Abstract
Background
PABA/NO, O2-{2,4-dinitro-5-[4-(N-methylamino) benzoyloxy] phenyl} 1-(N, N-dimethylamino) diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate, is a diazeniumdiolate-based NO-donor prodrug that releases exogenous nitric oxide at high concentrations to induce apoptosis in many tumor cell lines.
Purpose
This study aimed to determine the effects of PABA/NO on hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and apoptosis induction both in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Results
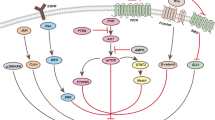
PABA/NO dramatically inhibited the growth of Bel-7402 hepatocellular carcinoma cells and significantly induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner, accompanied by down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, up-regulation of Bax and Bad, release of Cyt c and activation of cleaved-caspase-9/3 and cleaved-PARP, which were related to suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor) and U0126 (an ERK inhibitor) prior to PABA/NO were found to synergistically enhance PABA/NO-induced apoptosis. Carboxy-PTIO as a NO scavenger obviously attenuated PABA/NO-induced apoptosis. Additionally, H22 tumor-bearing mice experiments demonstrated that PABA/NO exerted good anti-tumor effects via reducing tumor volume, tumor weight and decreasing the expression of CD34. Furthermore, PABA/NO treatment strongly inhibited the phosphorylation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways in H22 hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.
Conclusions
PABA/NO induced apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikeda M, Morizane C, Ueno M, Okusaka T, Ishii H, Furuse J (2018) Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. Jpn J Clin Oncol 48(2):103–114. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyx180
Moriguchi M, Umemura A, Itoh Y (2016) Current status and future prospects of chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Gastroenterol 9(4):184–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-016-0670-7
Roof AK, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2018) Consider the context: Ras/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling outcomes are pituitary cell type-specific. Mol Cell Endocrinol 463:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.04.019
Ye C, Yu X, Liu X, Dai M, Zhang B (2018) miR-30d inhibits cell biological progression of Ewing’s sarcoma by suppressing the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in vitro. Oncol Lett 15(4):4390–4396. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7900
Asati V, Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK (2016) PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as anticancer agents: structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 109:314–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.012
Jokinen E, Koivunen JP (2015) MEK and PI3K inhibition in solid tumors: rationale and evidence to date. Ther Adv Med Oncol 7(3):170–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758834015571111
Zhou J, Zhao T, Ma L, Liang M, Guo YJ, Zhao LM (2017) Cucurbitacin B and SCH772984 exhibit synergistic anti-pancreatic cancer activities by suppressing EGFR, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, STAT3 and ERK signaling. Oncotarget 8(61):103167–103181. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21704
Zhu J, Yao J, Huang R, Wang Y, Jia M, Huang Y (2018) Ghrelin promotes human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/P70S6 K and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 498(3):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.031
Yasuda H (2008) Solid tumor physiology and hypoxia-induced chemo/radio-resistance: novel strategy for cancer therapy: nitric oxide donor as a therapeutic enhancer. Nitric Oxide 19(2):205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.026
Maher A, Abdel Rahman MF, Gad MZ (2017) The role of nitric oxide from neurological disease to cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 1007:71–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60733-7_5
Huang Z, Fu J, Zhang Y (2017) Nitric oxide donor-based cancer therapy: advances and prospects. J Med Chem 60(18):7617–7635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01672
Kang F, Ai Y, Zhang Y, Huang Z (2018) Design and synthesis of new hybrids from 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-9-dien-28-oic acid and O(2)-(2,4-dinitrophenyl) diazeniumdiolate for intervention of drug-resistant lung cancer. Eur J Med Chem 149:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.02.062
Findlay VJ, Townsend DM, Saavedra JE, Buzard GS, Citro ML, Keefer LK, Ji X, Tew KD (2004) Tumor cell responses to a novel glutathione S-transferase-activated nitric oxide-releasing prodrug. Mol Pharmacol 65(5):1070–1079. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.65.5.1070
Townsend DM, Findlay VJ, Fazilev F, Ogle M, Fraser J, Saavedra JE, Ji X, Keefer LK, Tew KD (2006) A glutathione S-transferase pi-activated prodrug causes kinase activation concurrent with S-glutathionylation of proteins. Mol Pharmacol 69(2):501–508. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.105.018523
Xiong Y, Manevich Y, Tew KD, Townsend DM (2012) S-Glutathionylation of protein disulfide isomerase regulates estrogen receptor alpha stability and function. Int J Cell Biol 2012:273549. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/273549
Hutchens S, Manevich Y, He L, Tew KD, Townsend DM (2011) Cellular resistance to a nitric oxide releasing glutathione S-transferase P-activated prodrug, PABA/NO. Invest New Drugs 29(5):719–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9407-5
Fu J, Liu L, Huang Z, Lai Y, Ji H, Peng S, Tian J, Zhang Y (2013) Hybrid molecule from O2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)diazeniumdiolate and oleanolic acid: a glutathione S-transferase pi-activated nitric oxide prodrug with selective anti-human hepatocellular carcinoma activity and improved stability. J Med Chem 56(11):4641–4655. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm400393u
Liu L, Fu J, Li T, Cui R, Ling J, Yu X, Ji H, Zhang Y (2012) NG, a novel PABA/NO-based oleanolic acid derivative, induces human hepatoma cell apoptosis via a ROS/MAPK-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 691(1–3):61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.07.031
