Abstract
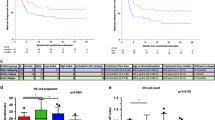
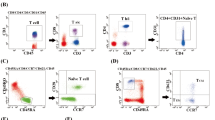
Recent studies have shown that approximately 50% of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy with a sustained deep molecular response (DMR) (BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.01%) can achieve treatment-free remission (TFR, stopping TKI without relapse) and that prior interferon (IFN)-α therapy and higher NK cell counts at and after TKI discontinuation are associated with TFR. We recently reported that post-TKI discontinuation of IFN-α therapy could prevent molecular relapse (MR, BCR-ABL1IS > 0.1%). Here, we evaluated whether NK cells are associated with MR and investigated the effects of post-TKI discontinuation IFN-α therapy on lymphocyte subsets. A total of 34 patients measuring blood lymphocyte subclasses were included. In the 22 patients who did not receive IFN-α therapy, at 1 month after TKI discontinuation, the nonrelapsed patients showed a significantly higher proportion and count of NK cells than the relapsed patients. In particular, the proportion and count of CD56dim NK cells were significantly higher in the nonrelapsed patients than in the relapsed patients. In the 12 patients who received IFN-α therapy, the level of CD56bright NK cells increased significantly after 3 and 6 months of IFN-α therapy. In summary, NK cells, in particular CD56dim NK cells, were associated with MR after TKI discontinuation in patients with CML. Additionally, IFN-α therapy gradually increased the level of CD56bright NK cells in patients with CML.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heisterkamp N, Stephenson JR, Groffen J, Hansen PF, de Klein A, Bartram CR, Grosveld G (1983) Localization of the c-ab1 oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 306:239–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/306239a0
Radich JP, Deininger M, Abboud CN, Altman JK, Berman E, Bhatia R, Bhatnagar B, Curtin P, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Hobbs G, Jagasia M, Kantarjian HM, Maness L, Metheny L, Moore JO, Pallera A, Pancari P, Patnaik M, Purev E, Rose MG, Shah NP, Smith BD, Snyder DS, Sweet KL, Talpaz M, Thompson J, Yang DT, Gregory KM, Sundar H (2018) Chronic myeloid leukemia, Version 1.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 16:1108–1135. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2018.0071 (version 1.2019)
Druker BJ, Lee SJ (2007) Chapter 43: Chronic leukemias: Section 1: Chronic myelogenous leukemia//cancer principles and practice of oncology
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Silver RT, Schiffer C, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE, Deininger MW, Guilhot F, Hjorth-Hansen H, Hughes TP, Janssen JJWM, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Larson RA, Lipton JH, Mahon FX, Mayer J, Nicolini F, Niederwieser D, Pane F, Radich JP, Rea D, Richter J, Rosti G, Rousselot P, Saglio G, Saußele S, Soverini S, Steegmann JL, Turkina A, Zaritskey A, Hehlmann R (2020) European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 34:966–984. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0776-2
Kalmanti L, Saussele S, Lauseker M, Müller MC, Dietz CT, Heinrich L, Hanfstein B, Proetel U, Fabarius A, Krause SW, Rinaldetti S, Dengler J, Falge C, Oppliger-Leibundgut E, Burchert A, Neubauer A, Kanz L, Stegelmann F, Pfreundschuh M, Spiekermann K, Scheid C, Pfirrmann M, Hochhaus A, Hasford J, Hehlmann R (2015) Safety and efficacy of imatinib in CML over a period of 10 years: data from the randomized CML-study IV. Leukemia 29:1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.36
Larson RA, Hochhaus A, Hughes TP, Clark RE, Etienne G, Kim DW, Flinn IW, Kurokawa M, Moiraghi B, Yu R, Blakesley RE, Gallagher NJ, Saglio G, Kantarjian HM (2012) Nilotinib vs imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENESTnd 3-year follow-up. Leukemia 26:2197–2203. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.134
Wang J, Shen ZX, Saglio G, Jin J, Huang H, Hu Y, Du X, Li J, Meng F, Zhu H, Hu J, Wang J, Hou M, Hertle S, Menssen HD, Ortmann CE, Tribouley C, Yuan Y, Baccarani M, Huang X (2015) Phase 3 study of nilotinib vs imatinib in Chinese patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENESTchina. Blood 125:2771–2778. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-09-601674
Cortes JE, Saglio G, Kantarjian HM, Baccarani M, Mayer J, Boqué C, Shah NP, Chuah C, Casanova L, Bradley-Garelik B, Manos G, Hochhaus A (2016) Final 5-year study results of DASISION: the dasatinib versus imatinib study in treatment-naïve chronic myeloid leukemia patients trial. J Clin Oncol 34:2333–2340. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.64.8899
