Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to clarify the structural arrangement of the orbicularis oris (OOr), the buccinator, and the other perioral muscles around the modiolus.
Methods
The perioral muscles in seventeen cadavers fixed with formalin were dissected in situ and/or in isolated muscle specimens, and their layers were reconstructed schematically upon pantomographic view of the skeleton to evaluate their actions.
Results
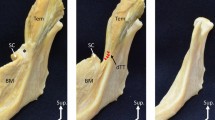
The buccinator was composed of three parts including upper and lower oblique parts in its superficial layer and a middle transverse part in its deep layer. The superior and inferior OOr were composed of an inner marginal part (IM) and an outer labial part (OL) in each. The perioral muscles as a whole were arranged in three layers. The first layer consisted of the depressor anguli oris and the OL of superior OOr connected at the modiolus in a vertical direction. The second layer consisted of the upper and inner oblique part of buccinator and a part of the OL of inferior OOr connected at the modiolus in a horizontal direction. The third layer contained the middle transverse part of buccinator continuous with the IM of both OOr and a part of the OL of inferior OOr without connection to the modiolus.
Conclusions
The different arrangement of the three layers of perioral muscles around the modiolus could serve as a good basis to predict the actions of the individual perioral muscles on the movement of lips in open/close of the oral fissure and widening/narrowing of the lip width.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
On reasonable request, the obtained data supporting the finding of the present study are available from the corresponding authors.
References
Ahn HJ, Cho HJ, Nam YS, Han SH, Chung IH, Kim IB (2013) The location of the modiolus in living Korean [in Korean]. Korean J Phys Anthropol 26(4):141–146. https://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2013.26.4.141
Bo C, Yin N (2014) Reconstruction of upper lip muscle system by anatomy, magnetic resonance imaging, and serial histological sections. J Craniofac Surg 25(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000496
Bonamy MC, Broca P, Beau É (1844) Atlas d’anatomie descriptive du corps humain, vol. 1. Victor Masson, Paris, plate 84
Choi YJ, Kim JS, Gil YC, Phetudom T, Kim HJ, Tansatit T, Hu KS (2014) Anatomical considerations regarding the location and boundary of the depressor anguli oris muscle with reference to botulinum toxin injection. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(5):917–921. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000589
Demiryurek D, Bayramoglu A, Erbil KM, Onderoglu S, Sargon MF, Aldur MM, Korkusuz P, Nazikoglu A (2003) Three-dimensional structure of the modiolus. A computerized reconstruction study. Saudi Med J 24:846–849
Gegenbaur C (1892) Lehrbuch Der Anatomie Des Menschen, vol 1, 5th edn. Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig, pp 358–369
Gray H, Lewis WH (1918) Anatomy of the human body, 20th edn. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 382–385
Green JR, Moore CA, Higashikawa M, Steeve RW (2000) The physiologic development of speech motor control: lip and jaw coordination. J Speech Lang Hear Res 43(1):239–255. https://doi.org/10.1044/jslhr.4301.239
Hu KS, Yang SJ, Kwak HH, Park HD, Youn KH, Jung HS, Kim HJ (2005) Location of the modiolus and the morphologic variations of the risorius and zygomaticus major muscle related to the facial expression in koreans [in Korean]. Korean J Phys Anthropol 18(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2005.18.1.1
Hur MS (2018) Anatomical features of the incisivus labii superioris muscle and its relationships with the upper mucolabial fold, labial glands, and modiolar area. Sci Rep 8(1):12879. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31334-4
Hur MS, Hu KS, Kwak HH, Lee KS, Kim HJ (2011) Inferior bundle (fourth band) of the buccinator and the incisivus labii inferioris muscle. J Craniofac Surg 22(1):289–292. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181f7df35
Kimura N, Kato K, Anetai H, Kawasaki Y, Miyaki T, Kudoh H, Sakai T, Ichimura K (2021) Anatomical study of the soleus: application to improved imaging diagnoses. Clin Anat 34(7):991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23667
Koh SH, Jeong YW, Han JJ, Jung S, Kook MS, Oh HK, Park HJ (2019) Orbicularis oris muscle reconstruction and cheiloplasty with Z-plasty in a patient with a transverse facial cleft. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2 41(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-019-0240-2
