Abstract
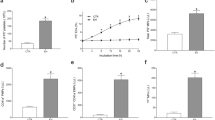
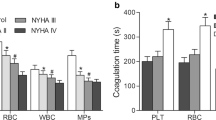
The mechanisms of thrombogenicity in essential thrombocythemia (ET) are complex and not well defined. Our objective was to explore whether phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure on blood cells and endothelial cells (ECs) can account for the increased thrombosis and distinct thrombotic risks among mutational subtypes in ET. Using flow cytometry and confocal microscopy, we found that the levels of PS-exposing erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes, and serum-cultured ECs were significantly higher in each ET group [JAK2, CALR, and triple-negative (TN) (all P < 0.001)] than those in controls. Among ET patients, those with JAK2 mutations showed higher levels of PS-positive erythrocytes, platelets, neutrophils, and serum-cultured ECs than TN patients or those with CALR mutations, which show similar levels. Coagulation function assays showed that higher levels of PS-positive blood cells and serum-cultured ECs led to markedly shortened coagulation time and dramatically increased levels of FXa, thrombin, and fibrin production. This procoagulant activity could be largely blocked by addition of lactadherin (approx. 70% inhibition). Confocal microscopy showed that the FVa/FXa complex and fibrin fibrils colocalized with PS on ET serum-cultured ECs. Additionally, we found a relationship between D-dimer, prothrombin fragment F1 + 2, and PS exposure. Our study reveals a previously unrecognized link between hypercoagulability and exposed PS on cells, which might also be associated with distinct thrombotic risks among mutational subtypes in ET. Thus, blocking PS-binding sites may represent a new therapeutic target for preventing thrombosis in ET.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cervantes F, Passamonti F, Barosi G (2008) Life expectancy and prognostic factors in the classic BCR/ABL-negative myeloproliferative disorders. Leukemia 22(5):905–914. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.72
Tefferi A, Barbui T (2017) Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 92(1):94–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24607
Carobbio A, Thiele J, Passamonti F et al (2011) Risk factors for arterial and venous thrombosis in WHO-defined essential thrombocythemia: an international study of 891 patients. Blood 17:5857–5859
Reikvam H (2012) Venous thromboembolism in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Leukemia 26(4):563–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.314
Harrison CN, Campbell PJ, Buck G, Wheatley K, East CL, Bareford D, Wilkins BS, van der Walt JD, Reilly JT, Grigg AP, Revell P, Woodcock BE, Green AR, United Kingdom Medical Research Council Primary Thrombocythemia 1 Study (2005) Hydroxyurea compared with anagrelide in high-risk essential thrombocythemia. N Engl J Med 353(1):33–45. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043800
Gisslinger H, Gotic M, Holowiecki J, Penka M, Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM, Kralovics R, Petrides PE, for all members of the ANAHYDRET Study Group (2013) Anagrelide compared with hydroxyurea in WHO-classified essential thrombocythemia: the ANAHYDRET Study, a randomized controlled trial. Blood 121(10):1720–1728. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-07-443770
Marchetti M, Castoldi E, Spronk HM et al (2008) Thrombin generation and activated protein C resistance in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 112(10):4061–4068. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-06-164087
Elliott MA, Tefferi A (2005) Thrombosis and haemorrhage in polycythaemia vera and essential thrombocythaemia. Br J Haematol 128(3):275–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05277.x
Elala YC, Lasho TL, Gangat N, Finke C, Barraco D, Haider M, Abou Hussein AK, Hanson CA, Ketterling RP, Pardanani A, Tefferi A (2016) Calreticulin variant stratified driver mutational status and prognosis in essential thrombocythemia. Am J Hematol 91(5):503–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24338
Al Assaf C, Van Obbergh F, Billiet J, Lierman E, Devos T, Graux C, Hervent AS, Emmerechts J, Tousseyn T, de Paepe P, Papadopoulos P, Michaux L, Vandenberghe P (2015) Analysis of phenotype and outcome in essential thrombocythemia with CALR or JAK2 mutations. Haematologica 100(7):893–897. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2014.118299
Gangat N, Wassie EA, Lasho TL, Finke C, Ketterling RP, Hanson CA, Pardanani A, Wolanskyj AP, Maffioli M, Casalone R, Passamonti F, Tefferi A (2015) Mutations and thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia: prognostic interaction with age and thrombosis history. Eur J Haematol 94(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12389
Arellano-Rodrigo E, Alvarez-Larran A, Reverter JC et al (2006) Increased platelet and leukocyte activation as contributing mechanisms for thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and correlation with the JAK2 mutational status. Haematologica 91(2):169–175
Patrono C, Rocca B (2013) Platelet activation and inhibition in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood 121(10):1701–1711. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-10-429134
Cervantes F, Arellano-Rodrigo E, Alvarez-Larrán A (2009) Blood cell activation in the myeloproliferative neoplasms. Haematologica 94(11):1484–1488. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.013375
