Abstract
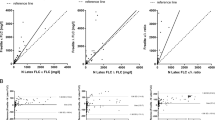
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) is a serious complication of solid organ transplantation. As early diagnosis remains challenging, we investigated the utility of serum-free light chain (FLC) and heavy chain/light chain pairs (HLC) as diagnostic biomarkers. Pre-treatment serum FLC and HLC levels were measured in 20 patients at their first diagnosis of B cell PTLD and in 14/20 patients during follow-up. Results were compared to serum FLC/HLC levels of 90 matched PTLD-free transplanted controls. Renal dysfunction was common in both cohorts, and combined FLC levels were often elevated above the conventional upper limit of normal (45.7 mg/L). Combined FLC levels were higher in patients with PTLD than in transplant controls (p = 0.013), and levels above the conventional ULN were associated with PTLD (OR 3.2, p = 0.05). Following adjustment to cystatin C as a marker of renal function an even stronger association was found for a (dimensionless) threshold value of 37.8 (OR 8.9, p < 0.001). In addition, monoclonal proliferation (abnormal FLC ratio, using an established renal range cutoff) was more common in PTLD than in controls (3/20 vs. 2/90, p = 0.04). Following therapy, at the time of protocolised restaging, patients experiencing subsequent sustained complete remission displayed lower FLC levels than those not experiencing such remission (p = 0.053). No relationship with HLC results was seen. Elevated polyclonal FLC levels (especially when adjusted for renal function) and monoclonal proliferation are a potential biomarker for PTLD diagnosis and disease surveillance. However, prospective validation is necessary before FLC measurement should be incorporated in follow-up of transplant recipients and PTLD management.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHOP:
-
Chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone
- cFLC:
-
Combined free light chain
- CR:
-
Complete remission
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DLCBL:
-
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- EBV:
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- ECOG :
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
- FLC:
-
Free light chain
- FLCadj :
-
Adjusted free light chain
- HLC:
-
Serum heavy/light chain
- MALT:
-
Mucosal-associated lymphoid tumour
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PTLD:
-
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
References
Clarke CA, Morton LM, Lynch C, Pfeiffer RM, Hall EC, Gibson TM, Weisenburger DD, Martínez-Maza O, Hussain SK, Yang J, Chang ET, Engels EA (2013) Risk of lymphoma subtypes after solid organ transplantation in the United States. Br J Cancer 109(1):280–288. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.294
Dispenzieri A, Kyle R, Merlini G et al (2009) International Myeloma Working Group guidelines for serum-free light chain analysis in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Leukemia 23(2):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.307
Landgren O, Goedert JJ, Rabkin CS, Wilson WH, Dunleavy K, Kyle RA, Katzmann JA, Rajkumar SV, Engels EA (2010) Circulating serum free light chains as predictive markers of AIDS-related lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 28(5):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.25.1322
Engels EA, Preiksaitis J, Zingone A, Landgren O (2012) Circulating antibody free light chains and risk of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Transplant 12(5):1268–1274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03954.x
Fernando RC, Rizzatti EG, Braga WMT, Santos MG, de Oliveira MB, Pestana JOM, Baiocchi OCG, Colleoni GWB (2013) Serum free light chains and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in patients with renal transplant. Leuk Lymphoma 54(10):2177–2180. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2013.764423
Hutchison CA, Harding S, Hewins P, Mead GP, Townsend J, Bradwell AR, Cockwell P (2008) Quantitative assessment of serum and urinary polyclonal free light chains in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(6):1684–1690. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02290508
Jardin F, Delfau-Larue MH, Molina TJ, Copie-Bergman C, Brière J, Petrella T, Canioni D, Fabiani B, Jais JP, Figeac M, Leroy K, Mareschal S, Salles GA, Coiffier B, Delarue R, Peyrade F, Bosly A, André M, Ketterer N, Haioun C, Tilly H (2013) Immunoglobulin heavy chain/light chain pair measurement is associated with survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 54(9):1898–1907. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2013.767456
Bradwell A, Harding S, Fourrier N, Mathiot C, Attal M, Moreau P, Harousseau JL, Avet-Loiseau H (2013) Prognostic utility of intact immunoglobulin Ig'κ/Ig'λ ratios in multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 27(1):202–207. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.159
