networks unravel the effects of silent plant phenotypes. Proc Acad Sci USA 101:7809–7814. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0303415101
Wiggins G, Thomas J, Rahmatallah Y, Deen C, Haynes A, Degon Z, Glazko G, Mukherjee A (2022) Common gene expression patterns are observed in rice roots during associations with plant growth-promoting bacteria, Herbaspirillum seropedicae and Azospirillum brasilense. Sci Rep 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12285-3
Yamaya T, Kusano M (2014) Evidence supporting distinct functions of three cytosolic glutamine synthetases and two NADH-glutamate synthases in rice. J Exp Bot 65:5519–5525. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru103
Yu XL, Wu DM, Fu YQ, Yang XJ, Baluška F, Shen H (2018) OsGLO4 is involved in the formation of iron plaques on surface of rice roots grown under alternative wetting and drying condition. Plant Soil 423:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3493-5
Yuttavanichakul W, Lawongsa P, Wongkaew S, Teaumroong N, Boonkerd N, Nomura N, Tittabutr P (2012) Improvement of peanut rhizobial inoculant by incorporation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as biocontrol against the seed borne fungus, Aspergillus niger. Biol Control 63:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2012.06.008
Zhang CS, Kong FY (2014) Isolation and identification of potassium-solubilizing bacteria from tobacco rhizospheric soil and their effect on tobacco plants. Appl Soil Ecol 82:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.05.002
Zhou J, Liu X, Sun C, Li G, Yang P, Jia Q, Cai X, Zhu Y, Yin J, Liu Y (2022) Silica nanoparticles enhance the disease resistance of ginger to rhizome rot during postharvest storage. Nanomaterials 12:1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091418
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31860360) and the Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Xinjiang (Grant No. 2020BC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
We certify that the submission is not under review at any other publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Prakash Lakshmanan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhang, F., Mickan, B. et al. Inoculation of wheat with Bacillus sp. wp-6 altered amino acid and flavonoid metabolism and promoted plant growth. Plant Cell Rep 42, 165–179 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02947-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02947-x