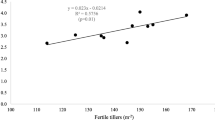
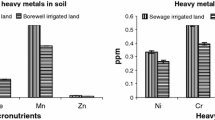
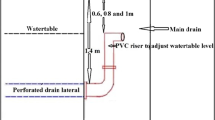
Abstract
Irrigating crops with reclaimed water from sewage treatment plants can contribute to the conservation and augmentation of the water resources in arid regions. Many countries in the Middle East, North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa are suffering from serious water shortages. Three field studies were conducted during the period 2010–2011 to assess yield components and chemical constituents of wheat, cowpea and maize crops grown in rotation with reclaimed water for irrigation in comparison with desalinated and groundwater. The reclaimed water irrigation increased wheat plant height (cm), chlorophyll, leaf area (cm2), leaf length (cm), grain yield (t ha−1) and the water productivity (kg grain m−3). It improved all cowpea growth parameters under study except the dry forage yield. Nitrogen was also higher under reclaimed water irrigation in wheat tissue, cowpea pods and maize cobs. Reclaimed water had no effect on the element concentrations in wheat, cowpea and maize except for nickel concentration in wheat plants, and Sodium and Manganese concentrations in maize plants. Using reclaimed water for irrigation increased the yield parameters of wheat, cowpea and maize. However, all the studied element concentrations in wheat, cowpea and maize were within the normal limits after irrigation by reclaimed water. It can be concluded that reclaimed water usage will have significant positive impacts on yield and water productivity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Rahman G (2009) Water use efficiency of wheat under drip irrigation systems. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 5(5):664–670
Abdelrahman AH, Alkhamisi SA, Ahmed M, Ali H (2011) Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on element concentrations in soil and maize plants. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 42(17):2046–2063
Adewumi JR, Ilemobade AA, Van Zyl JE (2010) Treated wastewater reuse in South Africa: overview, potential and challenges. Resour Conserv Recycl 55:221–231
Adriel F, Jose MA, Regina MC (2005) Maize growth and changes in soil fertility after irrigation with treated sewage effluent. I. Plant dry matter yield and soil nitrogen and phosphorus availability. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 36:13–14
Akhtar M, Nadaf SK (2002) Consolidated results of the experiments in field crops (1971–2000). Directorate General of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries, Sultanate of Oman
Al-Ajmi A, Salih A, Kadhim I, Othman Y (2009) Yield and water use efficiency of barley fodder produced under hydroponic system in GCC countries using tertiary treated sewage effluents. J Phytol 1(5):342–348
Ali H, Alkhamisi SA, Albakri A (2011) Utilization of tertiary treated wastewater in production of forage crops under Sultanate of Oman conditions. Jordan J Agric Sci 7(3):602–616
Alkhamisi SA, Abdelrahman HA, Ahmed M, Goosen MFA (2011) Assessment of reclaimed water irrigation on growth, yield, and water-use efficiency of forage crops. Appl Water Sci J 1:57–65
Alkhamisi SA (2013) Maximizing the use of reclaimed water for crop production in arid regions (Unpublished doctoral thesis). Sultan qaboos university, Muscat, Oman
Al-Lahham O, El Assi NM, Fayyad M (2003) Impact of treated wastewater irrigation on quality attributes and contamination of tomato fruit. Agric Water Manag 61:51–62
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements—irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO, Rome
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy Metals in soils, 2nd edition, Appendix 2. Blackie Academic and Professional, London (354)
Al-Nakshabandi GA, Saqqar MM, Shatanawi MR, Fayyad M, Al-Horani H (1997) Some environmental problems associated with the use of treated wastewater for irrigation in Jordan. Agric Water Manag 34:81–94
Al-Omron AM, El-Maghraby SE, Nadeem MEA, El-Eter AM, Al-Mohani H (2012) Long-term effect of irrigation with the treated sewage effluent on some soil properties of Al-Hassa Governorate, Saudi Arabia. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 11:15–18
AOAC (1994) Official method of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC), Washington, DC
Basahi JM, Al-Sulaimani SJ, El-Nakhlawy FS, Al-Facy FA, Hamo BT (2007) Effect of irrigation water mixed with wastewater on the alfalfa yield and its content of micronutrients and toxic elements. J King Abdulaziz Univ: Fac Meteorol, Environ Arid Land Agric 18(2):82–65