Panova-Noeva M, Marchetti M, Spronk HM, Russo L, Diani E, Finazzi G, Salmoiraghi S, Rambaldi A, Barbui T, ten Cate H, Falanga A (2011) Platelet-induced thrombin generation by the calibrated automated thrombogram assay is increased in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Am J Hematol 86(4):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21974
Chen VM, Hogg PJ (2013) Encryption and decryption of tissue factor. J Thromb Haemost 1(Suppl 1):277–284
Yeung T, Gilbert GE, Shi J, Silvius J, Kapus A, Grinstein S (2008) Membrane phosphatidylserine regulates surface charge and protein localisation. Science 319(5860):210–213. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1152066
He Z, Si Y, Jiang T, Ma R, Zhang Y, Cao M, Li T, Yao Z, Zhao L, Fang S, Yu B, Dong Z, Thatte HS, Bi Y, Kou J, Yang S, Piao D, Hao L, Zhou J, Shi J (2016) Phosphotidylserine exposure and neutrophil extracellular traps enhance procoagulant activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Thromb Haemost 115(4):738–751. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH15-09-0710
Bonomini M, Dottori S, Amoroso L, Arduini A, Sirolli V (2004) Increased platelet phosphatidylserine exposure and caspase activation in chronic uremia. J Thromb Haemost 2(8):1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2004.00837.x
Tan X, Shi J, Fu Y, Gao C, Yang X, Li J, Wang W, Hou J, Li H, Zhou J (2013) Role of erythrocytes and platelets in the hypercoagulable status in polycythemia vera through phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle generation. Thromb Haemost 109(6):1025–1032. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH12-11-0811
Arellano-Rodrigo E, Alvarez-Larran A, Reverter JC et al (2009) Platelet turnover, coagulation factors, and soluble markers of platelet and endothelial activation in essential thrombocythemia: relationship with thrombosis occurrence and JAK2 V617F allele burden. Am J Hematol 84(2):102–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21338
Hobbs CM, Manning H, Bennett C, Vasquez L, Severin S, Brain L, Mazharian A, Guerrero JA, Li J, Soranzo N, Green AR, Watson SP, Ghevaert C (2013) JAK2V617F leads to intrinsic changes in platelet formation and reactivity in a knock-in mouse model of essential thrombocythemia. Blood 122(23):3787–3797. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-06-501452
Hou J, Fu Y, Zhou J, Li W, Xie R, Cao F, Gilbert GE, Shi J (2011) Lactadherin functions as a probe for phosphatidylserine exposure and as an anticoagulant in the study of stored platelets. Vox Sang 100(2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1423-0410.2010.01375.x
Shi J, Gilbert GE (2003) Lactadherin inhibits enzyme complexes of blood coagulation by competing for phospholipid-binding sites. Blood 101(7):2628–2636. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-07-1951
Treliński J, Wierzbowska A, Krawczyńska A, Sakowicz A, Pietrucha T, Smolewski P, Robak T, Chojnowski K (2010) Circulating endothelial cells in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: correlation with JAK2-V617F mutational status, angiogenic factors and coagulation activation markers. Int J Hematol 91(5):792–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0596-7
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Evangelista V, Vignoli A, Licini M, Balicco M, Manarini S, Finazzi G, Cerletti C, Barbui T (2000) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation and hemostasis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 96(13):4261–4266
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ et al (2005) Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 365(9464):1054–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)74230-6
Nangalia J, Massie CE, Baxter EJ, Nice FL, Gundem G, Wedge DC, Avezov E, Li J, Kollmann K, Kent DG, Aziz A, Godfrey AL, Hinton J, Martincorena I, van Loo P, Jones AV, Guglielmelli P, Tarpey P, Harding HP, Fitzpatrick JD, Goudie CT, Ortmann CA, Loughran SJ, Raine K, Jones DR, Butler AP, Teague JW, O'Meara S, McLaren S, Bianchi M, Silber Y, Dimitropoulou D, Bloxham D, Mudie L, Maddison M, Robinson B, Keohane C, Maclean C, Hill K, Orchard K, Tauro S, Du MQ, Greaves M, Bowen D, Huntly BJP, Harrison CN, Cross NCP, Ron D, Vannucchi AM, Papaemmanuil E, Campbell PJ, Green AR (2013) Somatic CALR mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms with nonmutated JAK2. N Engl J Med 369(25):2391–2405. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1312542
Panova-Noeva M, Marchetti M, Russo L, Tartari CJ, Leuzzi A, Finazzi G, Rambaldi A, ten Cate H, Falanga A (2013) ADP-induced platelet aggregation and thrombin generation are increased in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Thromb Res 132(1):88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2013.05.003
Presseizen K, Friedman Z, Shapiro H, Radnay J, Ellis MH (2002) Phosphatidylserine expression on the platelet membrane of patients with myeloproliferative disorders and its effect on platelet-dependent thrombin formation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 8(1):33–39. https://doi.org/10.1177/107602960200800104
Covas DT, de Lucena AI, Vianna Bonini Palma P (2004) Effects of hydroxyurea on the membrane of erythrocytes and platelets in sickle cell anemia. Haematologica 89(3):273–280