Mahon FX, Réa D, Guilhot J, Guilhot F, Huguet F, Nicolini F, Legros L, Charbonnier A, Guerci A, Varet B, Etienne G, Reiffers J, Rousselot P, Français I, des LeucémiesMyéloïdesChroniques, (2010) Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained complete molecular remission for at least 2 years: the prospective, multicentre Stop Imatinib (STIM) trial. Lancet Oncol 11:1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70233-3
Saussele S, Richter J, Guilhot J, Gruber FX, Hjorth-Hansen H, Almeida A, Janssen JJWM, Mayer J, Koskenvesa P, Panayiotidis P, Olsson-Strömberg U, Martinez-Lopez J, Rousselot P, Vestergaard H, Ehrencrona H, Kairisto V, MachováPoláková K, Müller MC, Mustjoki S, Berger MG, Fabarius A, Hofmann WK, Hochhaus A, Pfirrmann M, Mahon FX, EURO-SKI investigators (2018) Discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia (EURO-SKI): a prespecified interim analysis of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, trial. Lancet Oncol 19:747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30192-X
Ross DM, Branford S, Seymour JF, Schwarer AP, Arthur C, Yeung DT, Dang P, Goyne JM, Slader C, Filshie RJ, Mills AK, Melo JV, White DL, Grigg AP, Hughes TP (2013) Safety and efficacy of imatinib cessation for CML patients with stable undetectable minimal residual disease: results from the TWISTER study. Blood 122:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-02-483750
Imagawa J, Tanaka H, Okada M, Nakamae H, Hino M, Murai K, Ishida Y, Kumagai T, Sato S, Ohashi K, Sakamaki H, Wakita H, Uoshima N, Nakagawa Y, Minami Y, Ogasawara M, Takeoka T, Akasaka H, Utsumi T, Uike N, Sato T, Ando S, Usuki K, Morita S, Sakamoto J, Kimura S, DADI Trial Group (2015) Discontinuation of dasatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained deep molecular response for longer than 1 year (DADI trial): a multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol 2:e528–e535. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00196-9
Rea D, Nicolini FE, Tulliez M, Guilhot F, Guilhot J, Guerci-Bresler A, Gardembas M, Coiteux V, Guillerm G, Legros L, Etienne G, Pignon JM, Villemagne B, Escoffre-Barbe M, Ianotto JC, Charbonnier A, Johnson-Ansah H, Noel MP, Rousselot P, Mahon FX, France Intergroupe des LeucémiesMyéloïdesChroniques (2017) France intergroupe des leucémies Myéloïdes chroniques. Discontinuation of dasatinib or nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: interim analysis of the STOP 2G-TKI study. Blood 129:846–854. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-09-742205
Hochhaus A, Masszi T, Giles FJ, Radich JP, Ross DM, Gómez Casares MT, Hellmann A, Stentoft J, Conneally E, García-Gutiérrez V, Gattermann N, Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W, le Coutre PD, Martino B, Saussele S, Menssen HD, Deng W, Krunic N, Bedoucha V, Saglio G (2017) Treatment-free remission following frontline nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: results from the ENESTfreedom study. Leukemia 31:1525–1531. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.63
Rea D, Henry G, Khaznadar Z, Etienne G, Guilhot F, Nicolini F, Guilhot J, Rousselot P, Huguet F, Legros L, Gardembas M, Dubruille V, Guerci-Bresler A, Charbonnier A, Maloisel F, Ianotto JC, Villemagne B, Mahon FX, Moins-Teisserenc H, Dulphy N, Toubert A (2017) Natural killer-cell counts are associated with molecular relapse-free survival after imatinib discontinuation in chronic myeloid leukemia: the IMMUNOSTIM study. Haematologica 102:1368–1377. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2017.165001
Ilander M, Olsson-Strömberg U, Schlums H, Guilhot J, Brück O, Lähteenmäki H, Kasanen T, Koskenvesa P, Söderlund S, Höglund M, Markevärn B, Själander A, Lotfi K, Dreimane A, Lübking A, Holm E, Björeman M, Lehmann S, Stenke L, Ohm L, Gedde-Dahl T, Majeed W, Ehrencrona H, Koskela S, Saussele S, Mahon FX, Porkka K, Hjorth-Hansen H, Bryceson YT, Richter J, Mustjoki S (2017) Increased proportion of mature NK cells is associated with successful imatinib discontinuation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 31:1108–1116. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.360
Kong J, Qin Y-Z, Shi H-X, Lai Y-Y, Liu K-Y, Huang X-J, Jiang H (2021) Interferon-α may help prevent molecular relapse of chronic myeloid leukemia after the discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ther Adv Hematol 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040620720986643
Burchert A, Müller MC, Kostrewa P, Erben P, Bostel T, Liebler S, Hehlmann R, Neubauer A, Hochhaus A (2010) Sustained molecular response with interferon alfa maintenance after induction therapy with imatinib plus interferon alfa in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 28:1429–1435. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.25.5075
Mahon FX, Delbrel X, Cony-Makhoul P, Fabères C, Boiron JM, Barthe C, Bilhou-Nabéra C, Pigneux A, Marit G, Reiffers J (2002) Follow-up of complete cytogenetic remission in patientswith chronic myeloid leukemia after cessation of interferon alfa. J Clin Oncol 20:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.20.1.214
