Abstract
Background
Abiraterone became a standard hormonal therapy for patients with metastatic castration-resistance prostate cancer (mCRPC). However, patients may experience primary resistance to treatment. To date, few predictive biomarkers of efficacy have been identified. Our aim was to investigate the association between the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) c.-362T>C in the CYP17A1 gene, and clinical outcome in mCRPC patients treated with abiraterone.
Patients and methods
mCRPC patients candidate to receive abiraterone were enrolled in the present retrospective pharmacogenetic study. Based on a literature selection, CYP17A1 rs2486758 (c.-362T > C) was selected and analysed by real-time PCR on genomic DNA extracted from whole blood. Univariate analysis was performed to test the association between the SNP and treatment-related clinical outcomes.
Results
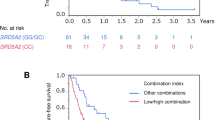
Sixty mCRPC patients were enrolled in the present study. Patients carrying the mutant CYP17A1 c.-362CT/CC genotypes showed a shorter median progression-free survival (PFS) and prostate-specific antigen-PFS (PSA-PFS) compared to patients carrying the TT genotype (10.7 vs 14.2 months and 8 vs 16 months, respectively; p = 0.04). No association between the selected SNP and the overall survival was found.
Conclusions
These findings suggest an association between CYP17A1 c.-362T>C polymorphism and poorer clinical outcome with abiraterone for mCRPC patients. However, further validations on larger cohort of patients are needed to confirm its role as a predictive biomarker for abiraterone resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epidemiology of prostate cancer in Europe [Internet]. European Commission (2015) https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/publication/epidemiology-prostate-cancer-europe
Arnold M, Karim-Kos HE, Coebergh JW, Byrnes G, Antilla A, Ferlay J, Renehan AG, Forman D, Soerjomataram I (2015) Recent trends in incidence of five common cancers in 26 European countries since 1988: analysis of the European Cancer Observatory. Eur J Cancer 51(9):1164–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2013.09.002
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Crawford ED, Petrylak D, Sartor O (2017) Navigating the evolving therapeutic landscape in advanced prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 35S:S1–S13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.01.020
Dong L, Zieren RC, Xue W, de Reijke TM, Pienta KJ (2019) Metastatic prostate cancer remains incurable, why? Asian J Urol 6(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2018.11.005
Kirby M, Hirst C, Crawford ED (2011) Characterising the castration-resistant prostate cancer population: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract 65(11):1180–1192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02799.x
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva B, Antipin Y, Mitsiades N, Landers T, Dolgalev I, Major JE, Wilson M, Socci ND, Lash AE, Heguy A, Eastham JA, Scher HI, Reuter VE, Scardino PT, Sander C, Sawyers CL, Gerald WL (2010) Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 18(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026
Higano CS, Crawford ED (2011) New and emerging agents for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 29(6 Suppl):S1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.08.013
Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN, Oudard S, Theodore C, James ND, Turesson I, Rosenthal MA, Eisenberger MA, Investigators TAX (2004) Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 351(15):1502–1512. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa040720
Nuhn P, De Bono JS, Fizazi K, Freedland SJ, Grilli M, Kantoff PW, Sonpavde G, Sternberg CN, Yegnasubramanian S, Antonarakis ES (2019) Update on systemic prostate cancer therapies: management of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in the era of precision oncology. Eur Urol 75(1):88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.03.028
Sartor O, de Bono JS (2018) Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med 378(7):645–657. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1701695
Chong JT, Oh WK, Liaw BC (2018) Profile of apalutamide in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: evidence to date. Onco Targets Ther 11:2141–2147. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S147168
O’Donnell A, Judson I, Dowsett M, Raynaud F, Dearnaley D, Mason M, Harland S, Robbins A, Halbert G, Nutley B, Jarman M (2004) Hormonal impact of the 17alpha-hydroxylase/C(17,20)-lyase inhibitor abiraterone acetate (CB7630) in patients with prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 90(12):2317–2325. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601879
Attard G, Reid AH, Yap TA, Raynaud F, Dowsett M, Settatree S, Barrett M, Parker C, Martins V, Folkerd E, Clark J, Cooper CS, Kaye SB, Dearnaley D, Lee G, de Bono JS (2008) Phase I clinical trial of a selective inhibitor of CYP17, abiraterone acetate, confirms that castration-resistant prostate cancer commonly remains hormone driven. J Clin Oncol 26(28):4563–4571. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.15.9749
Ferraldeschi R, Sharifi N, Auchus RJ, Attard G (2013) Molecular pathways: inhibiting steroid biosynthesis in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(13):3353–3359. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0931
Miller WL, Auchus RJ (2011) The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev 32(1):81–151. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2010-0013
Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F, Mulders PF, Sternberg CN, Miller K, Logothetis CJ, Shore ND, Small EJ, Carles J, Flaig TW, Taplin ME, Higano CS, de Souza P, de Bono JS, Griffin TW, De Porre P, Yu MK, Park YC, Li J, Kheoh T, Naini V, Molina A, Rathkopf DE, Investigators C-A (2015) Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16(2):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71205-7
Rydzewska LHM, Burdett S, Vale CL, Clarke NW, Fizazi K, Kheoh T, Mason MD, Miladinovic B, James ND, Parmar MKB, Spears MR, Sweeney CJ, Sydes MR, Tran N, Tierney JF, STA Collaborators (2017) Adding abiraterone to androgen deprivation therapy in men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 84:88–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.07.003
Beltran H, Antonarakis ES, Morris MJ, Attard G (2016) Emerging molecular biomarkers in advanced prostate cancer: translation to the clinic. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 35:131–141. https://doi.org/10.14694/EDBK_159248
