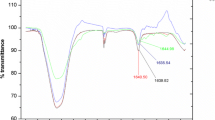
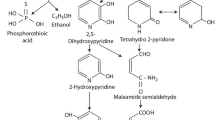
Abstract
Polyoxyethylene tallow amine (POEA) is a nonionic surfactant added to insecticide and herbicide formulations. Experimental data have been shown the toxic effects of POEA on aquatic organisms and remain to be a serious concern. In this study, total of thirty-two potential bacteria that were isolated from herbicide-contaminated soil samples showed the ability to use POEA as the sole carbon and energy source. In which, a bacterial strain LA was further investigated based on the efficiency utilization of POEA and classified as Kosakonia oryzae by the 16S rRNA gene. Response surface methodology was successfully applied to understand the interaction of distinct factors on POEA degradation by LA strain. Degradation of POEA was confirmed with UV–Visible spectrophotometric analysis and HPLC analysis. The POEA utilization mechanism was explored by target gene detection and carbon source utilization. The results indicate that strain LA has the potential to serve as an in situ candidate for bioremediation polluted by POEA.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Kolpin DW, Thurman EM, Lee EA, Meyer MT, Furlong ET, Glassmeyer ST (2006) Urban contributions of glyphosate and its degradate AMPA to streams in the United States. Sci Total Environ 354(2–3):191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.028
Martens MA, Bleeke MS, Leopold VA, Farmer DR (2019) Toxicology and human health risk assessment of polyethoxylated tallow amine surfactant used in glyphosate formulations. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol : RTP 107:104347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2019.03.014
Tush D, Meyer MT (2016) Polyoxyethylene tallow amine, a glyphosate formulation adjuvant: soil adsorption characteristics, degradation profile, and occurrence on selected soils from agricultural fields in Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Mississippi, and Missouri. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5781–5789. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00965
Tush D, Loftin KA, Meyer MT (2013) Characterization of polyoxyethylene tallow amine surfactants in technical mixtures and glyphosate formulations using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1319:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.032
Rodriguez-Gil JL, Prosser R, Poirier D, Lissemore L, Thompson D, Hanson M, Solomon KR 2017 Aquatic hazard assessment of MON 0818, a commercial mixture of alkylamine ethoxylates commonly used in glyphosate-containing herbicide formulations. Part 1: Species sensitivity distribution from laboratory acute exposures. Environmental toxicology and chemistry 36 (2): 501–511 Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3559
Brausch JM, Beall B, Smith PN (2007) Acute and sub-lethal toxicity of three POEA surfactant formulations to Daphnia magna. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78(6):510–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9091-0
Tsui MT, Chu LM (2003) Aquatic toxicity of glyphosate-based formulations: comparison between different organisms and the effects of environmental factors. Chemosphere 52(7):1189–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00306-0
Brausch JM, Smith PN (2007) Toxicity of three polyethoxylated tallowamine surfactant formulations to laboratory and field collected fairy shrimp, Thamnocephalus platyurus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52(2):217–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0151-y
Tush D, Maksimowicz MM, Meyer MT (2018) Dissipation of polyoxyethylene tallow amine (POEA) and glyphosate in an agricultural field and their co-occurrence on streambed sediments. Sci Total Environ 636:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.246
Williams GM, Kroes R, Munro IC (2000) Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol: RTP 31(2 Pt 1):117–165. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1999.1371
Vereecken H (2005) Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: a review. Pest Manag Sci 61(12):1139–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1122
Ross AR, Liao X (2015) A novel method for the rapid determination of polyethoxylated tallow amine surfactants in water and sediment using large volume injection with high performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 889:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.06.046
Rokade KB, Mali GV (2012) Biodegradation of tallowamine ethoxylate by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Int Res J Biol Sci 1(4):56–60
Kalme SD, Parshetti GK, Jadhav SU, Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of benzidine based dye Direct Blue-6 by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Biores Technol 98(7):1405–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.023
Ausubel FM, Roger. B, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Kevin S 2003 Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, ringbou edn., John Wiley & Sons
Johnson J (1994) Similarity analyses of rRNAs. In: Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Gerhardt P. Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology American Society for Microbiology, DC, pp 683–700
Nguyen NT (2018) Acinetobacter soli SP2 capable of high-efficiency degradation of food emulsifier polysorbate 80. Curr Microbiol 75(7):896–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1463-7
Dash DM, Osborne WJ (2020) Rapid biodegradation and biofilm-mediated bioremoval of organophosphorus pesticides using an indigenous Kosakonia oryzae strain -VITPSCQ3 in a Vertical-flow Packed Bed Biofilm Bioreactor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:110290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110290
Li Y, Li S, Chen M, Peng G, Tan Z, An Q (2017) Complete genome sequence of Kosakonia oryzae type strain Ola 51(T). Stand Genomic Sci 12:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-017-0240-8
Meng X, Bertani I, Abbruscato P, Piffanelli P, Licastro D, Wang C, Venturi V 2015 Draft Genome Sequence of Rice Endophyte-Associated Isolate Kosakonia oryzae KO348. Genome Announcements Doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00594-15
Semple KT, Reid BJ, Fermor TR (2001) Impact of composting strategies on the treatment of soils contaminated with organic pollutants. Environ Pollut 112(2):269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(00)00099-3
Soares A, Guieysse B, Jefferson B, Cartmell E, Lester JN (2008) Nonylphenol in the environment: a critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ Int 34(7):1033–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.01.004
Chen HJ, Huang SL, Tseng DH (2004) Aerobic biotransformation of octylphenol polyethoxylate surfactant in soil microcosms. Environ Technol 25(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330409355453
Sato H, Shibata A, Wang Y, Yoshikawa H, Tamura H 2003 Characterization of biodegradation intermediates of nonionic surfactants by MALDI-MS. 2 Oxidative biodegradation profiles of uniform octylphenol polyethoxylate in 18O-labeled water. Biomacromolecules 4 (1): 46–51 Doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/bm025616q
Nguyen TN, Yeh CW, Tsai PC, Lee K, Huang SL (2016) Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes critical for growth of pseudomonas nitroreducens TX1 on octylphenol polyethoxylates. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(22):6584–6592. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01907-16
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: N.T.N. and T.T.T.P. Methodology: N.T.N., T.T.T.P., T.N.T., and S.S. Investigation: N.T.N., R.K., and T.N.T. Writing—original draft: N.T.N., V.B.K., and S.S. Writing—review and editing: V.B.K. and R.K. Supervision: N.T.N.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, N.T., Pham, T.T.T., Tran, T.N. et al. Identification and Biodegradation Potential of a Novel Strain of Kosakonia oryzae Isolated from a Polyoxyethylene Tallow Amine Paddy Soil. Curr Microbiol 78, 3173–3180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02592-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02592-9