Choudri BS, Al-Busaidi A, Ahmed M (2013) Climate change, vulnerability and adaptation experiences of farmers in Al-Suwayq Wilayat, Sultanate of Oman. Int J Clim Change Strateg Manag 5(4):445–454
Choudri BS, Baawain M, Ahmed M, Al-Sidairi A, Al-Nadabi H (2015) An indicator based Vulnerability assessment of Wilayats to development. J Ecol Environ Conserv 21(2):1059–1066
FAO (2007) Joint FAO/WHO Food Standard Programme Codex Alimentarius Commission 13th Session. Report of the Thirty-Eight Session of the Codex Committee on Food Hygiene, Houston, United States of America, ALINORM 07/30/13
Food and Agriculture Organization (1998) Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements, Irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO, Rome
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. The International Rice Research Institute, Philippines
Hassanli AM, Ebrahimizadeh MA, Becham S (2009) The effects of irrigation methods with effluent and irrigation scheduling on water use efficiency and corn yields in an arid region. Agric Water Manag 96:93–99
Jun-feng W, Gen-xu W, Hua W (2007) Treated wastewater irrigation effect on soil, crop and environment: wastewater recycling in the loess of China. J Environ Manag 19:1093–1099
Kang S, Zhang L, Liang Y, Xiaotao H, Huanjie C, Binjie G (2002) Effects of limited irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 55:203–216
Karajeh F, Mukhamedjanov V, Vyshpolskiy F (2000) Using wastewater for agriculture, treated wastewater is being used to irrigate crops in Kazakhstan, making farmers happier and benefiting the environment. ICARDA Caravan 13,29
Khan IU, Muhammad JK, Naqib UK, Mohammad JK, Habib UR, Zarina B, Kalim U (2012) Wastewater impact on physiology, biomass and yield of canola (Brassica napus l.). Pak J Bot 44(2):781–785
Kiziloglu FM, Turan M, Sahin U, Kuslu Y, Dursun A (2008) Effects of untreated and treated wastewater irrigation on some chemical properties of cauliflower (Brassica olerecea L. var. botrytis) and red cabbage (Brassica olerecea L. var. rubra) grown on calcareous soil in Turkey. Agric Water Manag 95:716–724
Mapanda F, Mangwayana EN, Nyamangara J, Giller KE (2005) The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107:151–165
Mohammad JK, Jan MT, Mohammad D (2011) Heavy metal content of alfalfa irrigated with waste and tubewell water. Soil Environ 30(2):104–109
Mupangwa W, Twomlow S, Walker S (2012) Reduced tillage, mulching and rotational effects on maize (Zea mays L.), cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (Walp) L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. (Moench)) yields under semi-arid conditions. Field Crops Res 132(14):139–148
Rattan RK, Datta SP, Singh AK, Chhonkar PK, Suribabu K (2001) Effects of long-term application of sewage effluents on available nutrient and available water status in soils under Keshopur effluent irrigation scheme in Delhi. J. Water Manag 9(1–2):21–26
Rusan MJM, Hinnawi S, Rousam L (2007) Long-term effect of wastewater irrigation of forage crops on soil and plant quality parameters. Desalination 215(1–3):143–152
Saffari VR, Mahboub S (2012) Effect of treated municipal wastewater on bean growth, soil chemical properties, and chemical fractions of zinc and copper. Arab J Geosci 6:25–30
Tandon HLS (1999) Methods of analysis of soils, plants, waters and fertilizers. Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organization, New Delhi
Wang Y, Min Q, Yunxia L, Yongguan Z (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from wastewater irrigated area, Beijing–Tianjin city cluster, China. J Environ Sci 24(4):690–698
Yadar RK, Goyal R, Sharma RK, Dubey SK, Minchas RS (2002) Post irrigation impact of domestic sewage effluent on composition of soils, crops and ground water: a case study. J Environ Int 28(6):481–486
Zema DA, Giuseppe B, Serafina A, Santo MZ (2012) Irrigation of energy crops with urban wastewater: effects on biomass yields, soils and heating values. Agric Water Manag 115:55–65
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by Sultan Qaboos University through the project ‘Feasibility of Managed Aquifer Recharge Using Treated Wastewater in Oman (SR/AGR/SWAE/09/01).’
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Knox.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkhamisi, S.A., Ahmed, M., Al-Wardy, M. et al. Effect of reclaimed water irrigation on yield attributes and chemical composition of wheat (Triticum aestivum), cowpea (Vigna sinensis), and maize (Zea mays) in rotation. Irrig Sci 35, 87–98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-016-0522-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-016-0522-8