Sun S, Ji H, Feng Y, Kang Y, Yu J, Liu A (2018) A novel mechanism of tumor-induced thymic atrophy in mice bearing H22 hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 10:417–424. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S157512
Ji X, Pal A, Kalathur R, Hu X, Gu Y, Saavedra JE, Buzard GS, Srinivasan A, Keefer LK, Singh SV (2008) Structure-based design of anticancer prodrug PABA/NO. Drug Des Dev Ther 2:123–130
Cui SX, Shi WN, Song ZY, Wang SQ, Yu XF, Gao ZH, Qu XJ (2016) Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin antagonizes the effects of sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Oncotarget 7(24):36767–36782. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9168
Wu YL, Maachani UB, Schweitzer M, Singh R, Wang M, Chang R, Souweidane MM (2017) Dual inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways induces synergistic antitumor effects in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cells. Transl Oncol 10(2):221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2016.12.008
Kim Y, Maciag AE, Cao Z, Deschamps JR, Saavedra JE, Keefer LK, Holland RJ (2015) PABA/NO lead optimization: improved targeting of cytotoxicity to glutathione S-transferase P1-overexpressing cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem 23(15):4980–4988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.05.020
Kogias E, Osterberg N, Baumer B, Psarras N, Koentges C, Papazoglou A, Saavedra JE, Keefer LK, Weyerbrock A (2012) Growth-inhibitory and chemosensitizing effects of the glutathione-S-transferase-pi-activated nitric oxide donor PABA/NO in malignant gliomas. Int J Cancer 130(5):1184–1194. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.26106
Saunders IT, Mir H, Kapur N, Singh S (2019) Emodin inhibits colon cancer by altering BCL-2 family proteins and cell survival pathways. Cancer Cell Int 19:98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0820-3
Nishina A, Miura A, Goto M, Terakado K, Sato D, Kimura H, Hirai Y, Sato H, Phay N (2018) Mansonone E from Mansonia gagei inhibited alpha-MSH-induced melanogenesis in B16 cells by inhibiting CREB expression and phosphorylation in the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biol Pharm Bull 41(5):770–776. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b17-01045
Spangle JM, Roberts TM (1868) Zhao JJ (2017) The emerging role of PI3K/AKT-mediated epigenetic regulation in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.03.002
Ching CB, Hansel DE (2010) Expanding therapeutic targets in bladder cancer: the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Lab Invest 90(10):1406–1414. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2010.133
Matsuo FS, Andrade MF, Loyola AM, da Silva SJ, Silva MJB, Cardoso SV, de Faria PR (2018) Pathologic significance of AKT, mTOR, and GSK3beta proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma-affected patients. Virchows Arch 472(6):983–997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2318-0
Butler DE, Marlein C, Walker HF, Frame FM, Mann VM, Simms MS, Davies BR, Collins AT, Maitland NJ (2017) Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activates autophagy and compensatory Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signalling in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8(34):56698–56713. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18082
Luo L, Zhao H, Luo Q (2018) Swerchirin exerts anticancer activity on SKOV3 human ovarian cancer cells via induction of mitochondrial apoptosis, G2/M cell cycle arrest and inhibition of Raf/MEK/ERK cascade. J BUON 23(1):111–116
Zhang Y, Li G, Liu X, Song Y, Xie J, Li G, Ren J, Wang H, Mou J, Dai J, Liu F, Guo L (2018) Sorafenib inhibited cell growth through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Oncol Lett 15(4):5620–5626. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8010
Morales-Ibanez O, Affo S, Rodrigo-Torres D, Blaya D, Millan C, Coll M, Perea L, Odena G, Knorpp T, Templin MF, Moreno M, Altamirano J, Miquel R, Arroyo V, Gines P, Caballeria J, Sancho-Bru P, Bataller R (2016) Kinase analysis in alcoholic hepatitis identifies p90RSK as a potential mediator of liver fibrogenesis. Gut 65(5):840–851. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307979
Kim HS, Kim SJ, Bae J, Wang Y, Park SY, Min YS, Je HD, Sohn UD (2016) The p90rsk-mediated signaling of ethanol-induced cell proliferation in HepG2 cell line. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 20(6):595–603. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.6.595
Deliu IC, Neagoe CD, Bezna M, Genunche-Dumitrescu AV, Toma SC, Ungureanu BS, Uscatu CD, Bezna MC, Lungulescu CV, Padureanu V, Gheonea DI, Ciurea T, ForTofoiu M (2016) Correlations between endothelial cell markers CD31, CD34 and CD105 in colorectal carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol 57(3):1025–1030
Toma SC, Uscatu CD, Ungureanu BS, Mirea CS, Dumitrescu T, Georgescu EF, Schenker M, Surlin V, Georgescu I (2018) Correlations between CD34 immunolabelled blood vessels and CD34 mRNA expression in colorectal cancer. Curr Health Sci J 44(1):60–63. https://doi.org/10.12865/CHSJ.44.01.10
Okkenhaug K, Graupera M, Vanhaesebroeck B (2016) Targeting PI3K in cancer: impact on tumor cells, their protective stroma, angiogenesis, and immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 6(10):1090–1105. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0716
Zhang C, Hao Y, Wu L, Dong X, Jiang N, Cong B, Liu J, Zhang W, Tang D, De Perrot M, Zhao X (2018) Curcumin induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in murine malignant mesothelioma. Int J Oncol 53(6):2531–2541. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4569
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A, Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M, Carter C (2006) Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res 66(24):11851–11858. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1377
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81502627) and the Young Backbone Teachers Assistance Scheme of Henan Province Colleges and Universities (No. 2016GGJS-065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Chen, J., Cao, M. et al. NO donor inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 84, 1303–1314 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03965-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03965-5