Abstract
Purpose
To present our experience of the patterns of revascularisation of the prostate and efficacy of repeat prostate artery embolisation (rPAE) in patients with recurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms.
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively analysed 12 patients who underwent rPAE at a single centre between November 2015 and March 2020. The patients had their intraprocedural angiography and cone beam CT images as well as their pre-procedural CT retrospectively reviewed to establish the patterns of revascularisation. Clinical follow-up occurred at a minimum of 3 months.
Results
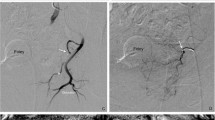
11/12 patients (91.6%) had significant international prostate symptom score (IPSS) reduction following rPAE with change in mean IPSS from 18.4 to 8.1 at 3 months (p < 0.0001). Mean prostate volume was reduced by 41.6% (p = 0.03). 8/12 (75%) had a complete clinical success. 20/24 hemiprostates demonstrated revascularisation angiographically, of which 16 (80%) had prostatic arterial supply at rPAE by the main prostatic artery. Other mechanisms of revascularisation included supply from capsular prostatic artery branches and supply from other internal iliac pelvic branches. Unilateral embolisation at rPAE, where bilateral embolisation was not feasible (4/12), resulted in no difference in clinical outcomes compared with bilateral rPAE (p = 0.55).
Conclusion
We have found rPAE to be an effective treatment for recurrent lower urinary tract symptoms in patients who had good clinical response to initial PAE. The mechanisms of revascularisation are variable, but most patients that underwent rPAE had recanalisation of their main prostatic artery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao Y, Huang Y, Zhang R, Yang Y, Zhang Q, Hou M, et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: prostatic arterial embolization versus transurethral resection of the prostate—a prospective, randomized, and controlled clinical trial. Radiology. 2013;270:920–8.
Carnevale FC, Iscaife A, Yoshinaga EM, Moreira AM, Antunes AA, Srougi M. Transurethral resection of the prostate (turp) versus original and perfected prostate artery embolization (pae) due to benign prostatic hyperplasia (bph): preliminary results of a single center, prospective urodynamic-controlled analysis. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2016;39:44–52.
Abt D, Hechelhammer L, Müllhaupt G, Markart S, Güsewell S, Kessler TM, et al. Comparison of prostatic artery embolisation (PAE) versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) for benign prostatic hyperplasia: randomised, open label, non-inferiority trial. BMJ. 2018;361:k2338.
Insausti I, Sáez de Ocáriz A, Galbete A, Capdevila F, Solchaga S, Giral P, et al. Randomized comparison of prostatic artery embolization versus transurethral resection of the prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31:882–90.
Zhu C, Lin W, Huang Z, Cai J. Prostate artery embolization and transurethral resection of prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Chin J Interv Imaging Ther. 2018;15:134–8.
Pisco JM, Bilhim T, Costa NV, Torres D, Pisco J, Pinheiro LC, et al. Randomised clinical trial of prostatic artery embolisation versus a sham procedure for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2020;77:354–62.
Shim SR, Kanhai KJ, Ko YM, Kim JH. Efficacy and safety of prostatic arterial embolization: systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Urol. 2017;197:465–79.
Xu XJ, Li J, Huang XZ, Liu Q. An updated meta-analysis of prostatic arterial embolization versus transurethral resection of the prostate in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-03044-7.
National institute for health and care excellence. Prostate artery embolisation for lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. Interventional procedures guidance [IPG611] [Internet]. 2020; Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg611.
McWilliams JP, Bilhim TA, Carnevale FC, Bhatia S, Isaacson AJ, Bagla S, et al. Society of Interventional radiology multisociety consensus position statement on prostatic artery embolization for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia: from the society of interventional radiology, the cardiovascular and interventional radiological society of Europe, Société Française de Radiologie, and the British society of interventional radiology: endorsed by the Asia Pacific Society of cardiovascular and interventional radiology, Canadian association for interventional radiology, Chinese college of interventionalists, interventional radiology society of Australasia, Japanese society of interventional radiology, and Korean society of interventional radiology. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30(627–637):e1.
Carnevale FC, Moreira AM, Harward SH, Bhatia S, de Assis AM, Srougi M, et al. Recurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms following prostate artery embolization for benign hyperplasia: single center experience comparing two techniques. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2017;40:366–74.
Grosso M, Balderi A, Arnò M, Sortino D, Antonietti A, Pedrazzini F, et al. Prostatic artery embolization in benign prostatic hyperplasia: preliminary results in 13 patients. Radiol Med. 2015;120:361–8.
Ray AF, Powell J, Speakman MJ, Longford NT, DasGupta R, Bryant T, et al. Efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: an observational study and propensity-matched comparison with transurethral resection of the prostate (the UK-ROPE study). BJU Int. 2018;122:270–82.
Maclean D, Harris M, Long J, Modi S, Bryant TJ, Hacking N. The first 48 consecutive patients with 3-year symptom score follow-up post-prostate artery embolization (PAE) at a single-centre university hospital. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2020;43:459–65.
Monreal R, Robles C, Sánchez-Casado M, Ciampi JJ, López-Guerrero M, Ruíz-Salmerón RJ, et al. Embolisation of prostate arteries in benign prostatic hyperplasia in non-surgical patients. Radiol Engl Ed. 2020;62:205–12.
Rampoldi A, Barbosa F, Secco S, Migliorisi C, Galfano A, Prestini G, et al. Prostatic artery embolization as an alternative to indwelling bladder catheterization to manage benign prostatic hyperplasia in poor surgical candidates. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2017;40:530–6.
Pisco JM, Bilhim T, Pinheiro LC, Fernandes L, Pereira J, Costa NV, et al. Medium- and long-term outcome of prostate artery embolization for patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: results in 630 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27:1115–22.
Kenny AG, Pellerin O, Moussa N, Del Giudice C, Déan C, Sapoval M. Repeat prostatic artery embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31(1090–1095):e1.
de Assis AM, Moreira AM, Carnevale FC. Angiographic findings during repeat prostatic artery embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:645–51.
Costa NV, Torres D, Pisco J, Pinheiro LC, Martins FE, Oliveira AG, et al. Repeat prostatic artery embolization for patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31:1272–80.
Cornelis FH, Bilhim T, Hacking N, Sapoval M, Tapping CR, Carnevale FC. CIRSE standards of practice on prostatic artery embolisation. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2020;43:176–85.
Bilhim T, Pisco JM, Rio Tinto H, Fernandes L, Pinheiro LC, Furtado A, et al. Prostatic arterial supply: anatomic and imaging findings relevant for selective arterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23:1403–15.
Uflacker AB, Haskal ZJ, Baerlocher MO, Bhatia SS, Carnevale FC, Dariushnia SR, et al. Society of interventional radiology research reporting standards for prostatic artery embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;31(891–898):e1.
Bilhim T. Prostatic artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a 10-year update. Endovasc Today. 2020;19:40–4.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
CRT has received research grants and consultancy fees from Boston Scientific and Merit Medical.
Ethical Approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kearns, D.J., Boardman, P. & Tapping, C.R. Patterns of Reperfusion and Clinical Findings in Repeat Prostate Artery Embolisation for Recurrent Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44, 95–101 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02671-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02671-7