Abstract
Purpose
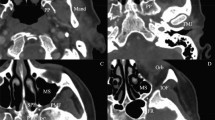
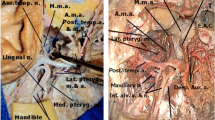
The aim of this study is to evaluate the branching patterns and topographical features of the third part of the maxillary artery (t-MA) and descending palatine artery (DPA) by 3-Dimensional Rotational Angiography (3DRA) images and to define the radiological classification of their variations, based upon the previous cadaveric studies and a review of the literature.
Method
This study was conducted from May 2020 through June 2021. All consecutive adult patients who were examined with 3D-RA were enrolled in the study. The morphological evaluations and measurements of t-MA, DPA and their branches were made on maximum intensity projection images with 10–20 mm slice thickness.
Results
Eighty-five hemifaces, including 58 females and 45 right sides, were evaluated. The diameter of the t-MA was measured as 1.73 ± 0.30 mm. The most common pattern of the t-MA according to its course was loop type (63/85, 74.1%) and according to branching pattern was Type Ib (29/85, 34.1%). The mean diameter of DPA was 1.19 ± 0.20 mm. The DPA presented as a single trunk in 11/85 cases. Type II, which was defined as one lesser palatine artery originating from distal-DPA, was the most common morphological variation (51.8%).
Conclusions
3DRA imaging provides valuable information for vascular anatomical studies. The most common morphological variation related to t-MA, DPA is the distal branching pattern.


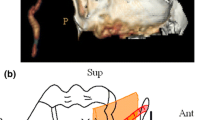
modified from Type M (Morton and Khan), the angulation between SPA and DPA is 0–30°. The subgroups were defined according to the location of the bifurcation. Type Ia was proximal (a) and Type Ib was distal (b). Type II: modified from Type T and Type intermediate (Morton and Khan), the angulation between SPA and DPA is 30–120°. The subgroups of Type II were defined according to the dominant branch of bifurcation. If SPA was the terminal branch and larger than DPA, it was Type IIa (Type T) (c) and otherwise, it was Type IIb (Type intermediate) (d). Type III; modified from Type Y (Morton and Khan), the angulation between SPA and DPA is > 120° (e)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shouk AAA-HM, Tatar İ (2021) The blood supply of the inferior nasal concha (turbinate): a cadaveric anatomical study. Anat Sci Int 96:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-020-00552-0
Apinhasmit W, Chompoopong S, Methathrathip D, Sangvichien S, Karuwanarint S (2005) Clinical anatomy of the posterior maxilla pertaining to Le Fort I osteotomy in Thais. Clin Anat 18:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20131
Assam JH, Quinn TH, Militsakh ON (2017) The maxillary artery as a recipient vessel option for complex midface and anterior skull base microsurgical repair: a cadaveric study. Microsurgery 37:611–617. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.30095
Awad AS, Tohamy HMA, Gadallah HN, Ibrahim MEE-D, Raafat TA (2020) Role of multi-detector CT in analysis of the greater and lesser palatine foramina. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med 51:150. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43055-020-00272-5
Bahşi İ, Orhan M, Kervancıoğlu P, Yalçın ED (2019) Morphometric evaluation and clinical implications of the greater palatine foramen, greater palatine canal and pterygopalatine fossa on CBCT images and review of literature. Surg Radiol Anat 41:551–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-019-02179-x
Cagimni P, Govsa F, Ozer MA, Kazak Z (2017) Computerized analysis of the greater palatine foramen to gain the palatine neurovascular bundle during palatal surgery. Surg Radiol Anat 39:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1691-0
Choi J, Park HS (2003) The clinical anatomy of the maxillary artery in the pterygopalatine fossa. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2003.50012
D’Souza AS, Mamatha H, Jyothi N (2012) Morphometric analysis of hard palate in south Indian skulls. Biomed Res 23:173–175
Hassanali J, Mwaniki D (1984) Palatal analysis and osteology of the hard palate of the Kenyan African skulls. Anat Rec 209:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092090213
Jotania B, Patel S, Patel S, Patel P, Patel S, Patel K (2013) Morphometric analysis of hard palate. Int J Res Med 2:72–75