Trappe R, Oertel S, Leblond V, Mollee P, Sender M, Reinke P, Neuhaus R, Lehmkuhl H, Horst HA, Salles G, Morschhauser F, Jaccard A, Lamy T, Leithäuser M, Zimmermann H, Anagnostopoulos I, Raphael M, Riess H, Choquet S (2012) Sequential treatment with rituximab followed by CHOP chemotherapy in adult B-cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). The prospective international multicentre phase 2 PTLD-1 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(2):196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70300-X
Trappe RU, Dierickx D, Zimmermann H, Morschhauser F, Mollee P, Zaucha JM, Dreyling MH, Dührsen U, Reinke P, Verhoef G, Subklewe M, Hüttmann A, Tousseyn T, Salles G, Kliem V, Hauser IA, Tarella C, van den Neste E, Gheysens O, Anagnostopoulos I, Leblond V, Riess H, Choquet S (2017) Response to rituximab induction is a predictive marker in B-cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder and allows successful stratification into rituximab or R-CHOP consolidation in an international, prospective, Multicenter Phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol 35(5):536–543. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.69.3564
Zimmermann H, Trappe RU (2013) EBV and posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease: what to do? Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2013:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2013.1.95
Katzmann JA, Clark RJ, Abraham RS et al (2002) Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free κ and free λ immunoglobulin light chains: relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin Chem 48(9):1437–1444
Trappe R, Zimmermann H, Fink S, Reinke P, Dreyling M, Pascher A, Lehmkuhl H, Gartner B, Anagnostopoulos I, Riess H (2011) Plasmacytoma-like post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, a rare subtype of monomorphic B-cell post-transplant lymphoproliferation, is associated with a favorable outcome in localized as well as in advanced disease: a prospective analysis of 8 cases. Haematologica 96(7):1067–1071. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2010.039214
Bargnoux A-S, Simon N, Garrigue V, Dupuy AM, Badiou S, Mourad G, Cristol JP (2013) Glomerular filtration rate as a determinant of free light chains in renal transplantation. Clin Biochem 46(16–17):1764–1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.08.024
Bradwell AR, Carr-Smith HD, Mead GP et al (2001) Highly sensitive, automated immunoassay for immunoglobulin free light chains in serum and urine. Clin Chem 47(4):673–680
Charafeddine KM, Jabbour MN, Kadi RH, Daher RT (2012) Extended use of serum free light chain as a biomarker in lymphoproliferative disorders: a comprehensive review. Am J Clin Pathol 137(6):890–897. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCP4INKZ6LYAQXW
Vendrame E, Martínez-Maza O (2011) Assessment of pre-diagnosis biomarkers of immune activation and inflammation: insights on the etiology of lymphoma. J Proteome Res 10(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr100729z
Bradwell AR, Carr-Smith HD, Mead GP, Harvey TC, Drayson MT (2003) Serum test for assessment of patients with Bence Jones myeloma. Lancet 361(9356):489–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12457-9
Hutchison CA, Landgren O (2011) Polyclonal immunoglobulin free light chains as a potential biomarker of immune stimulation and inflammation. Clin Chem 57(10):1387–1389. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2011.169433
Acknowledgments
We thank the Binding Site Ltd. for the provision of the assays for this study and for technical support, in particular, Dr. Anne Burmeister.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RB and RUT are the principal investigators, coordinated the research and take primary responsibility for the paper. HZ, HR and RUT recruited the patients and collected clinical data. FB, RB and PC recruited the controls. AS did the laboratory work. AS, RB, PC and RUT analysed and interpreted the data. IA served as reference pathologists. AS, RB, PC, HZ and RUT wrote the paper. All authors had full access to the final version of the manuscript and agreed to publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval for this study was provided by the local committees of both institutions. The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Disclosures
The Binding Site provided FLC, HLC and cystatin C assays free of charge. The Binding Site played no role in the analysis of the clinical data, its interpretation or the manuscript preparation. The content of the manuscript remains the responsibility of the listed authors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borrows, R., Scheer, A., Cockwell, P. et al. Serum-free light chains adjusted for renal function are a potential biomarker for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Ann Hematol 98, 625–632 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-03591-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-03591-w