Abstract
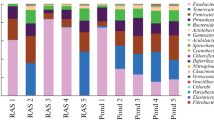
Determination of diversity and function of the bacteria in fish gut is essential to understanding the interaction between intestinal bacteria and their host organism. This study compared intestinal bacterial community of black seabass (Centropristis striata) hatched by the same breeding farm but reared in different aquaculture systems, an indoor recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) and an inshore net pen (INP). The fish were fed with formulated feed manufactured by same feed company. Bacteria in fish gut, formulated feed and seawater were identified by 16S rRNA high throughout sequencing (HTS). Total 1484 OTUs, which belonged to 34 phyla and 79 genera, were identified from fish gut, formulated feed and seawater. In fish gut, 24 phyla and 43 genera were identified. Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Firmicutes dominated at the phylum level in fish gut in INP, while Proteobacteria and Firmicutes dominated in fish gut in RAS. Photobacterium, Vibrio, and Cetobacterium dominated at the genus level in fish gut in both INP and RAS. One OTU of Photobacterium occurred in all the fish gut samples, suggesting this bacterium might be the main component of the core microbiota. No significant difference was found in bacterial diversity in fish gut between INP and RAS, suggesting genetic background should be a primary factor determining intestinal bacterial community of black seabass. Bacterial diversity in seawater was high relative to that in fish gut and formulated feed, regardless in INP or RAS. The common OTU between fish gut and seawater was more than that between fish gut and formulated feed in INP, while the common OTU between fish gut and seawater was slightly less than that between fish gut and formulated feed in RAS. These results reveal that the bacteria in formulated feed and seawater could influence the bacteria in fish gut, and their priority in shaping intestinal bacterial community depended on the bacterial composition in feed and seawater. This study reveals that intestinal bacterial community of black seabass was influenced by both genetic background and environmental factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the sequences data can be accessed in the GSA database under the accession number CRA004279 (https://bigd.big.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA004279). The data can also be asked from the corresponding author.
Code Availability
The data of this study are analyzed by QIIME2, figures are plotted by ggplot2.
References
O’Hara AM, Shanahan F (2006) The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep 7:688–693
Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, Sandhu KV, Bastiaanssen TFS, Boehme M, Codagnone MG, Cussotto S, Fulling C, Golubeva AV et al (2019) The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev 99:1877–2013
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Knights D, Walters WA, Peña AG, Pirrung M, Stombaugh J, Caporaso JG, Goodrich JK, Bittinger K, Lozupone CA, Costello EK et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Egerton S, Culloty S, Whooley J, Stanton C, Ross RP (2018) The gut microbiota of marine fish. Front Microbiol 9:873
Ou W, Yu G, Zhang Y, Mai K (2021) Recent progress in the understanding of the gut microbiota of marine fishes. Mar Life Sci Technol 3:434–448
Yukgehnaish K, Kumar P, Sivachandran P, Marimuthu K, Arshad A, Paray BA, Arockiaraj J (2020) Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Rev Aquac 12:1903–1927
Ringø E, Zhou Z, Vecino JLG, Wadsworth S, Romero J, Krogdahl Å, Olsen RE, Dimitroglou A, Foey A, Davies S et al (2016) Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. a never-ending story? Aquac Nutr 22:219–282
Tarnecki AM, Burgos FA, Ray CL, Arias CR (2017) Fish intestinal microbiome: diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J Appl Microbiol 123(1):2–17
Zhou Z, Ringø E, Olsen RE, Song SK (2018) Dietary effects of soybean products on gut microbiota and immunity of aquatic animals: a review. Aquac Nutr 24:644–665
Ghanbari M, Kneifel W, Domig KJ (2015) A new view of the fish gut microbiome: advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 448:464–475
Uma A, Subash P, Abraham TJ (2020) Importance of gut microbiota in fish—a review. Indian J Anim Hlth 59:181–194
Blancheton JP, Attramadal KJK, Michaud L, Roque d’Orbcastel D, Vadstein O (2013) Insight into bacterial population in aquaculture systems and its implication. Aquacult Eng 53:30–39
Buchan A, Lecleir GR, Gulvik CA, González JM (2014) Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:686–698
Huizinga HW, Esch GW, Hazen TC (1979) Histopathology of red-sore disease (Aeromonas Hydrophila) in naturally and experimentally infected largemouth bass Micropterus Salmoides (Lacepede). J Fish Dis 2:263–277
Melo Bolívar JF, Ruiz Pardo RY, Hume ME, Villamil Díaz LM (2021) Multistrain probiotics use in main commercially cultured freshwater fish: a systematic review of evidence. Rev Aquac 13(4):1758–1780.
