Abstract
Stain NN08200 was isolated from the surface-sterilized stem of sugarcane grown in Guangxi province of China. The stain was Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming bacteria. The complete genome SNP-based phylogenetic analysis indicate that NN08200 is a member of the genus Pantoea ananatis. Here, we summarize the features of strain NN08200 and describe its complete genome. The genome contains a chromosome and two plasmids, in total 5,176,640 nucleotides with 54.76% GC content. The chromosome genome contains 4598 protein-coding genes, and 135 ncRNA genes, including 22 rRNA genes, 78 tRNA genes and 35 sRNA genes, the plasmid 1 contains 149 protein-coding genes and the plasmid 2 contains 308 protein-coding genes. We identified 130 tandem repeats, 101 transposon genes, and 16 predicted genomic islands on the chromosome. We found an indole pyruvate decarboxylase encoding gene which involved in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid, it may explain the reason why NN08200 stain have growth-promoting effects on sugarcane. Considering the pathogenic potential and its versatility of the species of the genus Pantoea, the genome information of the strain NN08200 give us a chance to determine the genetic background of interactions between endophytic enterobacteria and plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The genus Pantoea comprises several species that are associated with plants have been found, either as pathogenic or beneficial bacteria to plants [1, 2]. Some of the first identified members of Pantoea were plant pathogens, but many studies subsequently indicated that Pantoea exist in a multitude of environments and most of them do beneficial to bioremediation and plant growth [3,4,5]. There are many Pantoea strains isolated from plants, soil and environment and are currently being explored for agricultural applications [6, 7]. Approximately, 20 Pantoea species have been identified, having diverse characteristics [8]. The ubiquity, versatility and genetic tractability of Pantoea make it ideal for exploring niche specific adaptation and opportunism, and for the development of agricultural and environmental products [9, 10].
To obtain endophytes that have growth-promoting effects on host sugarcane plants and have potential for agricultural application, we attempted to isolate and identify endophytic bacteria associated with sugarcane plants grown in Guangxi Province, the major sugarcane and sugar-producing area of China. Bacterial strain NN08200 was isolated from surface-sterilized stems of a ROC22 sugarcane plant grown in Nanning, Guangxi, China. We had determined the plant growth-promoting potential of strain NN08200 to sugarcane under a greenhouse condition [11]. Moreover, we observed the strain NN08200 colonization at the roots and aerial parts of micropropagated sugarcane plantlets with fluorescence microscopy and confocal microscopy. Sequence determinations and phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene indicated that strain NN08200 is affiliated with the genus Pantoea, and the strain was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, with the preservation number CGMCC No. 5438. Here, we present a summary of the features of strain NN08200 and its complete genome sequence, which provides a reference for resolving the phylogeny and taxonomy of closely related strains and genetic information to study the plant growth-promoting potential and plant-associated lifestyle of strain NN08200.
Organism Information
Classification and General Features
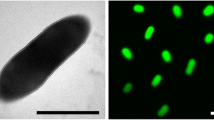
Strain NN08200 is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile rod with peritrichous flagella (Fig. 1). This bacterium was able to grow in anaerobic using cooked meat medium with thermal melting vaseline and aerobic using beef extract medium, and grew optimally between 28 and 32 °C (Table 1). It forms circular, convex, smooth colonies on nutrient agar; in addition, it grows well on Ashby nitrogen-free culture medium, showing round, transparent colonies. Strain NN08200 is a species of Pantoea, showing several differences from the Pantoea species described so far. The strain is an endophyte from sugarcane. It is positive for indole production, nitrate reduction and arginine decarboxylase and lysine decarboxylase activity.
A PHYML method phylogenetic tree based on SNP of complete genomes for strain belonging to the genus Pantoea constructed by TreeBeST (Fig. 2) showed that strain NN08200 is most closely related to strains belonging to the Pantoea ananatis [20]. Genomes gene sequences from the following strains were used to construct the phylogenetic tree: P. sesame Si-M154, taxonomy ID: 1881110; P. ananatis LMG 20103, taxonomy ID: 706191; P. ananatis AJ13355, taxonomy ID: 932677; P. ananatis R100, taxonomy ID:; P. ananatis PA13, taxonomy ID: 1095774; P. allii LMG_24248, taxonomy ID: 574096; P. stewartii subsp_indologenes LMG 2632, taxonomy ID: 66270; P. agglomerans Eh318, taxonomy ID: 1408177; P. septica LMG 5345, taxonomy ID: 472695; P. rwandensis ND04, taxonomy ID: 1076550; P. eucrina LMG 5346, taxonomy ID: 472693; P. wallisii LMG 26277, taxonomy ID: 1076551; P. cypripedii LMG 2657, taxonomy ID: 55209; P. alhagi LTYR-11Z, taxonomy ID: 1891675; 1 342, taxonomy ID: 1465635.
