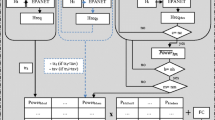
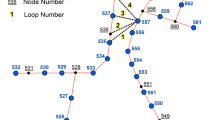
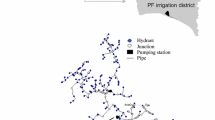
Abstract
Irrigation distribution systems are generally branched. They can be designed using optimization models that minimize the cost of the pipes under a number of constraints. Urban water distribution systems are generally designed as a series of interconnected closed loops which provide these systems with sufficient capability to overcome local physical failures . However, they enormously increase both the computational effort and the network cost. This research proposes an innovative approach where localized loops are used as a cost-effective solution to improve the performance of branched on-demand pressurized irrigation systems. The position of a localized loop is identified based on the overall performance improvement that can be achieved. This strategy, when necessary, also involves the increase in significantly smaller pipe diameters, where performance improvement cannot occur solely by introducing localized loops. The new approach was applied to an irrigation district in Southern Italy operating on demand. It demonstrated its effectiveness by improving the system’s overall hydraulic performance, while achieving more than 80 % cost savings, as compared to the classical rehabilitation approach. A dedicated software package that may serve, with further improvements, as a DSS platform, was developed and used to perform an accurate hydraulic performance analysis of the irrigation system.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alperovits E, Shamir U (1977) Design of optimal water distribution systems. Water Resour Res 13(6):885–900. doi:10.1029/WR013i006p00885
Alves Z, Muranho J, Albuquerque T, Ferreira A (2014) Water distribution network’s modeling and calibration. A case study based on scarce inventory data. Procedia Eng 70:31–40. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.02.005
Babayan A, Kapelan Z, Savic D, Walters G (2005) Least-cost design of water distribution networks under demand uncertainty. J Water Resour Plan Manag 131(5):375–382. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2005)131:5(375)
Baños R, Gil C, Reca J, Martínez J (2009a) Implementation of scatter search for multi-objective optimization: a comparative study. Comput Optim Appl 42(3):421–441. doi:10.1007/s10589-007-9121-1
Baños R, Gil C, Reca J, Ortega J (2009b) A Pareto-based memetic algorithm for optimization of looped water distribution systems. Eng Optim 42(3):223–240. doi:10.1080/03052150903110959
Baños R, Gil C, Reca J, Montoya FG (2010) A memetic algorithm applied to the design of water distribution networks. Appl Soft Comput 10(1):261–266. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2009.07.010
Čistý M (2010) Hybrid genetic algorithm and linear programming method for least-cost design of water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag 24(1):1–24. doi:10.1007/s11269-009-9434-1
Čistý M, Bajtek Z, Becová A (2014) Irrigation network design and reconstruction and its analysis by simulation model. Sel Sci Pap J Civil Eng. doi:10.2478/sspjce-2014-0001
da Conceição Cunha M, Ribeiro L (2004) Tabu search algorithms for water network optimization. Eur J Oper Res 157(3):746–758. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(03)00242-X
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2010a) Assessing pressure changes in an on-demand water distribution system on drip irrigation performance—case study in Italy. J Irrig Drain Eng 136(4):261–270. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000170
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2010b) On-demand pressurized water distribution system impacts on sprinkler network design and performance. Irrig Sci 28(4):331–339. doi:10.1007/s00271-009-0195-7
Estrada C, González C, Aliod R, Paño J (2009) Improved pressurized pipe network hydraulic solver for applications in irrigation systems. J Irrig Drain Eng 135(4):421–430. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000100
Farmani R, Walters G, Savic D (2005) Trade-off between total cost and reliability for Anytown water distribution network. J Water Resour Plan Manag 131(3):161–171. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2005)131:3(161)
Farmani R, Abadia R, Savic D (2007) Optimum design and management of pressurized branched irrigation networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 133(6):528–537. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:6(528)
Fujiwara O, Khang DB (1990) A two-phase decomposition method for optimal design of looped water distribution networks. Water Resour Res 26(4):539–549. doi:10.1029/WR026i004p00539
González Perea R, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2014) Critical points: interactions between on-farm irrigation systems and water distribution network. Irrig Sci 32(4):255–265. doi:10.1007/s00271-014-0428-2
González-Cebollada C, Macarulla B (2012) Comparative analysis of design methods of pressurized irrigation networks. Irrig Drain 61(1):1–9. doi:10.1002/ird.657
González-Cebollada C, Macarulla B, Sallán D (2011) Recursive design of pressurized branched irrigation networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 137(6):375–382. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000308
Hashimoto T (1980) Robustness, reliability, resiliency and vulnerability. Criteria for planning water resources system. PhD dissertation, Cornell University, USA
Hashimoto T, Stedinger JR, Loucks DP (1982) Reliability, resiliency, and vulnerability criteria for water resource system performance evaluation. Water Resour Res 18(1):14–20. doi:10.1029/WR018i001p00014
Jayaram N, Srinivasan K (2008) Performance-based optimal design and rehabilitation of water distribution networks using life cycle costing. Water Resour Res 44(1):W01417. doi:10.1029/2006WR005316
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2006) A simulation model to generate the demand hydrographs in large-scale irrigation systems. Biosyst Eng 93(3):335–346. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.12.006
