Abstract
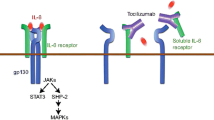
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is defined as a systemic inflammatory disorder of unknown aetiology and is classified as a multigene autoinflammatory disease. Treatment of AOSD still remains mostly empirical with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or cyclosporin A. Inhibitors of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 (IL-1) antagonists have shown efficacy in certain subsets of patients with AOSD. The IL-6 molecule is one of the potential targets in treating AOSD considering that its level is increased in both the systemic and chronic articular forms of the disease.
We present a series of eight patients from our centre with refractory AOSD treated with tocilizumab (TCZ). The drug was administered intravenously (6–8 mg/kg every 3–4 weeks) or subcutaneously (162 mg weekly). One patient had a disease relapse during TCZ therapy, and the drug had to be withdrawn in one patient due to a severe infection, while five out of six patients currently treated are in stable remission.
Many previous reports have suggested that TCZ is an efficacious option for the treatment of refractory AOSD and the cases presented herein support this finding. A literature search revealed two previous reports of subcutaneous TCZ administration TCZ in AOSD, and our experience supports subcutaneous TCZ as a promising option for treatment of refractory AOSD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y, Iwaz J, Sève P (2014) Adult-onset still’s disease. Autoimmun Rev 13(7):708–722
Iliou C, Papagoras C, Tsifetaki N, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2013) Adult-onset Still’s disease: clinical, serological and therapeutic considerations. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(1):47–52
Evensen KJ, Nossent HC (2006) Epidemiology and outcome of adult-onset Still’s disease in Northern Norway. Scand J Rheumatol 35(1):48–51
Magadur-Joly G, Billaud E, Barrier JH, Pennec YL, Masson C, Renou P et al (1995) Epidemiology of adult still’s disease: estimate of the incidence by a retrospective study in west France. Ann Rheum Dis 54(7):587–590
Wakai K, Ohta A, Tamakoshi A, Ohno Y, Kawamura T, Aoki R et al (1997) Estimated prevalence and incidence of adult Still’s disease: findings by a nationwide epidemiological survey in Japan. J Epidemiol 7(4):221–225
Nirmala N, Brachat A, Feist E, Blank N, Specker C, Witt M, et al (2015) Gene-expression analysis of adult-onset Still’s disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is consistent with a continuum of a single disease entity. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4654831/. Accessed May 27 2018.
Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Blanco R, Riancho-Zarrabeitia L, Castañeda S, Olivé A, Riveros A et al (2015) Efficacy of anakinra in refractory adult-onset still’s disease: multicenter study of 41 patients and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(39):e1554
Ohta A, Yamaguchi M, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima H, Kashiwagi H et al (1990) Adult Still’s disease: a multicenter survey of Japanese patients. J Rheumatol 17(8):1058–1063
Elkon KB, Hughes GR, Bywaters EG, Ryan PF, Inman RD, Bowley NB et al (1982) Adult-onset Still’s disease. Twenty-year followup and further studies of patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum 25(6):647–654
Nguyen KH, Weisman MH (1997) Severe sore throat as a presenting symptom of adult onset Still’s disease: a case series and review of the literature. J Rheumatol 24(3):592–597
Efthimiou P, Kadavath S, Mehta B (2014) Life-threatening complications of adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 33(3):305–314
Jamilloux Y, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Martinon F, Belot A, Henry T, Sève P (2015) Pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease: new insights from the juvenile counterpart. Immunol Res 61(1–2):53–62
Maria ATJ, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Touitou I, Rivière S, Guilpain P (2014) Adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) in the era of biologic therapies: dichotomous view for cytokine and clinical expressions. Autoimmun Rev 13(11):1149–1159
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H et al (1992) Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 19(3):424–430
Jiang L, Wang Z, Dai X, Jin X (2011) Evaluation of clinical measures and different criteria for diagnosis of adult-onset Still’s disease in a Chinese population. J Rheumatol 38(4):741–746
Castañeda S, Blanco R, González-Gay MA (2016) Adult-onset Still’s disease: advances in the treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 30(2):222–238
Yoo DH (2017) Treatment of adult-onset still’s disease: up to date. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13(9):849–866
Franchini S, Dagna L, Salvo F, Aiello P, Baldissera E, Sabbadini MG (2010) Efficacy of traditional and biologic agents in different clinical phenotypes of adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 62(8):2530–2535
Kim H-A, Sung J-M, Suh C-H (2012) Therapeutic responses and prognosis in adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatol Int 32(5):1291–1298
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Maucort-Boulch D, Hot A, Iwaz J, Ninet J, Durieu I et al (2014) Adult-onset Still disease: manifestations, treatment, outcome, and prognostic factors in 57 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 93(2):91–99
Yoo DH (2019) Biologics for the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther 19(11):1173–1190
Vercruysse F, Barnetche T, Lazaro E, Shipley E, Lifermann F, Balageas A et al (2019) Adult-onset Still’s disease biological treatment strategy may depend on the phenotypic dichotomy. Arthritis Res Ther 21(1):53
Giampietro C, Fautrel B (2012) Anti-Interleukin-1 Agents in Adult Onset Still’s Disease. International Journal of Inflammation. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/iji/2012/317820/. Accessed June 17 2018.