Phylogenetic tree based on the genome sequences showing the phylogenetic position of strain NN08200 and other strains belonging to the genus Pantoea. A PHYML method was beedn used to build the phylogenetic tree based on SNP of complete genomes for strain belonging to the genus Pantoea constructed by TreeBeST
Genome Sequencing Information Genome Project History
Pantoea ananatis strain NN08200 was selected for sequencing based on its taxonomic significance and because it could be used in promoting plant growth. The genome sequence is deposited in GenBank with the accession number CP035034. Information about the genome sequencing and its association with MIGS version 2.0 compliance is shown in Table 2.
Growth Conditions and DNA Isolation
P. ananatis strain NN08200 was grown in liquid Luria–Bertani medium at 28 °C until stationary phase. Genomic DNA was extracted using a TIANamp bacterial DNA kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). The quantity and quality of DNA were assessed using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, USA).
Genome Sequencing and Assembly
The genomic DNA of P. ananatis strain NN08200 was first constructed into a 10-kb SMRT Bell library and sequenced using the PacBio RS II sequencing system. Low-quality reads were filtered by the SMRT portal (version 2.3.0) and the filtered reads were assembled to generate five contigs containing 5,176,640 bases [21, 22]. The final assembly of the genome provided an average of 166-fold coverage. The five contigs were scaffolding to three circular sequences. The fully assembled P. ananatis strain NN08200 genome is composed of a 4.7-M base pair chromosome, and two plasmids, whose sizes were 125k and 307k base pairs, respectively.
Genome Annotation
The complete sequence of P. ananatis strain NN08200 was analyzed using GeneMarkS (version 4.17) to retrieve protein coding genes [23]. Transfer RNA (tRNA) genes were predicted by tRNAscan-SE [24]. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes were analyzed by rRNAmmer [25]. Transposon PSI was used to predict transposons based on the homologous blast method. RepeatMasker (version open-4.0.5) and TRF (tandem repeats finder, version 4.07b) were used for identification of interspersed nuclear elements and tandem repeats, respectively [26, 27]. SlandPath-DIOMB (version 0.2) was used for identification of genomic islands [28].
Genome Properties
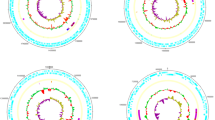
The genome of strain NN08200 contains a single chromosome of 4,743,568 nucleotides with 53.8% G+C content and two plasmids, one of 125,402 nucleotides with 56.47% G+C content and another of 307,670 nucleotides with 52.17% G+C content. The chromosome contains 4733 predicted genes: 4598 protein-coding genes and 135 RNA genes including 78 tRNA genes, 35 sRNA genes, and 22 rRNA genes (Table 3; Fig. 3). The plasmid 1 contains 149 protein-coding genes and the plasmid 2 contains 308 protein-coding genes. Ciros was used to show the genome and the result of gene function annotation [29]. In total, 4369 genes were assigned in Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins (COG) functional categories and they are listed in Table 4.
Insights from the Genome
Here we present the complete genome sequence of Pantoea ananatis strain NN08200. Protein-coding sequences accounted for 4598(97.15%) of the total of 4733 genes identified. 54 complete genomes of P. ananatis have been download from NCBI to performed an Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) analysis with strain NN08200 [30]. The results justified the conclusion of phylogenetic analysis, strain NN08200 with other strains resulted in a high ANI (> 95%). The results suggested that the strain NNo8200 belongs to the P. ananatis. NN08200 and P. ananatis S8 resulted in the highest ANI (99.2%) and show that they are similar than other strains.
Conclusion
In this study, we present the complete genome sequence of Pantoea ananatis strain NN08200, an endophyte from sugarcane. The genome of P. ananatis NN08200 consists of a 4,743,568-bp long chromosome, containing 4598 protein coding genes. P. ananatis NN08200 also contains two plasmids. To analyze the complete genome sequence of Pantoea ananatis strain NN08200, we found an indole pyruvate decarboxylase encoding gene which involved in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid [31], it may promote plant growth by improving the synthesis of indoleacetic acid. The new genomic data will facilitate future applications of this strain in agricultural production.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI repository, (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA514184).
