Abstract
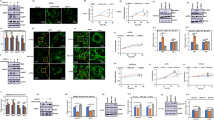
The nuclear transcription factor twist-related protein 1 (Twist1) is associated with tumor malignant transformation and metastasis in various types of carcinomas. We found that Twist1 was highly expressed in clinical multiple myeloma (MM) cells, and explored its roles in proliferation and apoptosis in human MM cell lines U266 and RPMI-8226. In these cells, Twist1 transcriptionally regulated the miRNA hsa-miR138-5p, which targeted caspase-3 to control apoptosis. Silencing of Twist1 significantly suppressed cell proliferation and increased apoptosis, which was reversed by overexpression of hsa-miR138-5p or simultaneous silencing of caspase-3. This reversion was further substantiated by attenuated apoptotic signaling, including downregulated expression of the cleaved forms of caspase-3 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor 1 (PPAR1). We demonstrate here for the first time that the novel Twist1/hsa-miR138-5p/caspase-3 pathway contributes significantly to the proliferation and survival of human MM cells. Our study provides new insight for novel MM treatments by developing Twist1-targeted therapeutics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fairfield H, Falank C, Avery L, Reagan MR (2016) Multiple myeloma in the marrow: pathogenesis and treatments. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1364:32–51
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV (2004) Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 351:1860–1873
Anderson KC (2003) Multiple myeloma: how far have we come? Mayo Clin Proc 78:15–17
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Fonseca R, Rajkumar SV, Offord JR, Larson DR, Plevak ME, Therneau TM, Greipp PR (2003) Review of 1027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin Proc 78:21–33
McCullough KB, Hobbs MA, Abeykoon JP et al (2018) Common adverse effects of novel therapies for multiple myeloma (MM) and their management strategies. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 13:114–124
Zhao Z, Rahman MA, Chen ZG, Shin DM (2017) Multiple biological functions of Twist1 in various cancers. Oncotarget. 8:20380–20393
Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, Qin C, Xu J (2012) Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms. Cell Res 22:90–106
Firulli AB, Conway SJ (2008) Phosphoregulation of Twist1 provides a mechanism of cell fate control. Curr Med Chem 15:2641–2647
Barsky D, Venclovas C (2005) DNA sliding clamps: just the right twist to load onto DNA. Curr Biol 15:R989–R992
Romero S, Musleh M, Bustamante M et al (2018) Polymorphisms in TWIST1 and ZEB1 are associated with prognosis of gastric cancer patients. Anticancer Res 38:3871–3877
Saxena M, Balaji SA, Deshpande N, Ranganathan S, Pillai DM, Hindupur SK, Rangarajan A (2018) AMP-activated protein kinase promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells through Twist1 upregulation. J Cell Sci 131:jcs208314
Parajuli P, Kumar S, Loumaye A, Singh P, Eragamreddy S, Nguyen TL, Ozkan S, Razzaque MS, Prunier C, Thissen JP, Atfi A (2018) Twist1 activation in muscle progenitor cells causes muscle loss akin to cancer cachexia. Dev Cell 45:712–725 e716
Grzegrzolka J, Biala M, Wojtyra P et al (2015) Expression of EMT markers SLUG and TWIST in breast cancer. Anticancer Res 35:3961–3968
Ji H, Lu HW, Li YM et al (2015) Twist promotes invasion and cisplatin resistance in pancreatic cancer cells through growth differentiation factor 15. Mol Med Rep 12:3841–3848
Han Z, Liu L, Liu Y, Li S (2014) Sirtuin SIRT6 suppresses cell proliferation through inhibition of Twist1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:4774–4781
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:178–196
Zhu QQ, Ma C, Wang Q, Song Y, Lv T (2016) The role of TWIST1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancers. Tumour Biol 37:185–197
Khanbabaei H, Teimoori A, Mohammadi M (2016) The interplay between microRNAs and Twist1 transcription factor: a systematic review. Tumour Biol 37:7007–7019
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408
Fu J, Qin L, He T, Qin J, Hong J, Wong J, Liao L, Xu J (2011) The TWIST/Mi2/NuRD protein complex and its essential role in cancer metastasis. Cell Res 21:275–289
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP, Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S, Maestro R, Voeltzel T, Selmi A, Valsesia-Wittmann S, Caron de Fromentel C, Puisieux A (2008) Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell 14:79–89
Gregorová J, Vrábel D, Radová L, Gablo NA, Almaši M, Štork M, et al. (2018) MicroRNA analysis for extramedullary multiple myeloma relapse. KlinOnkol;31(Supplementum1):148–150
Ma J, Gong W, Liu S et al (2018) Ibrutinib targets microRNA-21 in multiple myeloma cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB and STAT3. Tumour Biol 40:1010428317731369
Stamato MA, Juli G, Romeo E, Ronchetti D, Arbitrio M, Caracciolo D, Neri A, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P, Amodio N (2017) Inhibition of EZH2 triggers the tumor suppressive miR-29b network in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 8:106527–106537
Peng YG, Zhang L (2018) Baohuoside-I suppresses cell proliferation and migration by up-regulating miR-144 in melanoma. Pharm Biol 56:43–50
Gao D, Xiao Z, Li HP, Han DH, Zhang YP (2018) The mechanism study of miR-125b in occurrence and progression of multiple myeloma. Cancer Med 7:134–145
Tang B, Xu A, Xu J, Huang H, Chen L, Su Y, Zhang L, Li J, Fan F, Deng J, Tang L, Sun C, Hu Y (2018) MicroRNA-324-5p regulates stemness, pathogenesis and sensitivity to bortezomib in multiple myeloma cells by targeting hedgehog signaling. Int J Cancer 142:109–120
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C et al (2010) Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Src-mediated twist signaling, microRNA-10b expression, and RhoA/RhoC up-regulation, leading to Rho-kinase-associated cytoskeleton activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 285:36721–36735
Yang WH, Lan HY, Huang CH, Tai SK, Tzeng CH, Kao SY, Wu KJ, Hung MC, Yang MH (2012) RAC1 activation mediates Twist1-induced cancer cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 14:366–374
Tsai CH, Lin LT, Wang CY et al (1852) Over-expression of cofilin-1 suppressed growth and invasion of cancer cells is associated with up-regulation of let-7 microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015:851–861
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li M, Sun L, Ji G, Shi Y, Han Z, Han S, Nie Y, Chen X, Zhao Q, Ding J, Wu K, Daiming F (2011) miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res 9:824–833
Kumar SK, Callander NS, Hillengass J, Liedtke M, Baljevic M, Campagnaro E, Castillo JJ, Chandler JC, Cornell RF, Costello C, Efebera Y, Faiman M, Garfall A, Godby K, Holmberg L, Htut M, Huff CA, Kang Y, Landgren O, Malek E, Martin T, Omel J, Raje N, Sborov D, Singhal S, Stockerl-Goldstein K, Tan C, Weber D, Johnson-Chilla A, Keller J, Kumar R (2019) NCCN Guidelines Insights: Multiple Myeloma, Version 1.2020. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 17(10):1154–1165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee at the Huashan Hospital of Fudan University. Written, informed consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the ethical committee standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, W., Liu, Q., Xu, X. et al. A novel Twist1/hsa-miR138-5p/caspase-3 pathway regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of human multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol 100, 1815–1824 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04059-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04059-6