Abstract
Purpose
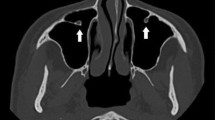
To analyze morphological characteristics and dimensions of the infraorbital canal-groove complex using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), and to evaluate its relationship with adjacent anatomical structures.
Methods
This retrospective study included CBCT scans of 100 patients taken between January and May 2014. Linear measurements of the infraorbital canal (IOC), the infraorbital groove (IOG) and the infraorbital canal-groove complex (IOC/G) were performed. Morphological variants of the IOC related to the maxillary sinus were classified into three types depending on the extent of protrusion of the canal into the sinus. Angles between the IOC and specific landmarks were measured to determine the direction of the IOC relative to the axial (A-ant) and sagittal (A-horiz) planes.
Results
A total of 127 IOCs were analyzed. The mean length of the IOC/G was 29 ± 3.0 mm. This value comprised the mean distances of the IOC (24.4 ± 2.9 mm) and the IOG (4.6 ± 1.7 mm). For the different types of IOC morphology, Type 1 (IOC embedded in maxillary sinus roof) was the most common (n = 87, 68.5%). The mean angles of A-ant and A-horiz measured 48.9° ± 7.5° and 20.3° ± 7.9°, respectively.
Conclusion
Knowledge of the IOC/G morphology and its variants is important for the prevention of infraorbital nerve injury due to anesthesia or surgical interventions in this area. The presented data of anatomical characteristics of the IOC/G could be helpful for the planning of surgeries in the maxillary region by means of CBCT imaging.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caspersen LM, Christensen IJ, Kjaer I (2009) Inclination of the infraorbital canal studied on dry skulls expresses the maxillary growth pattern: a new contribution to the understanding of change in inclination of ectopic canines during puberty. Acta Odontol Scand 67:341–345
Chandra RK, Kennedy DW (2004) Surgical implications of an unusual anomaly of the infraorbital nerve. Ear Nose Throat J 83:766–767
Cutler JL, Duncavage JA, Matheny K, Cross JL, Miman MC, Oh CK (2003) Results of Caldwell-Luc after failed endoscopic middle meatus antrostomy in patients with chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 113:2148–2150
Ference EH, Smith SS, Conley DC, Chandra RK (2015) Surgical anatomy and variations of the infraorbital nerve. Laryngoscope 125:1296–1300
Hwang SH, Kim SW, Park CS, Kim SW, Cho JH, Kang JM (2013) Morphometric analysis of the infraorbital groove, canal, and foramen on three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomography scans. Surg Radiol Anat 35:565–571
Kazakayasi M, Ergin A, Ersoy M, Bengi O, Tekdemir I, Elhan A (2001) Certain anatomical relations and the precise morphometry of the infraorbital foramen-canal and groove: an anatomical and cephalometric study. Laryngoscope 111:609–614
Kim E, Duncavage JA (2010) Prevention and management of complications in maxillary sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 43:865–873
Lawrence JE, Poole MD (1992) Mid-facial sensation following craniofacial surgery. Br J Plast Surg 45:519–522
Lee UY, Nam SH, Han SH, Choi KN, Kim TJ (2006) Morphological characteristics of the infraorbital foramen and infraorbital canal using three-dimensional models. Surg Radiol Anat 28:115–120
Ludow JB, Ivanovic M (2008) Comparative dosimetry of dental CBCT devices and 64-slice CT for oral and maxillofacial radiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 106:106–114
Olenczak JB, Hui-Chou HG, Aguila DJ III, Shaeffer CA, Dellon AL, Manson P (2015) Posttraumatic midface pain: clinical significance of the anterior superior alveolar nerve and canalis sinuosus. Ann Plast Surg 75:543–547
Orhan K, Misirli M, Aksoy S, Seki U, Hincal E, Ormeci T, Arslan A (2016) Morphometric analysis of the infraorbital foramen, canal and groove using cone beam CT: considerations for creating artificial organs. Int J Artif Organs 39:28–36
Przygocka A, Szymański J, Jakubczyk E, Jędrzejewski K, Topol M, Polguj M (2013) Variations in the topography of the infraorbital canal/groove complex: a proposal for classification and its potential usefulness in orbital floor surgery. Folia Morphol 72:311–317
Scarfe WC, Langlais RP, Ohba T, Kawamata A, Maselle I (1995) Panoramic radiographic patterns of the infraorbital canal and anterior superior dental plexus. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 27:85–92
Song WC, Kim JN, Yoo JY, Lee JY, Won SY, Hu KS, Kim HJ, Koh KS (2012) Microanatomy of the infraorbital canal and its connecting canals in the maxilla using 3-D reconstruction of microcomputed tomographic images. J Craniofac Surg 23:1184–1187
Tewfik MA, Wormald P-J (2013) Chapter 9: complications in endoscopic sinus surgery. In: Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Carrau RL, Dazert S et al (eds) Complications in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery. Thieme, New York
Von Arx T, Lozanoff S, Sendi P, Bornstein MM (2013) Assessment of bone channels other than the nasopalatine canal in the anterior maxilla using limited cone beam computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat 35:783–790
Wanzeler AMV, Marinho CG, Melo Alves S Jr, Manzi FR, Mesquita Tuji F (2013) Anatomical study of the canalis sinuosus in 100 cone beam computed tomography examinations. Oral Maxillofac Surg 19:49–53
Yenigun A, Gun C, Uysal II, Nayman A (2016) Radiological classification of the infraorbital canal and correlation with variants of neighboring structures. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:139–144
Zhao ZM, Zhu Y, Huo R, Su JR, Gao F (2014) Three-dimensional cephalometric analysis of adolescents with cleft lip and palate using computed tomography-guided imaging. J Craniofac Surg 25(6):1939–1942
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Bernadette Rawyler, Medical Illustrator, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern, Switzerland for the schematic illustrations. The authors are also grateful to Ms. Kar Yan Li, Centralised Research Lab, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong, for her valuable assistance regarding the statistical analysis.
Funding
No grants or funding have been received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M Fontolliet: Protocol/project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. MM Bornstein: Protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript editing. Th von Arx: Protocol/project development, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontolliet, M., Bornstein, M.M. & von Arx, T. Characteristics and dimensions of the infraorbital canal: a radiographic analysis using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Surg Radiol Anat 41, 169–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2108-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2108-z