References
Feng YJ, Shen DL, Dong XZ et al (2003) In vitro symplasmata formation in the rice diazotrophic endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19. Plant Soil 255(2):435–444
Brady C, Cleenwerck I, Venter S et al (2008) Phylogeny and identiication of Pantoea species associated with plants, humans and the natural environment based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA). Syst Appl Microbiol 31:447–460
Choi Q, Kim H, Lee Y et al (2012) First report of sheathrot of rice caused by Pantoea ananatis in Korea. Plant Pathol J 28(3):331
Zhang J, Zhang CW, Yang J et al (2019) Insights into endophytic bacterial community structures of seeds among various Oryza sativa L. rice genotypes. J Plant Growth Regul 38(1):93–102
Volksch B, Thon S, Jacobsen I et al (2009) Polyphasic study of plant and clinic-associated Pantoea agglomerans strains reveals indistinguishable virulence potential. Infect Genet Evol 9:1381–1391
Nadarasah G, Stavrinides J (2014) Quantitative evaluation of the host colonizing capabilities of the enteric bacterium Pantoea using plant and insect hosts. Microbiology 160:602–615
Selvakumar G, Kundu S, Joshi P et al (2008) Characterization of a cold-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacterium Pantoea dispersa 1A isolated from a sub-alpine soil in the North Western Indian Himalayas. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(7):955–960
Guo HB, He SW, Wang X et al (2017) Phylogenetic diversity and plant growth-promoting characteristics of endophytic Pantoea spp. in rice seeds. Acta Microbiol Sin. https://doi.org/10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20180581
Yoshida A, Kohchi C, Inagawa H et al (2009) Improvement of allergic dermatitis via regulation of the Th1/Th2 immune systembalance bymacrophages activated with lipopolysaccharide derived from Pantoea agglomerans (IP-PA1). Anticancer Res 29:4867–4870
Walterson AM, Stavrinides J (2015) Pantoea: insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39(6):968–984
Shi GY, Zeng Q, Nong ZM et al (2012) Identification of an endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacterium NN08200 from sugarcane and its growth promotion of sugarcane. Microbiol China. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.180523
Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (1990) Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4576–4579
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T (2005) Phylum XIV. Proteobacteria phyl. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn, vol. 2, Part B. Springer, New York, p 1
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T et al (2015) Gammaproteobacteria class. nov. Criminal behaviour and mental health
Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) (2005) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd edn, vol. 2. Springer, New York, p 1
List Editor (2005) Validation of publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSEM. List no. 106. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2235–2238.
Williams KP, Kelly DP (2013) Proposal for a new class within the phylum Proteobacteria, Acidithiobacillia classis nov., with the type order Acidithiobacillales, and emended description of the class Gammaproteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2901–2906
Garrity GM, Holt JG (2001) Taxonomic outline of the archaea and bacteria. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 155–166
Palmer M, Steenkamp ET, Coetzee MPA et al (2018) Mixta gen. nov. a new genus in the Erwiniaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(4):1396
Tamura K, Peterson DS, Peterson N et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Konstantin B, Sergey K, Chen-Shan C et al (2015) Assembling large genomes with single-molecule sequencing and locality sensitive hashing. Nat Biotechnol 33:623–630
Sergey K, Adam MP (2015) One chromosome, one contig: complete microbial genomes from long-read sequencing and assembly. Curr Opin Microbiol 23:110–120
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29(12):2607–2618
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25(5):955–964
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA et al (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35(9):3100–3108
Saha S, Bridges S, Magbanua ZV et al (2008) Empirical comparison of ab initio repeat finding programs. Nucleic Acids Res 36(7):2284–2294
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27(2):573
Hsiao W, Wan I, Jones SJ et al (2003) IslandPath: aiding detection of genomic islands in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 19(3):418–420
Krzywinski M et al (2009) Circos: an Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645
Richter M, Rossellomora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(45):19126–19131
Schutz A, Sandalova T, Ricagno S et al (2003) Crystal structure of thiamindiphosphate-dependent indolepyruvate decarboxylase from Enterobacter cloacae, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid. FEBS J 270(10):2312–2321
Acknowledgements
We thank Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101122 and 31660025), Guangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2016GXNSFBA380009 and 2017GXNSFBA198118), and the Sciences and Technology Development Foundation of Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2015YT76; 2017JM37), Scientific Research and Technology Development Program of Guangxi (AB18221048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Shi, G., Nong, Z. et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Pantoea ananatis Strain NN08200, an Endophytic Bacterium Isolated from Sugarcane. Curr Microbiol 77, 1864–1870 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01972-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01972-x