Abstract
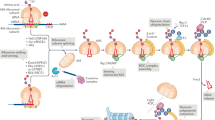
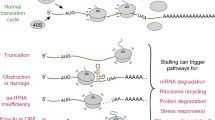
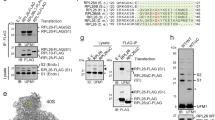
Proteostasis in eukaryotes is maintained by compartment-specific quality control pathways, which enable the refolding or the degradation of defective polypeptides to prevent the toxicity that may arise from their aggregation. Among these processes, translational protein quality control is performed by the Ribosome-bound Quality Control complex (RQC), which recognizes nascent peptides translated from aberrant mRNAs, polyubiquitylates these aberrant peptides, extracts them from the stalled 60S subunit and finally escorts them to the proteasome for degradation. In this review, we focus on the mechanism of action of the RQC complex from stalled 60S binding to aberrant peptide delivery to the proteasome and describe the cellular consequences of a deficiency in the RQC pathway, such as aberrant protein aggregation. In addition, this review covers the recent discoveries concerning the role of cytosolic chaperones, as well as Tom1, to prevent the accumulation of aberrant protein aggregates in case of a deficiency in the RQC pathway.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RQC:
-
Ribosome-bound Quality Control
- PQC:
-
Protein quality control
- eRF:
-
Eukaryotic recycling factor
- RING:
-
Really interesting new gene
- NEMF:
-
Nuclear export mediator factor
- CAT:
-
C-terminal alanine threonine
- HUWE1:
-
HECT, UBA and WWE domain-containing protein 1
References
Bengtson MH, Joazeiro CAP (2010) Role of a ribosome-associated E3 ubiquitin ligase in protein quality control. Nature 467:470–473
Besche HC, Haas W, Gygi SP, Goldberg AL (2009) Isolation of mammalian 26S proteasomes and p97/VCP complexes using the ubiquitin-like domain from HHR23B reveals novel proteasome-associated proteins. Biochemistry 48:2538–2549
Bhattacharyya S, Yu H, Mim C, Matouschek A (2014) Regulated protein turnover: snapshots of the proteasome in action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:122–133
Brandman O, Hegde RS (2016) Ribosome-associated protein quality control. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23:7–15
Brandman O et al (2012) A ribosome-bound quality control complex triggers degradation of nascent peptides and signals translation stress. Cell 151:1042–1054
Chernoff YO, Kiktev DA (2016) Dual role of ribosome-associated chaperones in prion formation and propagation. Curr Genet 62:677–685
Choe Y-J, Park S-H, Hassemer T, Körner R, Vincenz-Donnelly L, Hayer-Hartl M, Hartl FU (2016) Failure of RQC machinery causes protein aggregation and proteotoxic stress. Nature 531:191–195
Chu J, Hong NA, Masuda CA, Jenkins BV, Nelms KA, Goodnow CC, Glynne RJ, Wu H, Masliah E, Joazeiro CA (2009) A mouse forward genetics screen identifies LISTERIN as an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2097–2103
Ciechanover A, Kwon YT (2015) Degradation of misfolded proteins in neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic targets and strategies. Exp Mol Med 47:e147
Crowder JJ, Geigges M, Gibson RT, Fults ES, Buchanan BW, Sachs N, Schink A, Kreft SG, Rubenstein EM (2015) Rkr1/Ltn1 ubiquitin ligase-mediated degradation of translationally stalled endoplasmic reticulum proteins. J Biol Chem 290:18454–18466
Defenouillère Q et al (2013) Cdc48-associated complex bound to 60S particles is required for the clearance of aberrant translation products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5046–5051
Defenouillère Q, Zhang E, Namane A, Mouaikel J, Jacquier A, Fromont-Racine M (2016) Rqc1 and Ltn1 prevent C-terminal alanine-threonine tail (CAT-tail)-induced protein aggregation by efficient recruitment of Cdc48 on stalled 60S subunits. J Biol Chem 291:12245–12253
Defenouillère Q, Namane A, Mouaikel J, Jacquier A, Fromont-Racine M (2017) The ribosome-bound quality control complex remains associated to aberrant peptides during their proteasomal targeting and interacts with Tom1 to limit protein aggregation. Mol Biol Cell 28:1165–1176
Dimitrova LN, Kuroha K, Tatematsu T, Inada T (2009) Nascent peptide-dependent translation arrest leads to not4p-mediated protein degradation by the proteasome. J Biol Chem 284:10343–10352
Doamekpor SK et al (2016) Structure and function of the yeast listerin (Ltn1) conserved N-terminal domain in binding to stalled 60S ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:4151–4160
Doma MK, Parker R (2006) Endonucleolytic cleavage of eukaryotic mRNAs with stalls in translation elongation. Nature 440:561–564
Finger A, Knop M, Wolf DH (1993) Analysis of two mutated vacuolar proteins reveals a degradation pathway in the endoplasmic reticulum or a related compartment of yeast. Eur J Biochem FEBS 218:565–574
Frischmeyer PA, van Hoof A, O’Donnell K, Guerrerio AL, Parker R, Dietz HC (2002) An mRNA surveillance mechanism that eliminates transcripts lacking termination codons. Science 295:2258–2261
Guydosh NR, Green R (2014) Dom34 rescues ribosomes in 3′ untranslated regions. Cell 156:950–962
Izawa T, Tsuboi T, Kuroha K, Inada T, Nishikawa S, Endo T (2012) Roles of Dom34:Hbs1 in nonstop protein clearance from translocators for normal organelle protein influx. Cell Rep 2:447–453
Jin Y, Jin S, Wu W (2016) Regulation of bacterial gene expression by ribosome stalling and rescuing. Curr Genet 62:309–312