Waterman MR, Keeney DS (1992) Genes involved in androgen biosynthesis and the male phenotype. Horm Res 38(5–6):217–221. https://doi.org/10.1159/000182546
Mostaghel EA, Marck BT, Plymate SR, Vessella RL, Balk S, Matsumoto AM, Nelson PS, Montgomery RB (2011) Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer: induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants. Clin Cancer Res 17(18):5913–5925. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0728
Cai C, Chen S, Ng P, Bubley GJ, Nelson PS, Mostaghel EA, Marck B, Matsumoto AM, Simon NI, Wang H, Chen S, Balk SP (2011) Intratumoral de novo steroid synthesis activates androgen receptor in castration-resistant prostate cancer and is upregulated by treatment with CYP17A1 inhibitors. Cancer Res 71(20):6503–6513. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0532
Salvi S, Casadio V, Conteduca V, Burgio SL, Menna C, Bianchi E, Rossi L, Carretta E, Masini C, Amadori D, Calistri D, Attard G, De Giorgi U (2015) Circulating cell-free AR and CYP17A1 copy number variations may associate with outcome of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone. Br J Cancer 112(10):1717–1724. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.128
Binder M, Zhang BY, Hillman DW, Kohli R, Kohli T, Lee A, Kohli M (2016) Common genetic variation in CYP17A1 and response to abiraterone acetate in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071097
Salvi S, Casadio V, Burgio SL, Conteduca V, Rossi L, Menna C, Carretta E, Costantini M, Zoli W, De Giorgi U (2016) CYP17A1 polymorphisms and clinical outcome of castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone. Int J Biol Markers 31(3):e264–269. https://doi.org/10.5301/jbm.5000197
Sweeney CJ, Chen YH, Carducci M, Liu G, Jarrard DF, Eisenberger M, Wong YN, Hahn N, Kohli M, Cooney MM, Dreicer R, Vogelzang NJ, Picus J, Shevrin D, Hussain M, Garcia JA, DiPaola RS (2015) Chemohormonal therapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 373(8):737–746. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1503747
Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY, Ozguroglu M, Ye D, Feyerabend S, Protheroe A, De Porre P, Kheoh T, Park YC, Todd MB, Chi KN, Investigators L (2017) Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 377(4):352–360. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1704174
Cozar JM, Robles-Fernandez I, Martinez-Gonzalez LJ, Pascual-Geler M, Rodriguez-Martinez A, Serrano MJ, Lorente JA, Alvarez-Cubero MJ (2018) Genetic markers a landscape in prostate cancer. Mutat Res 775:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.11.004
Hendriks RJ, Dijkstra S, Smit FP, Vandersmissen J, Van de Voorde H, Mulders PFA, van Oort IM, Van Criekinge W, Schalken JA (2018) Epigenetic markers in circulating cell-free DNA as prognostic markers for survival of castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Prostate 78(5):336–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23477
Seisen T, Roupret M, Gomez F, Malouf GG, Shariat SF, Peyronnet B, Spano JP, Cancel-Tassin G, Cussenot O (2016) A comprehensive review of genomic landscape, biomarkers and treatment sequencing in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 48:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.06.005
Del Re M, Crucitta S, Restante G, Rofi E, Arrigoni E, Biasco E, Sbrana A, Coppi E, Galli L, Bracarda S, Santini D, Danesi R (2018) Pharmacogenetics of androgen signaling in prostate cancer: focus on castration resistance and predictive biomarkers of response to treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 125:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.03.002
Zhang B, Binder M, Costello B, Quevedo F, Kohli M (2016) Association of CYP17A1 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) with response to abiraterone acetate (AA) in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J Clin Oncol 34:e16603–e16603. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_suppl.e16603
Roden DM, Wilke RA, Kroemer HK, Stein CM (2011) Pharmacogenomics: the genetics of variable drug responses. Circulation 123(15):1661–1670. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.914820
Diver LA, MacKenzie SM, Fraser R, McManus F, Freel EM, Alvarez-Madrazo S, McClure JD, Friel EC, Hanley NA, Dominiczak AF, Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB, Connell JM, Davies E (2016) Common polymorphisms at the CYP17A1 locus associate with steroid phenotype: support for blood pressure genome-wide association study signals at this locus. Hypertension 67(4):724–732. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06925
Manolio TA (2010) Genomewide association studies and assessment of the risk of disease. N Engl J Med 363(2):166–176. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0905980
Bremmer F, Jarry H, Strauss A, Behnes CL, Trojan L, Thelen P (2014) Increased expression of CYP17A1 indicates an effective targeting of the androgen receptor axis in castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Springerplus 3:574. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-574
Auchus ML, Auchus RJ (2012) Human steroid biosynthesis for the oncologist. J Investig Med 60(2):495–503. https://doi.org/10.2310/JIM.0b013e3182408567
Wang F, Zou YF, Feng XL, Su H, Huang F (2011) CYP17 gene polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 38 independent studies. Prostate 71(11):1167–1177. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.21332
Qin S, Liu D, Kohli M, Wang L, Vedell PT, Hillman DW, Niu N, Yu J, Weinshilboum RM, Wang L (2018) TSPYL family regulates CYP17A1 and CYP3A4 expression: potential mechanism contributing to abiraterone response in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther 104(1):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.907
Benoist GE, Hendriks RJ, Mulders PF, Gerritsen WR, Somford DM, Schalken JA, van Oort IM, Burger DM, van Erp NP (2016) Pharmacokinetic aspects of the two novel oral drugs used for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide. Clin Pharmacokinet 55(11):1369–1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-016-0403-6
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
:The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crucitta, S., Del Re, M., Paolieri, F. et al. CYP17A1 polymorphism c.-362T>C predicts clinical outcome in metastatic castration-resistance prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 86, 527–533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04133-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04133-w