Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effect of anatomical variations in the sphenopalatine foramen and the lateral nasal wall on sphenopalatine foramen-related morphometric measurements.
Methods
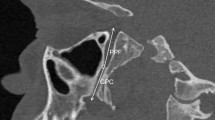
Paranasal sinus multidetector computed tomography records of 153 patients were evaluated. Morphometric measurements were made between the fixed bony landmarks and the sphenopalatine foramen. Number, shape, localization variations of the sphenopalatine foramen, concha bullosa, and septum deviation were noted and the results were compared with respect to sex, age, and laterality.
Results
No significant difference was detected with respect to laterality, whereas most of the measured distances were higher in males than females. There was a significant difference between the obtained morphometric data according to age groups. In our study, 91.2% single, 7.8% double, and 1% triple sphenopalatine foramen were detected and the most common irregularly shaped (37.3%). The location of sphenopalatine foramen was reported as the most common type II. Septum deviation types have no potential influence on the location of the foramen, but most of the measured parameters were found to be significantly smaller in the presence of concha bullosa, whereas the angle was found to be higher.
Conclusion
This study revealed a significant relationship between the morphometric measurements of the sphenopalatine foramen and concha bullosa, while septum deviation types did not affect these results. For a safer and more effective surgery with prevention of iatrogenic complications, a surgeon should be aware of this correlation, especially in endoscopic transnasal approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Jeong H, Choi B, Lee J, Kim KS, Min SJ, Kim JK (2021) Prevalence and characteristics of S-point bleeding compared to non S-point bleeding in severe epistaxis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 87(4):462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.07.008
Morosanu CO, Humphreys C, Egerton S, Tierney CM (2021) Woodruff’s plexus—arterial or venous? Surg Radiol Anat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02852-0
Traboulsi H, Alam E, Hadi U (2015) Changing trends in the management of epistaxis. Int J Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/263987
Alherabi A, Marglani O, Herzallah IR, Shaibah H, Alaidarous T, Alkaff H et al (2014) Endoscopic localization of the sphenopalatine foramen: do measurements matter? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(9):2455–2460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2881-1
De Bonnecaze G, Gallois Y, Chaynes P, Bonneville F, Dupret-Bories A, Chantalat E, Serrano E (2017) Intractable epistaxis: which arteries are responsible? Angiogr Study Surg Radiol Anat 39(11):1203–1207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1856-5
Prades JM, Asanau A, Timoshenko AP, Faye MB, Martin C (2008) Surgical anatomy of the sphenopalatine foramen and its arterial content. Surg Radiol Anat 30(7):583–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-008-0390-x
Scanavini ABA, Navarro JAC, Megale SRMCL, Anselmo-Lima WT (2009) Anatomical study of the sphenopalatine foramen. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75(1):37–41. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992009000100006
Maxwell AK, Barham HP, Getz AE, Kingdom TT, Ramakrishnan VR (2017) Landmarks for rapid localization of the sphenopalatine foramen: a radiographic morphometric analysis. Allergy Rhinol 8:63–66. https://doi.org/10.2500/ar.2017.8.0196
El-Shaarawy EAA, Hassan SS (2018) The sphenopalatine foramen in man: anatomical, radiological and endoscopic study. Folia morphol 77(2):345–355. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2017.0104
Özdoğan F, Özel HE, Esen E, Altıparmak E, Genç S, Selçuk A (2017) An often neglected area in crooked nose: middle turbinate pneumatization. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 83(5):563–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.06.006
Toplu Y, Bayindir T, Erkan Karatas E, Akarcay M (2013) All concha bullosa: an undefined abnormality of the lateral nasal wall. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65(1):86–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-012-0592-8
El-Anwar MW, Khazbak AO, Hussein A, Saber S, Bessar AA, Eldib DB (2020) Sphenopalatine foramen computed tomography landmarks. J Craniofac Surg 31(1):210–213. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005857
İla K, Yilmaz N, Öner S, Başaran E, Öner Z (2018) Evaluation of superior concha bullosa by computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat 40(7):841–846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2010-8
Nalavenkata S, Meller C, Novakovic D, Forer M, Patel NP (2015) Sphenopalatine foramen: endoscopic approach with bony landmarks. J Laryngol Otol 129(S3):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215115000766
Chitsuthipakorn W, Seresirikachorn K, Kanjanawasee D, Snidvongs K (2020) Endoscopic sphenopalatine foramen cauterization is an effective treatment modification of endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation for intractable posterior epistaxis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(9):2463–2467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06005-8
Sir E, Ekset S (2019) Morphological description and clinical implication of sphenopalatine foramen for accurate transnasal sphenopalatine ganglion block: an anatomical study. Medeniyet Med J 34(3):239–243. https://doi.org/10.5222/MMJ.2019.20586
Hadoura L, Douglas C, McGarry GW, Young D (2009) Mapping surgical coordinates of the sphenopalatine foramen: surgical navigation study. J Laryngol Otol 123(7):742–745. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215109004344
Midilli R, Orhan M, Saylam CY, Akyildiz S, Gode S, Karci B (2009) Anatomic variations of sphenopalatine artery and minimally invasive surgical cauterization procedure. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23(6):38–41. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2009.23.3403
Gras-Cabrerizo JR, Ademá-Alcover JM, Gras-Albert JR, Kolanczak K, Montserrat-Gili JR, Mirapeix-Lucas R et al (2014) Anatomical and surgical study of the sphenopalatine artery branches. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(7):1947–1951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2825-1
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ŞB, AG: conceptualization, methodology, software. AD: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. ŞB, AG, ÇAE: visualization, ınvestigation. GA, ÇAE supervision. AD: software, validation. ŞB, AG, ÇAE: writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests. The authors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was presented at the department of radiology between January 2019 and May 2020 and approved by our local Ethics Committee with an approval No. 2020/2906.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Şeker, B., Açar, G., Çiçekcibaşı, A.E. et al. Morphometric analysis of sphenopalatine foramen on computed tomography images with clinical significance. Surg Radiol Anat 44, 1521–1529 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-022-03044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-022-03044-0