Abstract
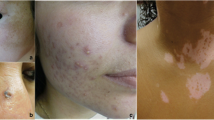
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multi-system autoimmune disease with varied dermatological manifestations that are almost universal. Overall, lupus disease has a major effect on the quality of life in these patients. We assessed the extent of cutaneous disease in early lupus and correlated it with the SLE quality-of-life (SLEQoL) index and disease activity measures. Patients diagnosed as SLE with the skin involved were recruited at the first presentation and were assessed for cutaneous and systemic disease activity using the cutaneous lupus erythematosus disease area and severity index (CLASI) and the Mexican-SLE disease activity index (Mex-SLEDAI), respectively. Quality of life was assessed with the SLEQoL tool while systemic damage was captured by the SLICC damage index. Fifty-two patients with SLE who had cutaneous involvement were enrolled (40, 76.9% females) with a median disease duration of 1 month (1–3.7). The median age was 27.5 years (IQR: 20–41). Median Mex-SLEDAI and SLICC damage index were 8(IQR: 4.5–11) and 0 (0–1), respectively. The median CLASI activity and damage scores were 3 (1–5) and 1 (0–1), respectively. Overall, there was no correlation between SLEQoL with CLASI or CLASI damage. Only the self-image domain of SLEQoL correlated with total CLASI (ρ = 0.32; p = 0.01) and CLASI-D (ρ = 0.35; p = 0.02). There was a weak correlation of CLASI with the Mexican-SLEDAI score (ρ = 0.30; p = 0.03) but not with the SLICC damage index. In this cohort of early lupus, cutaneous disease activity in lupus had a weak correlation with systemic disease. Cutaneous features did not appear to influence the quality of life except in the self-image domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Yell JA, Mbuagbaw J, Burge SM (1996) Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 135(3):355–362
Stull C, Sprow G, Werth VP (2023) Cutaneous Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Review for the Rheumatologist. J Rheumatol 50(1):27–35
Kuhn A, Landmann A (2014) The classification and diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 48–49:14–19
Gilliam JN, Sontheimer RD (1981) Distinctive cutaneous subsets in the spectrum of lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol 4(4):471–475
Albrecht J, Taylor L, Berlin JA, Dulay S, Ang G, Fakharzadeh S, Kantor J, Kim E, Militello G, McGinnis K, Richardson S, Treat J, Vittorio C, Van Voorhees A, Werth VP (2005) The CLASI (Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index): an outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 125(5):889–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23889.x
Kuhn A, Amler S, Beissert S, Böhm M, Brehler R, Ehrchen J et al (2010) Revised cutaneous lupus erythematosus disease area and severity index (RCLASI): a modified outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus: revised CLASI for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 163(1):83–92
Klein RS, Morganroth PA, Werth VP (2010) Cutaneous Lupus and the CLASI Instrument. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 36(1):33–51
Leong KP, Kong KO, Thong BYH, Koh ET, Lian TY, Teh CL et al (2005) Development and preliminary validation of a systemic lupus erythematosus-specific quality-of-life instrument (SLEQOL). Rheumatology 44(10):1267–76
Aziz MM, Galal MAA, Elzohri MH, El-Nouby F, Leong KP (2018) Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Quality of Life questionnaire into Arabic. Lupus 27(5):780–787
Jiang HZ, Lin ZG, Li HJ, Du Q, Tian W, Wang SY et al (2018) The Chinese version of the SLEQOL is a reliable assessment of health-related quality of life in Han Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 37(1):151–60
Finlay AY, Khan GK (1994) Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)-a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol 19(3):210–216
Ware JE, Sherbourne CD (1992) The MOS 36-Item short-form health survey (SF-36): I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 30(6):473–83
Ferraz LB, Almeida FA, Vasconcellos MR, Faccina AS, Ciconelli RM, Ferraz MB (2006) The impact of lupus erythematosus cutaneous on the Quality of life: the Brazilian-Portuguese version of DLQI. Qual Life Res Int J Qual Life Asp Treat Care Rehabil 15(3):565–570
Ogunsanya ME, Cho SK, Hudson A, Chong BF (2020) Factors associated with quality of life in cutaneous lupus erythematosus using the Revised Wilson and Cleary Model. Lupus 29(13):1691–1703
Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, Brinks R, Mosca M, Ramsey-Goldman R et al (2019) 2019 European league against rheumatism/american college of rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 71(9):1400–1412
Guzmán J, Cardiel MH, Arce-Salinas A, Sánchez-Guerrero J, Alarcón-Segovia D (1992) Measurement of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Prospective validation of 3 clinical indices. J Rheumatol 19(10):1551–8
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR et al (2012) Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2677–2686
Stoll T, Seifert B, Isenberg DA (1996) SLICC/ACR damage index is valid, and renal and pulmonary organ scores are predictors of severe outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 35(3):248–254
Albrecht J, Werth VP (2007) Development of the CLASI as an outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Ther 20(2):93–101
Albrecht J, Taylor L, Berlin JA, Dulay S, Ang G, Fakharzadeh S et al (2005) The CLASI (Cutaneous LE Disease Area and Severity Index): an outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 125(5):889–94
Chang AY, Ghazi E, Okawa J, Werth VP (2013) Quality of Life Differences Between Responders and Nonresponders in the Treatment of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. JAMA Dermatol 149(1):104
Verma SM, Okawa J, Propert KJ, Werth VP (2014) The impact of skin damage due to cutaneous lupus on quality of life. Br J Dermatol 170(2):315–321
Vasquez R, Wang D, Tran QP, Adams-Huet B, Chren MM, Costner MI et al (2013) A multicentre, cross-sectional study on quality of life in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Multicentre, cross-sectional quality of life study of patients with CLE. Br J Dermatol 168(1):145–153
Aggarwal R, Wilke CT, Pickard AS, Vats V, Mikolaitis R, Fogg L et al (2009) Psychometric properties of the euroQol-5D and short form-6D in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 36(6):1209–1216
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study concept and framework were devised by SA, SCR and HKK. All authors contributed substantially for data acquisition. Data analysis was done by SP. PMV, NG and SA drafted the manuscript, and all authors were involved in the critical revision for intellectual content. All authors take equal responsibility for the data published and the authenticity of the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hinduja, N., MV, P., Padhee, S. et al. Assessment of cutaneous disease activity in early lupus and its correlation with quality of life: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int 43, 1835–1840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05353-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05353-y