Olmos J, Acosta M, Mendoza G, Pitones V (2020) Bacillus Subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch Microbiol 202:427–435
Zhang C, Zheng X, Ren X, Li Y, Wang Y (2019) Bacterial diversity in gut of large yellow croaker Larimichthys Crocea and black sea bream sparus macrocephalus reared in an inshore net pen. Fish Sci 85:1027–1036
Chiarello M, Paz VI, Veyssière C, Santoul F, Loot G, Ferriol J, Boulêtreau S (2019) Environmental conditions and neutral processes shape the skin microbiome of European catfish (Silurus Glanis) populations of southwestern France. Environmental Microbiology Reports 11:605–614
Eichmiller JJ, Hamilton MJ, Staley C, Sadowsky MJ, Sorensen PW (2016) Environment shapes the fecal microbiome of invasive carp species. Microbiome 4:44–52
Llewellyn MS, Mcginnity P, Dionne M, Letourneau J, Thonier F, Carvalho GR, Creer S, Derome N (2016) The biogeography of the atlantic salmon (Salmo Salar) gut microbiome. ISME J 10:1280–1284
Romero J, Ringø E, Merrifield DL (2014) The gut microbiota of fish. In: Merrifield D, Ringø E (eds) Aquaculture nutrition: gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp 75–100
Kokou F, Sasson G, Friedman J, Eyal S, Ovadia O, Harpaz S, Cnaani A, Mizrahi I (2019) Core gut microbial communities are maintained by beneficial interactions and strain variability in fish. Nat Microbiol 4:2456–2465
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T et al (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65
Shade A, Handelsman J (2012) Beyond the venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environ Microbiol 14:4–12
Turnbaugh PJ, Gordon JI (2009) The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. J Physiol 587:4153–4158
Anderson W, Milagrosa Bustamante G, Carpenter KE, Gilmore G, Robertson R (2015) Centropristis striata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T16435325A16510242.en
Callahan BJ, Mcmurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V et al (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Douglas GM, Maffei VJ, Zaneveld JR, Yurgel SN, Brown JR, Taylor CM, Huttenhower C, Langille MGI (2020) PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat Biotechnol 38:685–688
Warnes GR, Bolker B, Bonebakker L, Gentleman R, Moeller S (2005) Gplots: various R programming tools for plotting data.https://cran.r-project.org/package=gplots
Wang AR, Ran C, Ringø E, Zhou ZG (2018) Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev Aquac 10:626–640
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M, Fraser-Liggett CM, Knight R, Gordon JI (2007) The human microbiome project. Nature 449:804–810
Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM, Guillemin K, Rawls JF (2011) Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J 5:1595–1608
Wong S, Rawls JF (2012) Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol Ecol 21:3100–3102
Yan Q, Li J, Yu Y, Wang J, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Kempher ML, Wu L, Wang Y, Liao L et al (2016) Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol 18:4739–4754
Le D, Nguyen P, Nguyen D et al (2020) Gut microbiota of migrating wild rabbit fish (Siganus guttatus) larvae have low spatial and temporal variability. Microb Ecol 79:539–551
Dehler CE, Secombes CJ, Martin SAM (2017) Environmental and physiological factors shape the gut microbiota of atlantic salmon parr (Salmo Salar L.). Aquaculture 467:149–157
Lauzon HL, Gudmundsdottir S, Petursdottir SK, Reynisson E, Steinarsson A, Oddgeirsson M, Bjornsdottir R, Gudmundsdottir BK (2010) Microbiota of atlantic cod (Gadus Morhua L.) rearing systems at pre-and posthatch stages and the effect of different treatments. J Appl Microbiol 109:1775–1789
Mcintosh D, Ji B, Forward BS, Puvanendran V, Boyce D, Ritchie R (2008) Culture-independent characterization of the bacterial populations associated with cod (Gadus Morhua L.) and live feed at an experimental hatchery facility using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Aquaculture 275:42–50
Blanch AR, Alsina M, Simon M, Jofre J (1997) Determination of bacteria associated with reared turbot (Scophthalmus Maximus) larvae. J Appl Microbiol 82:729–734
Hansen GH, Olafsen JA (1999) Bacterial interactions in early life stages of marine cold water fish. Microb Ecol 38:1–26
Giatsis C, Sipkema D, Smidt H, Verreth JAJ, Verdegem MCJ, Jiravanichpaisal P (2014) The colonization dynamics of the gut microbiota in tilapia larvae. PLoS ONE 9:e103641
Tsuchiya C, Sakata T, Sugita H (2008) Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium Somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett Appl Microbiol 46:43–48
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31772868). We thank Dr. Jingan Wang and Victor Hector for their suggestion in revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CY participated in sample collection, conducted data analysis and drafted the manuscript. CZ conducted sample collection and bacterial DNA extraction. AS revised grammar of English of the manuscript. YW designed the experiment and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was conducted following the guideline of Administration of Laboratory Animals published by the State Science and Technology Commission of China (Beijing, China), https://www.lac.zju.edu.cn/cms/26788.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Zhang, C., Salisu, A. et al. Comparison of the Intestinal Bacteria Between Black Seabass Centropristis striata Reared in Recirculating Aquaculture System and Net Pen. Curr Microbiol 79, 109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02789-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02789-6