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2010) Development of a decision support system for irrigation systems analysis. Water Resour Manag 24(12):3279–3297. doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9606-z
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N, Inoubli N (2013) Optimization of on demand pressurized irrigation networks and on-farm constraints. Procedia Environ Sci 19:942–954. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2013.06.104
Labye Y, Olson MA, Galand A, Tsiourtis N (1988) Design and optimization of irrigation distribution networks. FAO irrigation and drainage paper, vol 44. FAO, Rome
Lamaddalena N (1997) Integrated simulation modeling for design and performance analysis of on-demand pressurized irrigation systems. PhD thesis, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Lisboa
Lamaddalena N, Sagardoy JA (2000) Performance analysis of on-demand pressurized irrigation systems. FAO irrigation and drainage paper, vol 59. FAO, Rome
Lamaddalena N, Khadra R, Tlili Y (2012) Reliability-based pipe size computation of on-demand irrigation systems. Water Resour Manag 26(2):307–328. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9919-6
Lansey K, Duan N, Mays L, Tung Y (1989) Water distribution system design under uncertainties. J Water Resour Plan Manag 115(5):630–645. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1989)115:5(630)
Lejano RP (2006) Optimizing the layout and design of branched pipeline water distribution systems. Irrig Drain Syst 20(1):125–137. doi:10.1007/s10795-006-3140-4
Malossi D, Santovito L (1975) Progetto esecutivo dell’adduttore e della rete irrigua a servizio della zona bassa del comprensorio in Sinistra Ofanto—Relazione generale. [Executive project of the conveyance line and the distribution network of the low zone of the Sinistra Ofanto irrigation scheme—General report]
Muranho J, Ferreira A, Sousa J, Gomes A, Marques AS (2014) Pressure-dependent demand and leakage modelling with an EPANET extension—WaterNetGen. Procedia Eng 89:632–639. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.488
Murphy LJ, Dandy GC, Simpson AR, Gransbury JC (1998) Optimisation of irrigation infrastructure rehabilitation using genetic algorithms. Paper presented at the national conference, Irrigation Association of Australia, Brisbane, Australia
Olsson RJ, Kapelan Z, Savic DA (2009) Probabilistic building block identification for the optimal design and rehabilitation of water distribution systems. J Hydroinf 11(2):89–105. doi:10.2166/hydro.2009.047
Planells Alandí P, Ortega Álvarez JF, Tarjuelo Martín-Benito JM (2007) Optimization of irrigation water distribution networks, layout included. Agric Water Manag 88(1–3):110–118. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2006.10.004
Reca J, Martínez J (2006) Genetic algorithms for the design of looped irrigation water distribution networks. Water Resour Res 42(5):W05416. doi:10.1029/2005WR004383
Reca J, Martínez J, Baños R, Gil C (2008) Optimal design of gravity-fed looped water distribution networks considering the resilience index. J Water Resour Plan Manag 134(3):234–238. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2008)134:3(234)
Renault D (1999) Modernization of irrigation systems: a continuing process. In: FAO (ed) Modernization of irrigation system operations. Proceedings of the fifth international ITIS (information techniques for irrigation systems) network meeting, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India, 28–30 October 1998, pp 7–12
Rezaei G, Afshar MH, Rohani M (2014) Layout optimization of looped networks by constrained ant colony optimisation algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 70:123–133. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2014.01.009
Rossman LA (2000) EPANET 2 users manual. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati
Savic D, Walters G (1997) Genetic algorithms for least-cost design of water distribution networks. J Water Resour Plan Manag 123(2):67–77. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1997)123:2(67)
Simpson A, Dandy G, Murphy L (1994) genetic algorithms compared to other techniques for pipe optimization. J Water Resour Plan Manag 120(4):423–443. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1994)120:4(423)
Todini E (2000) Looped water distribution networks design using a resilience index based heuristic approach. Urban Water 2(2):115–122. doi:10.1016/S1462-0758(00)00049-2
van Zyl J, Savic D, Walters G (2004) Operational optimization of water distribution systems using a hybrid genetic algorithm. J Water Resour Plan Manag 130(2):160–170. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2004)130:2(160)
Walski TM, Chase DV, Savic DA, Grayman W, Beckwith S, Koelle E (2003) Advanced water distribution modeling and management, 1st edn. Haestad Methods Inc, Waterbury
Wu W, Maier HR, Simpson AR (2013) Multiobjective optimization of water distribution systems accounting for economic cost, hydraulic reliability, and greenhouse gas emissions. Water Resour Res 49(3):1211–1225. doi:10.1002/wrcr.20120
WWAP (2012) The United Nations world water development report 4: managing water under uncertainty and risk, vol 1. UNESCO, Paris
Xu C, Goulter I (1999) Reliability-based optimal design of water distribution networks. J Water Resour Plan Manag 125(6):352–362. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1999)125:6(352)
Yoo DG, Lee HM, Sadollah A, Kim JH (2014) Optimal pipe size design for looped irrigation water supply system using harmony search: Saemangeum project area. Sci World J Article ID 651763 (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Merkley.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamaddalena, N., Khadra, R. & Fouial, A. Use of localized loops for the rehabilitation of on-demand pressurized irrigation distribution systems. Irrig Sci 33, 453–468 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-015-0481-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-015-0481-5