Passamonti F, Caramazza D, Mora B, Casalone R, Maffioli M (2014) It is time to change thrombosis risk assessment for PV and ET? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 27(2):121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2014.07.005
Buxhofer-Ausch V, Gisslinger B, Schalling M et al (2016) Impact of white blood cell counts at diagnosis and during follow-up in patients with essential thrombocythaemia and prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis. Br J Haematol 179:166–169
Barbui T, Carobbio A, Finazzi G, Vannucchi AM, Barosi G, Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Pancrazzi A, Salmoiraghi S, Zilio P, Ottomano C, Marchioli R, Cuccovillo I, Bottazzi B, Mantovani A, Rambaldi A, on behalf of the AGIMM and IIC Investigators (2011) Inflammation and thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: different role of C-reactive protein and pentraxin 3. Haematologica 96(2):315–318. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2010.031070
Koschmieder S, Mughal TI, Hasselbalch HC, Barosi G, Valent P, Kiladjian JJ, Jeryczynski G, Gisslinger H, Jutzi JS, Pahl HL, Hehlmann R, Maria Vannucchi A, Cervantes F, Silver RT, Barbui T (2016) Myeloproliferative neoplasms and inflammation: whether to target the malignant clone or the inflammatory process or both. Leukemia 30(5):1018–1024. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.12
Falanga A, Marchetti M (2012) Thrombotic disease in the myeloproliferative neoplasms. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2012:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.571
Afshar-Kharghan V, Thiagarajan P (2006) Leukocyte adhesion and thrombosis. Curr Opin Hematol 13(1):34–39. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.moh.0000190107.54790.de
Turitto VT, Weiss HJ (1980) Red blood cells: their dual role in thrombus formation. Science 207(4430):541–543. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7352265
Zidova Z, Kapralova K, Koralkova P, Mojzikova R, Dolezal D, Divoky V, Horvathova M (2014) DMT1-mutant erythrocytes have shortened life span, accelerated glycolysis and increased oxidative stress. Cell Physiol Biochem 34(6):2221–2231. https://doi.org/10.1159/000369665
Grechowa I, Horke S, Wallrath A, Vahl CF, Dorweiler B (2017) Human neutrophil elastase induces endothelial cell apoptosis by activating the PERK-CHOP branch of the unfolded protein response. FASEB J 31(9):3868–3881. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700012R
Cao M, Li T, He Z, Wang L, Yang X, Kou Y, Zou L, Dong X, Novakovic VA, Bi Y, Kou J, Yu B, Fang S, Wang J, Zhou J, Shi J (2017) Promyelocytic extracellular chromatin exacerbates coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 129(13):1855–1864. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-09-739334
Godfrey AL, Chen E, Pagano F, Silber Y, Campbell PJ, Green AR (2013) Clonal analyses reveal associations of JAK2V617F homozygosity with hematologic features, age and gender in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Haematologica 98(5):718–721. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2012.079129
Torregrosa JM, Ferrer-Marín F, Lozano ML, Moreno MJ, Martinez C, Anton AI, Rivera J, Vicente V (2016) Impaired leucocyte activation is underlining the lower thrombotic risk of essential thrombocythaemia patients with CALR mutations as compared with those with the JAK2 mutation. Br J Haematol 172(5):813–815. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13539
Kubota Y, Ohnishi H, Kitanaka A, Ishida T, Tanaka T (2004) Constitutive activation of PI3K is involved in the spontaneous proliferation of primary acute myeloid leukemia cells: direct evidence of PI3K activation. Leukemia 18(8):1438–1440. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403402
Rafail S, Ritis K, Schaefer K, Kourtzelis I, Speletas M, Doumas M, Giaglis S, Kambas K, Konstantinides S, Kartalis G (2008) Leptin induces the expression of functional tissue factor in human neutrophils and peripheral blood mononuclear cells through JAK2-dependent mechanisms and TNF alpha involvement. Thromb Res 122(3):366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2007.12.018
Asp J, Andréasson B, Hansson U, Wasslavik C, Abelsson J, Johansson P, Palmqvist L (2016) Mutation status of essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis defines clinical outcome. Haematologica 101(4):e129–e132. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2015.138958
Myssina S, Huber SM, Birka C, Lang PA, Lang KS, Friedrich B, Risler T, Wieder T, Lang F (2003) Inhibition of erythrocyte cation channels by erythropoietin. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(11):2750–2757. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000093253.42641.C1
Acknowledgements
We thank Yanming Xue for the sample collection and Lu Zhao for the excellent technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (81470301, 81670128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University according to the Helsinki Declaration and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 61 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, D., Yu, M., Guo, L. et al. Phosphatidylserine-exposing blood and endothelial cells contribute to the hypercoagulable state in essential thrombocythemia patients. Ann Hematol 97, 605–616 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3228-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3228-6