Abstract
Purpose
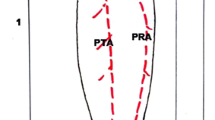
Initially described by Baudet in 1982, the fibula flap including the lateral head of the soleus muscle allows a one-stage reconstruction for large maxillo-mandibular defects. The aim of this study was to evaluate the number of muscular branches destined to the soleus muscle and their distance from the origin of the fibular artery, to assess the vascular anatomy of the free fibula flap including the lateral head of the soleus muscle applied to maxillo-mandibular reconstruction.
Methods
We performed a cadaveric anatomic study on ten lower limbs, and a CT angiography anatomic study on 38 legs. The number of soleus branches originating from the fibular artery, and the distance between the origin of the fibular artery and each of the identified branches were measured.
Results
The number of soleus branches destined to the lateral head of the soleus muscle is variable, with in our study 1–3 branches found. Soleus branches destined to the lateral head of the soleus muscle emerged at a distance ranging between 0 and 2.9 cm (mean value = 1.82 cm) from the origin of the fibular artery in 40% of cases, between 3 and 5.9 cm (mean value = 4.27 cm) from the origin of the fibular artery in 37% of cases, and was at a distance of 6 cm or more (mean value = 6.93 cm) from the origin of the fibular artery in 20% of cases.
Conclusions
An origin of the soleus vessels in close proximity to the origin of the fibular artery represents the main limitation of this flap, the length of the remaining fibular pedicle making it difficult to achieve secure anastomosis in the cervical area. The vascular distribution of the proximal part of the lateral head of the soleus muscle being segmental, it is possible to lengthen the flap pedicle ligating the most proximal soleus branches originating from the fibular artery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian D, Thankappan K, Kuriakose MA et al (2012) Reconstructive indications of simultaneous double free flaps in the head and neck: a case series and literature review. Microsurgery 32:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.21963
Baudet J, Panconi B, Caix P (1982) The composite fibula and soleus free transfer. Int J Microsurg 4:10
Blackwell KE, Urken ML (1996) Iliac crest free flap. Facial Plast Surg FPS 12:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1064491
Chang EI, Yu P (2017) Prospective series of reconstruction of complex composite mandibulectomy defects with double island free fibula flap. J Surg Oncol 116:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.24647
Cheng M-H, Saint-Cyr M, Ali RS et al (2009) Osteomyocutaneous peroneal artery-based combined flap for reconstruction of composite and en bloc mandibular defects. Head Neck 31:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20969
El Zawawy EMM, El Sekily NM (2012) An anatomical study of the blood supply of the soleus muscle in humans. Alex J Med 48:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2012.05.001
Ersoy B, Sönmez A, Bayramiçli M (2011) Sternocleidomastoid region restoration with lateral hemisoleus muscle incorporatied in free fibular flap for reconstruction of radical neck dissection and hemimandibulectomy. Microsurgery 31:401–403. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20908
Fathi M, Hassanzad Azar M, Arab Kheradmand A, Shahidi S (2011) Anatomy of arterial supply of the soleus muscle. Acta Med Iran 49:237–240
Fayman MS, Orak F, Hugo B, Berson SD (1987) The distally based split soleus muscle flap. Br J Plast Surg 40:20–26
Foy J-P, Qassemyar Q, Assouly N et al (2016) Harvesting technique of chimeric multiple paddles fibular flap for wide oromandibular defects. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 61:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2015.09.002
Garvey PB, Chang EI, Selber JC et al (2012) A prospective study of preoperative computed tomographic angiographic mapping of free fibula osteocutaneous flaps for head and neck reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 130:541e–549e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318262f115
Gérard R, Rizzo C, Hu W et al (2010) Lambeau d’hémi-soléaire latéral en îlot vasculaire à pédicule fibulaire distal: une nouvelle option pour traiter les défects cutanés de la jambe. Rev Chir Orthopédique Traumatol 96:S54–S59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcot.2010.03.027
Hanasono MM, Corbitt CA, Yu P, Skoracki RJ (2014) Success of sequential free flaps in head and neck reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg JPRAS 67:1186–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2014.05.012
Hidalgo DA, Pusic AL (2002) Free-flap mandibular reconstruction: a 10-year follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:438–449 (discussion 450–451)
Huang Y-C, Leong C-P, Pong Y-P et al (2012) Functional assessment of donor-site morbidity after harvest of a fibula chimeric flap with a sheet of soleus muscle for mandibular composite defect reconstruction. Microsurgery 32:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20955
