Abstract
Introduction
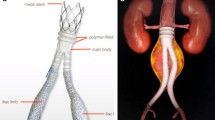
The use of and results with the Endurant stent-graft have been reported extensively. However, there has been little if any focus placed on performance and outcomes when a 36-mm-diameter device is used.
Methods
Data were collected and retrospectively analyzed on EVAR patients treated with a 36-mm-diameter Endurant device at 3 European academic vascular centers between 2007 and 2015. Primary endpoints were the absence of type Ia endoleak in the early and mid-term follow-up period, and aneurysm sac stabilization or shrinkage. Secondary endpoints were 30-day mortality, overall survival and secondary interventions. Subgroup analysis of outcomes in the on-label (ONL) versus off-label (OFL) device use cohorts was also performed.
Results
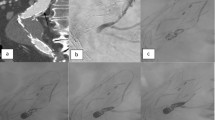
Seventy-three patients were included in the study. Mean follow-up was 30.1 ± 16.2 months. Mean aortic neck diameter was 29.5 ± 1.9. Primary technical success was achieved in 69 patients (94.5%). Five patients (6.8%) were found to have developed a type Ia endoleak, 3 during the first month, and the other 2 at 2 years. Overall EVAR-related mortality was 4.1% (n = 3). Subgroup analysis focused on the OFL cohort (n = 44) versus the ONL patients (n = 29). Two of the OFL patients (4.5%) had a type Ia endoleak, and 3 (10.3%) in the ONL group.
Conclusion
The use of the largest diameter Endurant stent-graft device emerges as a reasonable option for EVAR treatment of AAA featuring a large-diameter proximal neck. Assessment of a larger group of patients followed in the long term will be necessary for a more definitive statement on such strategy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prinssen M, Verhoeven EL, Buth J, Cuypers PW, van Sambeek MR, Balm R, et al. A randomized trial comparing conventional and endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1607–18.
Sachs T, Schermerhorn M, Pomposelli F, Cotterill P, O’Malley J, Landon B. Resident and fellow experiences after the introduction of endovascular aneurysm repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:881–8.
Zandvoort HJ, Gonçalves FB, Verhagen HJ, Werson DA, Moll FL, de Vries JP, van Herwaarden JA. Results of endovascular repair of infrarenal aortic aneurysms using the Endurant stent graft. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59(5):1195–202. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.031 Epub 2014 Jan 14.
Böckler D, Riambau V, Fitridge R, Wolf Y, Hayes P, Silveira P, Numan F, Engage Investigators. Worldwide experience with the Endurant Stent graft: review of the literature. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2011;52(5):669–81 Epub 2011 Jul 28.
Bisdas T, Weiss K, Eisenack M, Austermann M, Torsello G, Donas KP. Durability of the Endurant stent graft in patients undergoing endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60(5):1125–31. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.04.070 Epub 2014 Jun 26.
Torsello G, Troisi N, Donas KP, Austermann M. Evaluation of the Endurant stent graft under instructions for use vs off-label conditions for endovascular aorticaneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(2):300–6. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.12.062 Epub 2011 Mar 11.
Troisi N, Torsello G, Weiss K, Donas KP, Michelagnoli S, Austermann M. Midterm results of endovascular aneurysm repair using the Endurant stent-graft according to the instructions for use vs. off-label conditions. J Endovasc Ther. 2014;21(6):841–7. doi:10.1583/14-4795MR.1.
Matsagkas M, Kouvelos G, Peroulis M, Avgos S, Arnaoutoglou E, Papa N, Papadopoulos G. Standard endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms in patients with very short proximal necks using the Endurant stent graft. J Vasc Surg. 2015;61(1):9–15. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.07.002 Epub 2014 Aug 8.
Kaladji A, Steintmetz E, Gouëffic Y, Bartoli M, Cardon A, Academic Association for Surgical Research (AURC). Long-term results of large stent grafts to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015;29(7):1416–25. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2015.04.088 Epub 2015 Jul 10.
Pitoulias GA, Donas KP, Schulte S, Aslanidou EA, Papadimitriou DK. Two-dimensional versus three-dimensional CT angiography in analysis of anatomical suitability for stentgraft repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Acta Radiol. 2011;52:317–23.
Schanzer A, Greenberg RK, Hevelone N, et al. Predictors of abdominal aortic aneurysm sac enlargement after endovas- cular repair. Circulation. 2011;123:2848e55.
Kaladji A, Cardon A, Laviolle B, et al. Evolution of the upper and lower landing site after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:24e32.
Reyes A, Donas K, Pitoulias G, Austermann M, Gandarias C, Torsello G. Complementary role of fenestrated/branched endografting and the chimney technique in the treatment of pararenal aneurysms after open abdominal aortic repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2016;23(4):599–605. doi:10.1177/1526602816647363.
Aburahma AF, Campbell JE, Mousa AY, et al. Clinical outcomes for hostile versus favorable aortic neck anatomy in endovascular aortic aneurysm repair using modular devices. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:13e21.
Georgiadis GS, Trellopoulos G, Antoniou GA, et al. Early results of the Endurant endograft system in patients with friendly and hostile infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm anatomy. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:61627.
Goodman M, Lawrence-Brown MM, Hartley D, Allen YB, Semmens JB. Treatment of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms with oversized (36-mm) Zenith endografts. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):23–9.
Corriere MA, Islam A, Craven TE, Conlee TD, Hurie JB, Edwards MS. Influence of computed tomography angiography reconstruction software on anatomic measurements and endograft component selection for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59(5):1224–1231. e1–3. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2013.11.003 Epub 2014 Jan 16.
Oliveira NF, Bastos Gonçalves FM, Van Rijn MJ, de Ruiter Q, Hoeks S, de Vries JP, et al. Standard endovascular aneurysm repair in patients with wide infrarenal aneurysm necks is associated with increased risk of adverse events. J Vasc Surg. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.09.052.
van Keulen JW, Moll FL, van Herwaarden JA. Tips and techniques for optimal stent graft placement in angulated aneurysm necks. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52(4):1081–6. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.02.024 Epub 2010 May 15.
van Prehn J, Schlösser FJ, Muhs BE, Verhagen HJ, Moll FL, van Herwaarden JA. Oversizing of aortic stent grafts for abdominal aneurysm repair: a systematic review of the benefits and risks. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009;38(1):42–53.
Gonthier C, Deglise S, Brizzi V, Ducasse E, Midy D, Lachat M, Berard X. Hemodynamic conditions may influence the oversizing of stent grafts and the postoperative surveillance of patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm treated by EVAR. Ann Vasc Surg. 2016;30:308. e5–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reyes Valdivia, A., Pitoulias, G., Criado, F.J. et al. Multicenter European Registry for Patients with AAA Undergoing EVAR Evaluating the Performance of the 36-mm-Diameter Endurant Stent-Graft. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40, 1514–1521 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1665-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1665-6