Abstract
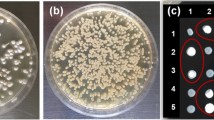
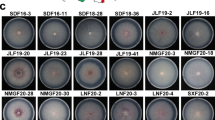
Strains A-15, S11, S-140, and U3 of Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach, were used as parent strains for raising single spore homokaryotic isolates. Out of total 1,642 single spore isolates, only 36 single spore isolates were homokaryons and exhibited slow mycelial growth rate (≤2.0 mm/day) and appressed colony morphology. All these SSIs failed to produce pinheads in Petri plates even after 65 days of incubation, whereas the strandy slow growing SSIs along with parent strains were able to form the fructification in petriplates after 30 days. Out of 24, six ISSR primers, exhibited scorable bands. In the ISSR fingerprints, single spore isolates, homokaryons, lacked amplification products at multiple loci; they grow slowly and all of them had appressed types of colony morphology. The study revealed losses of ISSR polymorphic patterns in non-fertile homokaryotic single spore isolates compared to the parental control or fertile heterokaryotic single spore isolates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Challen MP, Kerrigan RW, Callac P (2003) A phylogenetic reconstruction and emendation of Agaricus section Duploannulatae. Mycologia 95:61–73
Elliott TJ (1985) The genetics and breeding of species of Agaricus. Bio tech culti mush. John Wiley and Sons, Chichestar, pp 111–139
Horgen PA, Anderson JB (1989) The germination of basidiospores from commercial and wild collected isolates of Agaricus bisporus. Can J Microbiol 35:492–498
Jianping X, Kerrigan W, Paul A, Horgen PA, Anderson JB (1993) Localization of the mating type gene in Agaricus bisporus. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(9):3044–3049
Kavousi HR, Farsi M, Shahriari F (2008) Comparison of RAPD markers and morphological characters in identification of homokaryon isolates in white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. Pak J Biol Sci 11(4):1771–1778
Khush RS, Becker E, Wach M (1992) DNA amplification polymorphisim of the cultivated mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1735–1739
Malekzadeh K, Shahri BJM, Mohsenifard E (2011) Use of ISSR markers for strain identification in the button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on mushroom biology and mushroom products (ICMBMP7), pp 30–34
Nazrul MI, Yinbing B (2009) ISSR as new markers for identification of homokaryotic protoclones of Agaricus bisporus. Curr Microbiol 60:92–98
Nazrul MI, Yinbing B (2011) Differentiation of homokaryons and heterokaryons of Agaricus bisporus with inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Microbiol Res 166(3):226–236
Nazrul MI, Lin FX, Yinbing B (2010) Screening of homokaryotic protoclones of Agaricus bisporus (J. Lge) Imbach by colony characters and ISSR markers. Bangladesh J Bot 39(1):119–122
Raper CA, Raper JR, Miller RE (1972) Genetic analysis of the life cycle of Agaricus bisporus. Mycologia 64:1088–1117
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS-P-numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.0. Exeter Software, New York
Summerbell RC, Castle AJ, Horgen PA, Anderson JB (1989) Inheritance of restriction fragment length polymorphism in Agaricus brunnescens. Genetics 123:293–300
Yadav MC (2003) Molecular breeding for development of genetically improved strain and hybrids of Agaricus bisporus. Current vistas in mushroom biology and production. Nirmal Vijay Press, New Delhi, pp 261–274
Yan PS, Jiang JH (2005) Preliminary research of the RAPD molecular marker-assisted breeding of the edible Basidiomycete Stropharia rugoso-annulata. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:559–563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M., Suman, B.C. & Gupta, D. Characterization of Single Spore Isolates of Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach Using Conventional and Molecular Methods. Curr Microbiol 69, 474–483 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0608-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0608-6