Lightoller GH (1925) The modiolus and muscles surrounding the Rima Oris with some remarks about the panniculus adiposus. J Anat 60(1):1–85
Merkel FS (1914) Die Anatomie Des Menschen Mit Hinweisen auf die ärztliche Praxis. Division 3, atlas. J. F. Bergmann, Wiesbaden, p p38
Mikami DLY, Furia CLB, Welker AF (2019) Addition of Kinesio Taping of the orbicularis oris muscles to speech therapy rapidly improves drooling in children with neurological disorders. Dev Neurorehabil 22(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518423.2017.1368729
Patel PN, Owen SR, Norton CP, Emerson BT, Bronaugh AB, Ries WR, Stephan SJ (2018) Outcomes of buccinator treatment with botulinum toxin in facial synkinesis. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 20(3):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2017.1385
Poirier P (1896) Traité d’anatomie humaine, vol 2. Masson et Cie, Paris, pp 384–431
Sakai T, Kato K (2021) Skeletal muscles in the human body: upper limbs [in Japanese]. Igaku-Shoin, Tokyo
Sasakawa Y, Nakamura Y, Saitoh I, Nakajima T, Tsukuno S, Hozawa M, Sotome T, Nogami Y, Kurosawa M, Iwase Y, Hayashi T, Hayasaki H (2021) Lip-closing pressure during food intake from a spoon in normal children. J Oral Rehabil 48(6):711–719. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.13155
Schäfer E, Thane GD (1894) Quain’s elements of anatomy. 10th edn, vol. II, part II. Longmans, Green, and Co., London, pp199-350
Spalteholz W (1898) Handatlas Der Anatomie Des Menschen. S. Hirzel, Leipzig, p 241
Standring S (2008) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice, 40th edn. Churchill Livingstone, London, pp 486–489
Sun M, Chen GC, Wang YQ, Song T, Li HD, Wu D, Yin NB (2018) Anatomical characterization and three-dimensional modeling of the muscles at the corner of the mouth: an iodine staining technique based on micro–computed tomography. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(3):782–785. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004687
Takeda K, Kato K, Ichimura K, Sakai T (2023) Unique morphological architecture of the hamstring muscles and its functional relevance revealed by analysis of isolated muscle specimens and quantification of structural parameters. J Anat 243(2):284–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13860
Testut L (1899) Traité d’anatomie humaine, vol 1. Octave Doin, Paris, pp 708–718
Tillmann B, Töndury G (1987) Rauber/Kopsch Anatomie Des Menschen: Lehrbuch Und Atlas. Bd. 1 Bewegungsapparat. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 758–763
Widman-Valencia ME, Gongora-Meza LF, Rubio-Zapata H, Zapata-Vázquez RE, Lizama EV, Salomón MR, Estrella-Castillo D (2021) Oral motor treatment efficacy: feeding and swallowing skills in children with cerebral palsy. Behav Neurol 2021:6299462. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6299462
Williams PL (1995) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine and surgery, 38th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 794–799
Yu SK, Lee MH, Kim HS, Park JT, Kim HJ, Kim HJ (2013) Histomorphologic approach for the modiolus with reference to reconstructive and aesthetic surgery. J Craniofac Surg 24(4):1414–1417. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e318292c939
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the individuals who donated their bodies to Juntendo University School of Medicine so the anatomical research could be performed. Results from such research can potentially increase mankind’s overall knowledge that can them improve patient care. Therefore, those donors and their families deserve our highest gratitude.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, MI and TS; cadaver preparation, KI and KK; data curation, MI, KK and TS; data validation, KK and TS; and manuscript writing, MI and TS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All cadavers examined were from persons who had donated their bodies to Juntendo University School of Medicine for medical education and research. Prior to donation, written consent was obtained from the individuals and families. The protocol for the present research project was approved by the Ethics Committee of Juntendo University School of Medicine (approval No. 2014138).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, M., Kato, K., Ichimura, K. et al. The three layered structure of orbicularis oris and buccinator complex with partial connection at the modiolus and partial direct continuation. Surg Radiol Anat 46, 649–657 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-024-03354-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-024-03354-5