Abstract
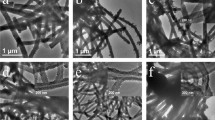
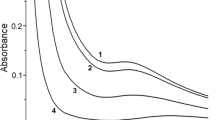
Different nanostructure shapes of polyaniline (PAni) particles such as rod and spherical shapes were prepared using gamma radiation. Gamma radiation is advantageous over other conventional methods because it provides a pure nanoparticle without by-products or any additives. The four solutions of aniline monomer Ani were dissolved in aprotic polar solvent N,N-dimethyl formamide (DMF) in different pH values and exposed to gamma radiation at a dosage of 50 kGy. The pH effect in terms of size and structure of PAni was investigated with four values 1, 5, 8 and 13 adjusted by adding HCl. A common polymerization mechanism induced by radiation is proposed as a radical cation polymerization, which is an environment friendly and cost effective mechanism without any side products or contaminants. The size and size distribution of PAni NPs suspension in DMF solvent were investigated by TEM and DLS. The results clearly showed that the ionizing radiation is an effective tool to produce a shape-controllable size. The changes of the spectrum with the pH of the polymerization solution obtained from UV–visible spectroscopy revealed that the smallest particles of PAni NPs can easily be obtained at low pH. The PAni particles are obtained with two morphologies (such as rod and spherical shapes).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghobashy MM and Khafaga MR (2016) J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0805-4
Abdel-Fattah AA, Soliman YS, Ghobashy MM (2018) J Polym Res 25: 106
Dole M (ed) (2013) The radiation chemistry of macromolecules, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Ghobashy MM, Younis SA, Elhady MA, Serp P (2018) Radiation induced in situ cationic polymerization of polystyrene organogel for selective absorption of chlorophenols from petrochemical wastewater. J Environ Manag 210:307–315
Ghobashy MM (2018) Ionizing radiation-induced polymerization. Ion Radiat Effects Appl. InTech, London, UK
Ghobashy MM, Younis SA, Elhady MA, Serp P (2018) Radiation induced in situ cationic polymerization of polystyrene organogel for selective absorption of cholorophenols from petrochemical wastewater. J Environ Manag 210:307–315
Rosiak JM (2004) Radiation polymerization in solution in: IAEA-TECDOC-1420 advances in radiation chemistry of polymers. In: Proceedings of a technical meeting held in Notre Dame, Indiana, USA 13–17 September 2003. International Atomic Energy Agency. Vienna, Austria, 2004
Gospodinova N, Terlemezyan L (1998) Conducting polymers prepared by oxidative polymerization: polyaniline. Prog Polym Sci 23(8):1443–1484
Sapurina Irina, Stejskal Jaroslav (2008) The mechanism of the oxidative polymerization of aniline and the formation of supramolecular polyaniline structures. Polym Int 57(12):1295–1325
Higashimura H, Kobayashi S (2004) Encyclopedia of polymer science and technology. In: Kroschwitz JI (ed) Oxidative polymerization,3 rol ed, vol 10. Wiley, New York
Chiang CK, Druy MA, Gau SC, Heeger AJ, Louis EJ, Alan G, MacDiarmid AG, Park Y, Shirakawa H (1978) Synthesis of highly conducting films of derivatives of polyacetylene,(CH) x. J Am Chem Soc 100(3):1013–1015
Jotiram KP, Prasad RGSV, Jakka VS, Aparna RSL, Phani AR (2012) Antibacterial activity of nanostructured polyaniline combined with mupirocin. Nano Biomed Eng 4(3):144–149
Feast WJ, Tsibouklis J, Pouwer KL, Groenendaal L, Meijer EW (1996) Synthesis, processing and material properties of conjugated polymers. Polymer 37(22):5017
Wang B, Tang J, Wang F (1987) Electrochemical polymerization of aniline. Synth Met 18(1):323–328
Stevens Malcolm P (1999) Polymer Chemistry: an Introduction. Oxford University Press, New York
Gospodinova N, Terlemezyan L (1998) Conducting polymers prepared by oxidative polymerization: polyaniline. Prog Polym Sci 23(8):1443–1484
Gospodinova N, Mokreva P, Terlemezyan L (1995) Oxidative polymerization of aniline: a new area in cationic polymerization. Polymer 36(18):3585–3587
Ghobashy MM, Khafaga MR (2016) Radiation synthesis and magnetic property investigations of the graft copolymer poly (Ethylene-g-Acrylic Acid)/Fe3O4 Film. J Supercond Novel Magn 30(2):401–406
Ghobashy MM and Abdeen ZI (2016) Radiation crosslinking of polyurethanes: characterization by FTIR, TGA, SEM, XRD, and Raman spectroscopy. J Polym 2016:9802514-1–9802514-9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9802514
Ghobashy Mohamed Mohamady (2017) Combined ultrasonic and gamma-irradiation to prepare TiO2@ PET-g-PAAc fabric composite for self-cleaning application. Ultrason Sonochem 37:529–535
Ghobashy MM, Abdel Reheem AM, Mazied NA (2017) Ion etching induced surface patterns of blend polymer (poly ethylene glycol–poly methyl methacrylate) irradiated with gamma rays. Int Polym Proc 32(2):174–182
Moreno-Castilla C (2004) Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon 42(1):83–94
