Abstract
Purpose
To date, no study has explored the inferior sagittal sinus (ISS) using neuroimaging modalities. This investigation aimed to characterize it using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
A total of 77 patients with intact cerebral hemispheres and covering meninges underwent thin-sliced, contrast-enhanced MRI.
Results
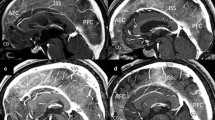
The ISS was well delineated as a linear structure with a constant diameter in 97% of the patients. The maximum intensity projection (MIP) images well delineated the three-dimensional architecture of the ISS and relevant veins. The identified ISSs could be classified into three different types, with the underdeveloped type being the most frequent at 47%. In addition, the ISSs showed considerable variability both in the original site and course along the lower margin of the falx cerebri. Furthermore, in 22% of the cases, fenestrations were identified in the falx cerebri adjacent to or near the ISS. More than 70% of them were located in the middle third of the falx, followed by the anterior and middle thirds of the falx.
Conclusions
The ISS is a constant venous structure characterized by morphological variability and may function as an adjunctive or assistive venous drainage route. Thin-sliced, post-contrast-enhanced sagittal MRI combined with MIP imaging is useful for exploring the ISS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsherbiny SM, Grünewald RA, Powell T (1997) Isolated inferior sagittal sinus thrombosis: a case report. Neuroradiology 39:411–413
Erbaş G, Oner AY, Akpek S, Tokgoz N (2006) Corpus callosum hematoma secondary to isolated inferior sagittal sinus thrombosis. Acta Radiol 47:1085–1088
Kaplan HA, Browder J (1973) Venous aneurysm of the inferior sagittal sinus. C rep J Neurol Surg 39:537–539
Kędzia W, Kędzia E, Kędzia A, Derkowski W (2017) Anatomy of the falcine sinus during the prenatal period. Surg Radiol Anat 39:753–758
McCord GM, Goree JA, Jimenez JP (1972) Venous drainage to the inferior sagittal sinus. Radiology 105:583–589
Morgan MK, Sundt TM, Houser OW (1989) Arterio-inferior sagittal sinus fistulae: case report. Neurosurgery 25:971–975
Nayak SB, Vasudeva SK (2020) Fenestrated falx cerebri and additional sinuses in the tentorium cerebelli. J Craniofac Surg 31:e585–e586
Rhoton AL Jr (2002) The cerebral veins. Neurosurgery 51(4):S159–S205
Ryu CW (2010) Persistent falcine sinus: is it really rare? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:367–369
Seljeskog EL, Rogers HM, French LA (1968) Arteriovenous malformation involving the inferior sagittal sinus in an infant. C rep J Neurol Surg 29:623–628
Topsakal C, Cihangiroglu M, Kaplan M, Akdemir I, Tiftikci M (2002) Complete superior and inferior sagittal sinus thromboses with multiple cranial nerve pareses and transient ischemic attack—case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 42:383–386
Tsutsumi S, Ono H, Yasumoto Y, Ishii H (2019) Venous channels of the falx cerebri in adult Japanese population: delineation using magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 41:203–207
Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Louis RG Jr, Shoja MM, Acakpo-Satchivi L, Blount JP, Salter EG, Oakes WJ, Wellons JC 3rd (2007) Anatomy of the falcine venous plexus. J Neurol Surg 107:155–157
Yamakawa K, Naganawa S, Maruyama K, Kato T, Fukatsu H, Ishigaki T (1999) Clinical evaluation of three-dimensional MR-cholangiopancreatography using three-dimensional Fourier transform fast asymmetric spin echo method (3DFT-FASE): usefulness of observation by multi-planar reconstruction. Radiat Med 17:15–19
Yoneoka Y, Watanabe M, Nishino K, Ito Y, Kwee IL, Nakada T, Fujii Y (2008) Evaluation of post-procedure changes in aneurysmal lumen following detachable coil-placement using multi-planar reconstruction of high-field (3.0T) magnetic resonance angiography. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:351–358 (discussion 358)
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST: conceived the study and wrote the manuscript, HO: collected the imaging data, and ST and HI: analyzed the imaging data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare regarding the materials or methods used in this study or the findings presented in this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures in this study were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsutsumi, S., Ono, H. & Ishii, H. Inferior sagittal sinus: magnetic resonance imaging study. Surg Radiol Anat 43, 1353–1357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02701-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02701-0