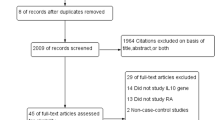
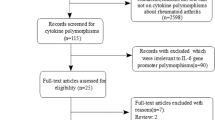
Abstract
Several studies have examined the effects of tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) 1 +38 A/G and TNFR2 196 M/R polymorphisms on susceptibility to RA and have reported conflicting results. The purpose of this study was to examine whether the TNFR1 +38 A/G and TNFR2 196 M/R polymorphisms are associated with RA susceptibility. We performed a literature search using the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online and Embase citation indices, and conducted a meta-analysis to examine the association between the TNFR1 +38 A/G and TNFR2 196 M/R polymorphisms and RA. Our meta-analysis included a total of 13 studies from 11 articles, consisting of 11 studies of the TNFR2 polymorphism (2,092 cases and 1,483 controls), and two studies of the TNFR1 polymorphism (672 cases and 288 controls). The meta-analysis revealed a significant association between the TNFR2 196 RR genotype and RA risk (OR 1.737, 95 % CI 1.275–2.367, P = 4.6 × 10−5). Stratification by ethnicity indicated an association between the TNFR2 196 RR genotype and RA in Europeans (OR 2.054, 95 % CI 1.305–3.232, P = 0.002), but not in East Asians (OR 1.596, 95 % CI 0.642–3.971, P = 0.314). Analysis using a homozygote contrast model showed the same pattern for the TNFR2 196 RR genotype in a European and East Asian population. However, no association was found between the TNFR1 +36 A/G polymorphism and RA in a European population. Our meta-analysis demonstrated that the functional TNFR2 196 M/R polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to RA in the European population.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SJ, Rho YH, Ji JD, Song GG, Lee YH (2006) Genome scan meta-analysis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:166–170. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei128
Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2007) PADI4 polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 27:827–833. doi:10.1007/s00296-007-0320-y
Rooney M, David J, Symons J, Di Giovine F, Varsani H, Woo P (1995) Inflammatory cytokine responses in juvenile chronic arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 34:454–460
Kim HR, Heo YM, Jeong KI, Kim YM, Jang HL, Lee KY, Yeo CY, Kim SH, Lee HK, Kim SR, Kim EG, Choi JK (2012) FGF-2 inhibits TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis through upregulation of Bcl2-A1 and Bcl-xL in ATDC5 cells. BMB Rep 45:287–292
Constantin A, Dieude P, Lauwers-Cances V, Jamard B, Mazieres B, Cambon-Thomsen A, Cornelis F, Cantagrel A (2004) Tumor necrosis factor receptor II gene polymorphism and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:742–747. doi:10.1002/art.20113
Kemper O, Derre J, Cherif D, Engelmann H, Wallach D, Berger R (1991) The gene for the type II (p75) tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-RII) is localized on band 1p36.2-p36.3. Hum Genet 87:623–624
Till A, Rosenstiel P, Krippner-Heidenreich A, Mascheretti-Croucher S, Croucher PJ, Schafer H, Scheurich P, Seegert D, Schreiber S (2005) The Met-196 - > Arg variation of human tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) affects TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by impaired NF-kappaB signaling and target gene expression. J Biol Chem 280:5994–6004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411541200
Hussein YM, Mohamed RH, Pasha HF, El-Shahawy EE, Alzahrani SS (2011) Association of tumor necrosis factor alpha and its receptor polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in female patients. Cell Immunol 271:192–196. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.06.023
Oregon-Romero E, Vazquez-Del Mercado M, Navarro-Hernandez RE, Torres-Carrillo N, Martinez-Bonilla G, Estrada-Garcia I, Rangel-Villalobos H, Munoz-Valle JF (2006) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 M196R polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: relationship with sTNFR2 levels and clinical features. Rheumatol Int 27:53–59. doi:10.1007/s00296-006-0159-7
Yen JH, Tsai WC, Chen CJ, Ou TT, Lin CH, Hu CJ, Liu HW (2003) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 microsatellite and exon 6 polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan. J Rheumatol 30:438–442
Dahlqvist SR, Arlestig L, Sikstrom C, Linghult S (2002) Tumor necrosis factor receptor type II (exon 6) and interleukin-6 (-174) gene polymorphisms are not associated with family history but tumor necrosis factor receptor type II is associated with hypertension in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from northern Sweden. Arthritis Rheum 46:3096–3098. doi:10.1002/art.10592
Fabris M, Tolusso B, Di Poi E, Assaloni R, Sinigaglia L, Ferraccioli G (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor II polymorphism in patients from southern Europe with mild-moderate and severe rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 29:1847–1850
Bridges SL Jr, Jenq G, Moran M, Kuffner T, Whitworth WC, McNicholl J (2002) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in tumor necrosis factor receptor genes: definition of novel haplotypes and racial/ethnic differences. Arthritis Rheum 46:2045–2050. doi:10.1002/art.10463
Shibue T, Tsuchiya N, Komata T, Matsushita M, Shiota M, Ohashi J, Wakui M, Matsuta K, Tokunaga K (2000) Tumor necrosis factor alpha 5′-flanking region, tumor necrosis factor receptor II, and HLA-DRB1 polymorphisms in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:753–757. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<753:AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-O
Bayley JP, Bakker AM, Kaijzel EL, Huizinga TW, Verweij CL (2003) Association of polymorphisms of the tumour necrosis factor receptors I and II and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:969–971. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg267
Ghelani AM, Samanta A, Jones AC, Mastana SS (2011) Association analysis of TNFR2, VDR, A2 M, GSTT1, GSTM1, and ACE genes with rheumatoid arthritis in South Asians and Caucasians of East Midlands in the United Kingdom. Rheumatol Int 31:1355–1361