Kadavath S, Efthimiou P (2015) Adult-onset Still’s disease-pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and new treatment options. Ann Med 47(1):6–14
de Boysson H, Février J, Nicolle A, Auzary C, Geffray L (2013) Tocilizumab in the treatment of the adult-onset Still’s disease: current clinical evidence. Clin Rheumatol 32(1):141–147
Puéchal X, DeBandt M, Berthelot J-M, Breban M, Dubost J-J, Fain O et al (2011) Tocilizumab in refractory adult Still’s disease. Arthritis Care Res 63(1):155–159
Cipriani P, Ruscitti P, Carubbi F, Pantano I, Liakouli V, Berardicurti O et al (2014) Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease: results from a case series. Clin Rheumatol 33(1):49–55
Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Blanco R, Calvo-Rio V, Narvaez J, Rubio Romero E, Olivé A et al (2014) Efficacy of tocilizumab in conventional treatment-refractory adult-onset Still’s disease: multicenter retrospective open-label study of thirty-four patients. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ 66(6):1659–1665
Bannai E, Yamashita H, Kaneko S, Ueda Y, Ozaki T, Tsuchiya H et al (2016) Successful tocilizumab therapy in seven patients with refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Mod Rheumatol 26(2):297–301
Elkayam O, Jiries N, Dranitzki Z, Kivity S, Lidar M, Levy O et al (2014) Tocilizumab in adult-onset Still’s disease: the Israeli experience. J Rheumatol 41(2):244–247
Nishina N, Kaneko Y, Kameda H, Takeuchi T (2015) The effect of tocilizumab on preventing relapses in adult-onset Still’s disease: a retrospective, single-center study. Mod Rheumatol 25(3):401–404
Castañeda S, Martínez-Quintanilla D, Martín-Varillas JL, García-Castañeda N, Atienza-Mateo B, González-Gay MA (2019) Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther 4:273–286
Song ST, Kim JJ, Lee S, Kim H-A, Lee EY, Shin KC et al (2016) Efficacy of tocilizumab therapy in Korean patients with adult-onset Still’s disease: a multicentre retrospective study of 22 cases. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34(6 Suppl 102):S64–71
Wang C-Y, Guo S-H, Wang L-P, Shen H-L (2019) Refractory adult-onset Still disease treated by tocilizumab combined with methotrexate: a STROBE-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(32):e16682
Ma Y, Wu M, Zhang X, Xia Q, Yang J, Xu S et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab with inhibition of interleukin-6 in adult-onset Still’s disease: a meta-analysis. Mod Rheumatol 28(5):849–857
Kaneko Y, Kameda H, Ikeda K, Ishii T, Murakami K, Takamatsu H et al (2018) Tocilizumab in patients with adult-onset still’s disease refractory to glucocorticoid treatment: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Ann Rheum Dis 77(12):1720–1729
Yamada H, Kaneko Y, Tamai H, Takeuchi T (2020) Biomarkers for disease flare in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease undergoing treatment with tocilizumab. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 59(2):440–442
Shimizu M, Nakagishi Y, Kasai K, Yamasaki Y, Miyoshi M, Takei S et al (2012) Tocilizumab masks the clinical symptoms of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated macrophage activation syndrome: the diagnostic significance of interleukin-18 and interleukin-6. Cytokine 58(2):287–294
Tsuchida Y, Sumitomo S, Shoda H, Kubo K, Fujio K, Yamamoto K (2017) Macrophage activation syndrome associated with tocilizumab treatment in adult-onset Still’s disease. Mod Rheumatol 27(3):556–557
Li T, Gu L, Wang X, Guo L, Shi H, Yang C et al (2017) A pilot study on tocilizumab for treating refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):13477
Savage E, Wazir T, Drake M, Cuthbert R, Wright G (2014) Fulminant myocarditis and macrophage activation syndrome secondary to adult-onset Still’s disease successfully treated with tocilizumab. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 53(7):1352–1353
Rubbert-Roth A, Furst DE, Nebesky JM, Jin A, Berber E (2018) A Review of recent advances using tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Ther 5(1):21–42
Park EH, Lee EY, Shin K, Kim H-A (2020) Tocilizumab-induced anaphylaxis in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a case-based review. Rheumatol Int 40(5):791–798
Choy E, Caporali R, Xavier R, Fautrel B, Sanmarti R, Bao M et al (2018) Subcutaneous tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: findings from the common-framework phase 4 study programme TOZURA conducted in 22 countries. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 57(3):499–507
Vandemergel X, Vandergheynst F (2016) Efficacy of low-dose tocilizumab on relapsing adult-onset still’s disease. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 59(1):22–25
Ebstein E, Ea H-K (2018) Spontaneous resolution of Epstein-Barr virus-induced haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Still’s disease treated by tocilizumab: a case report. Scand J Rheumatol 47(1):84–85
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors, including pharmaceutic agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept: M.M., M.R.C., A.B.; design: M.R.C., D.Č.; supervision: B.A., M.M.; materials: M.M., A.B.; data collection and/or processing: D.Č., A.B., M.R.C.; analysis and/or interpretation: B.A.; literature search: M.R., D.Č.; writing manuscript: M.R., D.Č.; critical review: B.A.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reihl Crnogaj, M., Čubelić, D., Babić, A. et al. Treatment of refractory adult onset Still’s disease with tocilizumab—a single centre experience and literature review. Rheumatol Int 40, 1317–1325 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04622-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04622-4