Kim BJ, Oh SG, Han MG, Im SS (2001) Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline nanoparticles in SDS micellar solutions. Synth Met 122(2):297–304
Hasik M, Drelinkiewicz A, Wenda E, Paluszkiewicz C, Quillard S (2001) FTIR spectroscopic investigations of polyaniline derivatives–palladium systems. J Mol Struct 596(1):89–99
Werake LK, Story JG, Bertino MF, Pillalamarri SK, Blum FD (2005) Photolithographic synthesis of polyaniline nanofibres. Nanotechnology 16(12):2833
Rana S, Jadhav NV, Barick KC, Pandey BN, Hassan PA (2014) Polyaniline shell cross-linked Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for heat activated killing of cancer cells. Dalton Trans 43(32):12263–12271
Jurisson SS, Hirth W, Linder KE, Di Rocco RJ, Narra RK, Nowotnik DP, Nunn AD (1991) Chloro → hydroxy substitution on technetium BATO [TcCl (dioxime) 3BR] complexes. Int J Rad Appl Instr Part B Nucl Med Biol 18(7):735–744
Morales GM, Llusa M, Miras MC, Barbero C (1997) Effects of high hydrochloric acid concentration on aniline chemical polymerization. Polymer 38(20):5247–5250
Stejskal J, Kratochvil P, Radhakrishnan N (1993) Polyaniline dispersions 2. UV–vis absorption spectra. Synth Met 61(3):225–231
Dai L, Lu J, Matthews B, Mau AAW (1998) Doping of conducting polymers by sulfonated fullerene derivatives and dendrimers. J Phys Chem B 102(21):4049–4053
Schemid AL, Torresi SI, Bassetto AN, Carlos IA (2000) Structural, morphological and spectroelectrochemical characterization of poly (2-ethyl aniline). J Braz Chem Soc 11(3):317–323
Wan M (1992) Absorption spectra of thin film of polyaniline. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 30(4):543–549
Monkman AP, Adams P (1991) Structural characterisation of polyaniline free standing films. Synth Met 41(3):891–896
Stafström S, Bredas JL, Epstein AJ, Woo HS, Tanner DB, Huang WS, MacDiarmid AG (1987) Polaron lattice in highly conducting polyaniline: theoretical and optical studies. Phys Rev Lett 59(13):1464
Do Nascimento GM (2010) Spectroscopy of polyaniline nanofibers. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Ballauff M (1989) Stiff-chain polymers—structure, phase behavior, and properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 28(3):253–267
Lauter U, Meyer WH, Wegner G (1997) Molecular composites from rigid-rod poly (p-phenylene) s with oligo (oxyethylene) side chains as novel polymer electrolytes. Macromolecules 30(7):2092–2101
Platé NA, Shibaev VP (2012) Comb-shaped polymers and liquid crystals. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Sapurina Irina, Stejskal Jaroslav (2008) The mechanism of the oxidative polymerization of aniline and the formation of supramolecular polyaniline structures. Polym Int 57(12):1295–1325
Stejskal J, Hlavata D, Holler P, Trchová M, Prokeš J, Sapurina Irina (2004) Polyaniline prepared in the presence of various acids: a conductivity study. Polym Int 53(3):294–300
Baker CO, Huang X, Nelson W, Kaner RB (2017) Polyaniline nanofibers: broadening applications for conducting polymers. Chem Soc Rev 46(5):1510–1525
Thema FT, Beukes P, Nuru ZY, Kotsedi L, Khenfouch M, Dhlamini MS, Maaza M (2015) Physical properties of graphene via γ-radiolysis of exfoliated graphene oxide. Mater Today: Proc 2(7):4038–4045
Chow TJ (ed) (2014) Organic structures design: applications in optical and electronic devices. CRC Press, Boca Roton
Sapurina I, Stejskal J (2008) The mechanism of the oxidative polymerization of aniline and the formation of supramolecular polyaniline structures. Polym Int 57(12):1295–1325
Ding Y, Buyle Padias A, Hall HK (1999) Chemical trapping experiments support a cation-radical mechanism for the oxidative polymerization of aniline. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 37(14):2569–2579
Wei Y et al (1989) A study of the mechanism of aniline polymerization. J Poly Sci Part A Polym Chem 27(7):2385–2396
Shim YB, Won MS, Park SM (1990) Electrochemistry of conductive polymers VIII in situ spectroelectrochemical studies of polyaniline growth mechanisms. J Electrochem Soc 137(2):538–544
Felix JF, Barros RA, De Azevedo WM, Da Silva EF (2011) X-ray irradiation: a non-conventional route for the synthesis of conducting polymers. Synth Met 161(1):173–176
Wang J, Zhang D (2013) One-dimensional nanostructured polyaniline: syntheses, morphology controlling, formation mechanisms, new features, and applications. Adv Polym Technol 32(S1):E323–E368
Genies EM, Lapkowski M (1987) Spectroelectrochemical evidence for an intermediate in the electropolymerization of aniline. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 236(1–2):189–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghobashy, M.M., Alkhursani, S.A. & Madani, M. Radiation-induced nucleation and pH-controlled nanostructure shape of polyaniline dispersed in DMF. Polym. Bull. 75, 5477–5492 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2336-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2336-8