Kreutzman A, Rohon P, Faber E, Indrak K, Juvonen V, Kairisto V, Voglová J, Sinisalo M, Flochová E, Vakkila J, Arstila P, Porkka K, Mustjoki S (2011) Chronic myeloid leukemia patients in prolonged remission following interferon-α monotherapy have distinct cytokine and oligoclonal lymphocyte profile. PLoS ONE 6:e23022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023022
Kärre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G, Kiessling R (1986) Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature 319:675–678. https://doi.org/10.1038/319675a0
Najima Y, Yoshida C, Iriyama N, Fujisawa S, Wakita H, Chiba S, Okamoto S, Kawakami K, Takezako N, Kumagai T, Ohyashiki K, Taguchi J, Yano S, Igarashi T, Kouzai Y, Morita S, Sakamoto J, Sakamaki H, Inokuchi K (2018) Regulatory T cell inhibition by dasatinib is associated with natural killer cell differentiation and a favorable molecular response-The final results of the D-first study. Leuk Res 66:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2018.01.010
Larmonier N, Marron M, Zeng Y, Cantrell J, Romanoski A, Sepassi M, Thompson S, Chen X, Andreansky S, Katsanis E (2007) Tumor-derived CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell suppression of dendritic cell function involves TGF-beta and IL-10. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-006-0160-8
Szczepanski MJ, Szajnik M, Czystowska M, Mandapathil M, Strauss L, Welsh A, Foon KA, Whiteside TL, Boyiadzis M (2009) Increased frequency and suppression by regulatory T cells in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 15:3325–3332. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3010
Idris SZ, Hassan N, Lee LJ, Noor MdS, Osman R, Abdul-Jalil M, Nordin AJ, Abdullah M (2015) Increased regulatory T cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Hematology 20:523–529. https://doi.org/10.1179/1607845415Y.0000000025
D’Arena G, Laurenti L, Minervini MM, Deaglio S, Bonello L, De Martino L, De Padua L, Savino L, Tarnani M, De Feo V, Cascavilla N (2011) Regulatory T-cell number is increased in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients and correlates with progressive disease. Leuk Res 35:363–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2010.08.010
Anguille S, Lion E, Willemen Y, Van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN, Smits EL (2011) Interferon-α in acute myeloid leukemia: an old drug revisited. Leukemia 25:739–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.324
Alves R, McArdle SEB, Vadakekolathu J, Gonçalves AC, Freitas-Tavares P, Pereira A, Almeida AM, Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Rutella S (2020) Flow cytometry and targeted immune transcriptomics identify distinct profiles in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without interferon-α. J Transl Med 18:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-02194-x
Michel T, Poli A, Cuapio A, Briquemont B, Iserentant G, Ollert M, Zimmer J (2016) Human CD56bright NK cells: an update. J Immunol 196:2923–2931. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1502570
Wagner JA, Rosario M, Romee R, Berrien-Elliott MM, Schneider SE, Leong JW, Sullivan RP, Jewell BA, Becker-Hapak M, Schappe T, Abdel-Latif S, Ireland AR, Jaishankar D, King JA, Vij R, Clement D, Goodridge J, Malmberg KJ, Wong HC, Fehniger TA (2017) CD56bright NK cells exhibit potent antitumor responses following IL-15 priming. J Clin Invest 127:4042–4058. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90387
Ilander M, Kreutzman A, Rohon P, Melo T, Faber E, Porkka K, Vakkila J, Mustjoki S (2014) Enlarged memory T-cell pool and enhanced Th1-type responses in chronic myeloid leukemia patients who have successfully discontinued IFN-α monotherapy. PLoS ONE 9:e87794. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087794
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the faculty members who helped with this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Capital Characteristic Clinic Project Foundation (Z181100001718126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jun Kong and Hao Jiang designed the study, and Jun Kong analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. Ya-zhen Qin and Xiao-su Zhao performed the RT-qPCR and FCM experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, revised in 2008.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, J., Qin, Yz., Zhao, XS. et al. Profiles of NK cell subsets are associated with successful tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation in chronic myeloid leukemia and changes following interferon treatment. Ann Hematol 100, 2557–2566 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04606-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04606-9