Abstract
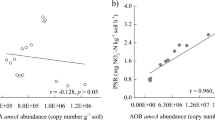
Nitrification plays a significant role in soil nitrogen cycling, a process in which the first step can be catalyzed by ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB). In this study, six soil samples with distinct land-use regimes (forestland soil, paddy soil, wheat-planted soil, fruit-planted soil, grassland soil, and rape-planted soil) were collected from Chuzhou city in the Anhui province to elucidate the effects of land use on the abundance and diversity of AOA and AOB. The abundance of the archaeal amoA gene ranged from 2.12 × 104 copies per gram of dry soil to 2.57 × 105 copies per gram of dry soil, while the abundance of the bacterial amoA gene ranged from 5.58 × 104 copies per gram of dry soil to 1.59 × 108 copies per gram of dry soil. The grassland and the rape-planted soil samples maintained the highest abundance of the bacterial and archaeal amoA genes, respectively. The abundance of the archaeal amoA gene was positively correlated with the pH (P < 0.05). The ammonia concentrations exhibited a significantly positive relation with the abundance of the bacterial amoA gene (P < 0.01) and the number of OTUs of AOB (P < 0.05). The community composition of AOB was more sensitive to the land-use regimes than that of AOA. The data obtained in this study may be useful to better understand the nitrification process in soils with different land-use regimes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair KL, Schwartz E (2008) Evidence that ammonia-oxidizing archaea are more abundant than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in semiarid soils of northern Arizona, USA. Microb Ecol 56:420–426
Avrahami S, Conrad R (2003) Patterns of community change among ammonia oxidizers in meadow soils upon long-term incubation at different temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6152–6164
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahia del Tobari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7767–7777
Bernhard AE, Bollmann A (2010) Estuarine nitrifiers: new players, patterns and processes. Estuar Coast Shelf S 88:1–11
Boyle-Yarwood SA, Bottomley PJ, Myrold DD (2008) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils under stands of red alder and Douglas fir in Oregon. Environ Microbiol 10:2956–2965
Briones AM, Okabe S, Umemiya Y, Ramsing NB, Reichardt W, Okuyama H (2002) Influence of different cultivars on populations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the root environment of rice. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3067–3075
Chen X, Zhang LM, Shen JP, Xu Z, He JZ (2010) Soil type determines the abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in flooded paddy soils. J Soils Sediments 10:1510–1516
Chen XP, Zhu YG, Xia Y, Shen JP, He JZ (2008) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil. Environ Microbiol 10:1978–1987
De BW, Kowalchuk GA (2001) Nitrification in acid soils: micro-organisms and mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 33:853–866
Di HJ, Cameron KC, Shen JP, Winefield CS, O’Callaghan M, Bowatte S, He JZ (2009) Nitrification driven by bacteria and not archaea in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. Nat Geosci 2:621–624
Francis CA, Beman JM, Kuypers MM (2007) New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: the microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. The ISME J 1:19–27
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. P Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14683–14688
Girvan MS, Bullimore J, Pretty JN, Osborn AM, Ball AS (2003) Soil type is the primary determinant of the composition of the total and active bacterial communities in arable soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1800–1809
Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:566–574
Hastings RC, Butler C, Singleton I, Saunders JR, McCarthy AJ (2000) Analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria populations in acid forest soil during conditions of moisture limitation. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:14–18
Hermansson A, Lindgren PE (2001) Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in arable soil by real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:972–976
He JZ, Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zheng YM, Xu MG, Di H (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Hu A, Yao T, Jiao N, Liu Y, Yang Z, Liu X (2010) Community structures of ammonia-oxidising archaea and bacteria in high-altitude lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Freshw Biol 55:2375–2390
Jia Z, Conrad R (2009) Bacteria rather than archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ Microbiol 11:1658–1671
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, José R, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Koski-Vähälä J, Hartikainen H, Tallberg P (2001) Phosphorus mobilization from various sediment pools in response to increased pH and silicate concentration. J Environ Qual 30:546–552
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidising bacteria in soil of successional grasslands of the Drentsche A (The Netherlands). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:207–215
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Changes in the community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria during secondary succession of calcareous grasslands. Environ Microbiol 2:99–110
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Li XR, Xiao YP, Ren WW, Liu ZF, Shi JH, Quan ZX (2012) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in different types of soil in the Yangtze River estuary. JZUS-B 13:769–782
Morimoto S, Hayatsu M, Takada HY, Nagaoka K, Yamazaki M, Karasawa T, Takenaka M, Akiyama H (2011) Quantitative analyses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in fields with different soil types. Microbes Environ 26:248–253
Mosier AC, Francis CA (2008) Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ Microbiol 10:3002–3016
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Okano Y, Hristova KR, Leutenegger CM, Jackson LE, Denison RF, Gebreyesus B, Lebauer D, Scow KM (2004) Application of real-time PCR to study effects of ammonium on population size of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1008–1016
Onodera Y, Nakagawa T, Takahashi R, Tokuyama T (2009) Seasonal change in vertical distribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their nitrification in temperate forest soil. Microbes Environ 25:28–35
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Schauss K, Focks A, Leininger S, Kotzerke A, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Sharma S, Wilke BM, Matthies M, Smalla K, Munch JC, Amelung W, Kaupenjohann M, Schloter M, Schleper C (2009) Dynamics and functional relevance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in two agricultural soils. Environ Microbiol 11:446–456
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Di HJ, He JZ (2012) A review of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chinese soils. Front Microbiol 3:296–302
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zhang JB, He JZ (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10:1601–1611
Suzuki C, Nagaoka K, Shimada A, Takenaka M (2009) Bacterial communities are more dependent on soil type than fertilizer type, but the reverse is true for fungal communities. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:80–90
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7:1985–1995
Wang Y, Ke X, Wu L, Lu Y (2009) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in rice field soil as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Syst Appl Microbiol 32:27–36
Webster G, Embley TM, Freitag TE, Smith Z, Prosser JI (2005) Links between ammonia oxidizer species composition, functional diversity and nitrification kinetics in grassland soils. Environ Microbiol 7:676–684
Webster G, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of β-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30
Weidler GW, Dornmayr-Pfaffenhuemer M, Gerbl FW, Heinen W, Stan-Lotter H (2007) Communities of archaea and bacteria in a subsurface radioactive thermal spring in the Austrian Central Alps, and evidence of ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeota. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:259–270
Zeng J, Zhao DY, Huang R, Wu QL (2012) Abundance and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in two different zones of Lake Taihu. Can J Microbiol 58:1018–1026
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Water Resources’ Special Funds for Scientific Research on Public Causes (201201026), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371098), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014T70470, 2014M561568) and Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (1401093C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dayong Zhao and Juan Luo have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Luo, J., Wang, J. et al. The Influence of Land Use on the Abundance and Diversity of Ammonia Oxidizers. Curr Microbiol 70, 282–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0714-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0714-5