Kannan RY, Mathur BS, Tzafetta K (2013) Single flap reconstruction for complex oro-facial defects using chimeric free fibular flap variants. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg JPRAS 66:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2012.10.012
Kheradmand AA, Garajei A, Kiafar M, Nikparto N (2016) Assessing the anatomical variability of deep circumflex iliac vessels in harvesting of iliac crest-free flap for mandibular reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg 27:e320–e323. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000002576
Konschake M, Brenner E (2014) “Mors auxilium vitae”—causes of death of body donors in an Austrian Anatomical Department. Ann Anat 196:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2014.07.002
Kuo Y-R, Shih H-S, Chen C-C et al (2010) Free fibula osteocutaneous flap with soleus muscle as a chimeric flap for reconstructing mandibular segmental defect after oral cancer ablation. Ann Plast Surg 64:738–742. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181a72f62
Le Nen D, Rizzo C, Hu W et al (2009) The island hemisoleus flap on distal vascular pedicle: anatomical bases and clinical applications. Surg Radiol Anat SRA 31:715–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0509-8
McHanwell S, Brenner E, Chirculescu ARM, Drukker J, van Mameren H, Mazzotti G, Pais D, Paulsen F, Plaisant O, Caillaud M, Laforêt E, Riederer BM, Sanudo JR, Bueno-Lopez JL, Donate F, Sprumont P, Teofilovski-Parapid G, Moxham BJ (2008) The legal and ethical framework governing Body Donation in Europe—a review of current practice and recommendations for good practice. Eur J Anat 12:1–24
Mathes SJ, Nahai F (1981) Classification of the vascular anatomy of muscles: experimental and clinical correlation. Plast Reconstr Surg 67:177–187
Mo KWL, Vlantis A, Wong EWY, Chiu TW (2014) Double free flaps for reconstruction of complex/composite defects in head and neck surgery. Hong Kong Med J Xianggang Yi Xue Za Zhi 20:279–284. https://doi.org/10.12809/hkmj134113
Pelissier P, Casoli V, Demiri E et al (2000) Soleus-fibula free transfer in lower limb reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:567–573
Prathapamchandra V, Prabhu LV, Pai MM et al (2015) Arterial supply to the soleus muscle: an anatomical study with emphasis on its application in the pedicle flap surgery. Surg Radiol Anat SRA 37:1055–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-015-1485-9
Raveendran SS, Kumaragama KGJL (2003) Arterial supply of the soleus muscle: anatomical study of 50 lower limbs. Clin Anat NY N 16:248–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.10098
Ribuffo D, Atzeni M, Saba L et al (2010) Clinical study of peroneal artery perforators with computed tomographic angiography: implications for fibular flap harvest. Surg Radiol Anat SRA 32:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0559-y
Riederer BM, Bolt S, Brenner E, Bueno-Lopez JL, Chirculescu ARM, Davies DC, De Caro R, Gerrits PO, McHanwell S, Pais D, Paulsen F, Plaisant O, Sendemir E, Stabile I, Moxham BJ (2012) The legal and ethical framework governing Body Donation in Europe—1st update on current practice. Eur J Anat 16:1–21
Singh T, Andi K (2017) Iliolumbar artery: a useful pedicle for the iliac crest free flap in maxillofacial reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:270–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.12.012
Taylor GI, Pan WR (1998) Angiosomes of the leg: anatomic study and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:599–616 (discussion 617–618)
Tobin GR (1985) Hemisoleus and reversed hemisoleus flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 76:87–96
Wagner AJ, Bayles SW (2008) The angular branch: maximizing the scapular pedicle in head and neck reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:1214–1217. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.134.11.1214
Wehage IC, Fansa H (2011) Complex reconstructions in head and neck cancer surgery: decision making. Head Neck Oncol 3:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-3284-3-14
Wolff K-D, Bauer F, Dobritz M et al (2012) Further experience with the free soleus perforator flaps using CT-angiography as a planning tool—a preliminary study. J Cranio-Maxillo-fac Surg Off Publ Eur Assoc Cranio-Maxillo-fac Surg 40:e253–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2011.10.030
Wong C-H, Ong Y-S, Chew K-Y et al (2009) The fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap incorporating the hemisoleus muscle for complex head and neck defects: anatomical study and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:1956–1964. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181bf83b0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LN: protocol development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. JD: data analysis, manuscript writing. FB: data collection. BD: other. SD: other. CV: protocol development, data analysis, manuscript writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nokovitch, L., Davrou, J., Bidault, F. et al. Vascular anatomy of the free fibula flap including the lateral head of the soleus muscle applied to maxillo-mandibular reconstruction. Surg Radiol Anat 41, 447–454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2166-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2166-2