Johnston JA, Ward CL, Kopito RR (1998) Aggresomes: a cellular response to misfolded proteins. J Cell Biol 143:1883–1898
Kuroha K, Akamatsu M, Dimitrova L, Ito T, Kato Y, Shirahige K, Inada T (2010) Receptor for activated C kinase 1 stimulates nascent polypeptide-dependent translation arrest. EMBO Rep 11:956–961
Lyumkis D, Oliveira Dos Passos D, Tahara EB, Webb K, Bennett EJ, Vinterbo S, Potter CS, Carragher B, Joazeiro CAP (2014) Structural basis for translational surveillance by the large ribosomal subunit-associated protein quality control complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:15981–15986
Matsuda R, Ikeuchi K, Nomura S, Inada T (2014) Protein quality control systems associated with no-go and nonstop mRNA surveillance in yeast. Genes Cells Devoted Mol Cell Mech 19:1–12
Meyer HH, Shorter JG, Seemann J, Pappin D, Warren G (2000) A complex of mammalian ufd1 and npl4 links the AAA-ATPase, p97, to ubiquitin and nuclear transport pathways. EMBO J 19:2181–2192
Ozsolak F, Kapranov P, Foissac S, Kim SW, Fishilevich E, Monaghan AP, John B, Milos PM (2010) Comprehensive polyadenylation site maps in yeast and human reveal pervasive alternative polyadenylation. Cell 143:1018–1029
Preissler S, Reuther J, Koch M, Scior A, Bruderek M, Frickey T, Deuerling E (2015) Not4-dependent translational repression is important for cellular protein homeostasis in yeast. EMBO J 34:1905–1924
Richly H, Rape M, Braun S, Rumpf S, Hoege C, Jentsch S (2005) A series of ubiquitin binding factors connects CDC48/p97 to substrate multiubiquitylation and proteasomal targeting. Cell 120:73–84
Richter K, Haslbeck M, Buchner J (2010) The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Mol Cell 40:253–266
Rosenbaum JC et al (2011) Disorder targets misorder in nuclear quality control degradation: a disordered ubiquitin ligase directly recognizes its misfolded substrates. Mol Cell 41:93–106
Ross CA, Poirier MA (2004) Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med 10(Suppl):S10–S17
Saarikangas J, Barral Y (2016) Protein aggregation as a mechanism of adaptive cellular responses. Curr Genet 62:711–724
Schmidt C et al (2016) The cryo-EM structure of a ribosome-Ski2-Ski3-Ski8 helicase complex. Science 354:1431–1433
Shao S, Hegde RS (2014) Reconstitution of a minimal ribosome-associated ubiquitination pathway with purified factors. Mol Cell 55:880–890
Shao S, von der Malsburg K, Hegde RS (2013) Listerin-dependent nascent protein ubiquitination relies on ribosome subunit dissociation. Mol Cell 50:637–648
Shao S, Brown A, Santhanam B, Hegde RS (2015) Structure and assembly pathway of the ribosome quality control complex. Mol Cell 57:433–444
Shen PS et al (2015) Protein synthesis. Rqc2p and 60S ribosomal subunits mediate mRNA-independent elongation of nascent chains. Science 347:75–78
Shoemaker CJ, Green R (2011) Kinetic analysis reveals the ordered coupling of translation termination and ribosome recycling in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1392–1398
Shoemaker CJ, Eyler DE, Green R (2010) Dom34:Hbs1 promotes subunit dissociation and peptidyl-tRNA drop-off to initiate no-go decay. Science 330:369–372
Sitron CS, Park JH, Brandman O (2017) Asc1, Hel2, and Slh1 couple translation arrest to nascent chain degradation. RNA 23:798–810
Sung M-K, Porras-Yakushi TR, Reitsma JM, Huber FM, Sweredoski MJ, Hoelz A, Hess S, Deshaies RJ (2016) A conserved quality-control pathway that mediates degradation of unassembled ribosomal proteins. eLife 5:e19105
van Hoof A, Frischmeyer PA, Dietz HC, Parker R (2002) Exosome-mediated recognition and degradation of mRNAs lacking a termination codon. Science 295:2262–2264
Verma R, Aravind L, Oania R, McDonald WH, Yates JR, Koonin EV, Deshaies RJ (2002) Role of Rpn11 metalloprotease in deubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome. Science 298:611–615
Verma R, Oania RS, Kolawa NJ, Deshaies RJ (2013) Cdc48/p97 promotes degradation of aberrant nascent polypeptides bound to the ribosome. eLife 2:e00308
von der Malsburg K, Shao S, Hegde RS (2015) The ribosome quality control pathway can access nascent polypeptides stalled at the Sec61 translocon. Mol Biol Cell 26:2168–2180
Wang Y, Meriin AB, Zaarur N, Romanova NV, Chernoff YO, Costello CE, Sherman MY (2008) Abnormal proteins can form aggresome in yeast: aggresome-targeting signals and components of the machinery. FASEB J 23:451–463
Yang J, Hao X, Cao X, Liu B, Nyström T (2016) Spatial sequestration and detoxification of Huntingtin by the ribosome quality control complex. eLife 5:e11792
Yonashiro R et al (2016) The Rqc2/Tae2 subunit of the ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) complex marks ribosome-stalled nascent polypeptide chains for aggregation. eLife 5:e11794
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by ANR-14-CE-10-0014-01 from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche, the Institut Pasteur, and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. Q.D. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (SPF20150934065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Defenouillère, Q., Fromont-Racine, M. The ribosome-bound quality control complex: from aberrant peptide clearance to proteostasis maintenance. Curr Genet 63, 997–1005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-017-0708-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-017-0708-5