Klosek SK, Rungruang T (2009) Anatomical study of the greater palatine artery and related structures of the palatal vault: considerations for palate as the subepithelial connective tissue graft donor site. Surg Radiol Anat 31:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-008-0432-4
Kwak HH, Jo JB, Hu KS, Oh CS, Koh KS, Chung IH, Kim HJ (2010) Topography of the third portion of the maxillary artery via the transantral approach in Asians. J Craniofac Surg 21:1284–1289. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181e1b33c
Lee HY, Kim HU, Kim SS, Son EJ, Kim JW, Cho NH, Kim KS, Lee JG, Chung IH, Yoon JH (2002) Surgical anatomy of the sphenopalatine artery in lateral nasal wall. Laryngoscope 112:1813–1818. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200210000-00020
MacArthur FJ, McGarry GW (2017) The arterial supply of the nasal cavity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274:809–815
Miwa Y, Asaumi R, Kawai T, Maeda Y, Sato I (2018) Morphological observation and CBCT of the bony canal structure of the groove and the location of blood vessels and nerves in the palatine of elderly human cadavers. Surg Radiol Anat 40:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1952-6
Morton AL, Khan A (1991) Internal maxillary artery variability in the pterygopalatine fossa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 104:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989110400208
Mostafa BE, Elsamny TA, Youssef TA, Elserwi AB, Teaima AA (2018) Arterial blood supply of the nose: an angiographic study. J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 80:238–247. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490254
Neruntarat C (2007) Uvulopalatal flap. In: Kountakis SE, Önerci M (eds) Rhinologic and sleep apnea surgical techniques. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 309–314
Odabaşı O, Erkmen E, ÖzlemÜçok C, AkifBakir M, YıldızerKeriş E, Şahin O (2021) Morphometric analysis of pterygomaxillary region by using cone beam computed tomography. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg 122:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2020.06.006
Orhan M, Midilli R, Gode S, Saylam CY, Karci B (2010) Blood supply of the inferior turbinate and its clinical applications. Clin Anat 23:770–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.21019
Osborn AG (1979) Radiology of the pterygoid plates and pterygopalatine fossa. Am J Roentgenol 132:389–394
Padgham N, Vaughan-Jones R (1991) Cadaver studies of the anatomy of arterial supply to the inferior turbinates. J R Soc Med 84:728–730
Scott JR, Psaltis AJ, Wormald P-J (2020) Vascular anatomy of the inferior turbinate and its clinical implications. Am J Rhinol Allergy 34:604–609
Standring S (2016) Gray’s anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier Limited, New York
Tashi S, Purohit BS, Becker M, Mundada P (2016) The pterygopalatine fossa: imaging anatomy, communications, and pathology revisited. Insights Imaging 7:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-016-0498-1
Touré G (2019) Distribution of the maxillary artery in the deep regions of the face and the maxilla: clinical applications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 72:1020–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2019.02.008
Ueki K, Hashiba Y, Marukawa K, Nakagawa K, Okabe K, Yamamoto E (2009) Determining the anatomy of the descending palatine artery and pterygoid plates with computed tomography in Class III patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 37:469–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2009.03.010
Uysal II, Buyukmumcu M, Dogan NU, Seker M, Ziylan T (2011) Clinical significance of maxillary artery and its branches: a cadaver study and review of the literature. Int J Morphol 29:1274–1281
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IIOZ: protocol/project development, data collection or management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing. AA: data analysis, data collection or management, manuscript writing/editing. TFY: data collection or management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OZ, I.I., Aydogdu, A. & Yilmaz, T.F. Radiological evaluation of maxillary artery and descending palatine artery in the pterygopalatine fossa by 3D rotational angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 44, 535–542 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-022-02916-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-022-02916-9