Potter C, Worthington J, Silman A, Barton A (2005) TNFR2 is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in a Caucasian population [3]. Arthritis Rheum 52:2579–2581
Barton A, John S, Ollier WE, Silman A, Worthington J (2001) Association between rheumatoid arthritis and polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor receptor II, but not tumor necrosis factor receptor I, in Caucasians. Arthritis Rheum 44:61–65. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<61:AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-Q
Lee YH, Bae SC, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2011) Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 38:3643–3651. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0477-4
Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2006) Association of TNF-alpha -308 G/A polymorphism with responsiveness to TNF-alpha-blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 27:157–161. doi:10.1007/s00296-006-0175-7
Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG, Nath SK, Harley JB (2007) The PTPN22 C1858T functional polymorphism and autoimmune diseases–a meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:49–56. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kel170
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558. doi:10.1002/sim.1186
Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN (1997) Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ 315:1533–1537
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
You CG, Li XJ, Li YM, Wang LP, Li FF, Guo XL, Gao LN (2013) Association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms of proinflammatory cytokine and their receptors genes with rheumatoid arthritis in northwest Chinese Han population. Cytokine 61:133–138. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.09.007
Goeb V, Dieude P, Vittecoq O, Mejjad O, Menard JF, Thomas M, Gilbert D, Boumier P, Pouplin S, Daragon A, Fardellone P, Tron F, Cornelis F, Le Loet X (2005) Association between the TNFRII 196R allele and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1056–R1062. doi:10.1186/ar1777
Dieude P, Petit E, Cailleau-Moindrault S, Osorio J, Pierlot C, Martinez M, Faure S, Alibert O, Lasbleiz S, De Toma C, Bardin T, Prum B, Cornelis F, European Consortium on Rheumatoid Arthritis F (2002) Association between tumor necrosis factor receptor II and familial, but not sporadic, rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Arthritis Rheum 46:2039–2044. doi:10.1002/art.10101
Glossop JR, Dawes PT, Mattey DL (2011) Antinuclear antibodies are associated with tumor necrosis factor receptor I gene polymorphism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:609–615
Mrazek F, Holla LI, Hutyrova B, Znojil V, Vasku A, Kolek V, Welsh KI, Vacha J, du Bois RM, Petrek M (2005) Association of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, lymphotoxin-alpha and HLA-DRB1 gene polymorphisms with Lofgren’s syndrome in Czech patients with sarcoidosis. Tissue Antigens 65:163–171. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2005.00370.x
Pandey JP, Frederick M, Sarcoidosis ARGACCESo (2002) TNF-alpha, IL1-beta, and immunoglobulin (GM and KM) gene polymorphisms in sarcoidosis. Hum Immunol 63:485–491
Yamaguchi E, Itoh A, Hizawa N, Kawakami Y (2001) The gene polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor-beta, but not that of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, is associated with the prognosis of sarcoidosis. Chest 119:753–761
Somoskovi A, Zissel G, Seitzer U, Gerdes J, Schlaak M, Muller Quernheim J (1999) Polymorphisms at position -308 in the promoter region of the TNF-alpha and in the first intron of the TNF-beta genes and spontaneous and lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha release in sarcoidosis. Cytokine 11:882–887. doi:10.1006/cyto.1999.0498
Seitzer U, Swider C, Stuber F, Suchnicki K, Lange A, Richter E, Zabel P, Muller-Quernheim J, Flad HD, Gerdes J (1997) Tumour necrosis factor alpha promoter gene polymorphism in sarcoidosis. Cytokine 9:787–790. doi:10.1006/cyto.1997.0224
Cornelis F, Faure S, Martinez M, Prud’homme JF, Fritz P, Dib C, Alves H, Barrera P, de Vries N, Balsa A, Pascual-Salcedo D, Maenaut K, Westhovens R, Migliorini P, Tran TH, Delaye A, Prince N, Lefevre C, Thomas G, Poirier M, Soubigou S, Alibert O, Lasbleiz S, Fouix S, Bouchier C, Liote F, Loste MN, Lepage V, Charron D, Gyapay G, Lopes-Vaz A, Kuntz D, Bardin T, Weissenbach J, Ecraf S (1998) New susceptibility locus for rheumatoid arthritis suggested by a genome-wide linkage study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10746–10750
Mori L, Iselin S, De Libero G, Lesslauer W (1996) Attenuation of collagen-induced arthritis in 55-kDa TNF receptor type 1 (TNFR1)-IgG1-treated and TNFR1-deficient mice. J Immunol 157:3178–3182
Heilig B, Mapara M, Brockhaus M, Krauth K, Dorken B (1991) Two types of TNF receptors are expressed on human normal and malignant B lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 61:260–267
Abe Y, Yamauchi K, Kimura S (1995) 75- but not 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor is active in the homotypic aggregation and proliferation of human lymphokine-activated T killer (T-LAK) cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol 57:462–468
Horiuchi T, Kiyohara C, Tsukamoto H, Sawabe T, Furugo I, Yoshizawa S, Ueda A, Tada Y, Nakamura T, Kimoto Y, Mitoma H, Harashima S, Yoshizawa S, Shimoda T, Okamura S, Nagasawa K, Harada M (2007) A functional M196R polymorphism of tumour necrosis factor receptor type 2 is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study and a meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:320–324. doi:10.1136/ard.2006.058917
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D project, Ministry for Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI12C1834).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or nonfinancial conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, G.G., Bae, SC. & Lee, Y.H. Associations between functional TNFR2 196 M/R polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 34, 1529–1537 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3027-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3027-x