Abstract
Purpose
This multicenter prospective study was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for painful osteoid osteoma (OO).
Materials and Methods
Patients with OO (femur: n = 17, tibia: n = 2, humerus: n = 1, rib: n = 1) were enrolled and treated with RFA. In phase I, nine patients were evaluated for safety. In phase II, 12 patients were accrued, and an intent-to-treat analysis was performed on all patients. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the treatment safety. The secondary endpoint was to evaluate the efficacy for pain relief by the visual analogue scale (VAS) at 4 weeks after RFA. Treatment efficacy was classified as significantly effective (SE) when VAS score decreased by ≥5 or score was <2, moderately effective when VAS score decreased by <5–≥2 and score was ≥2, and not effective (NE) when VAS score decreased by <2 or score was increased. Cases where the need for analgesics increased after treatment were also NE.
Results
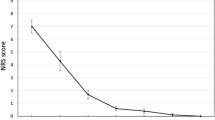
RFA procedures were completed in all patients. Minor adverse effects (AEs) were observed as 4.8–14.3 % in 12 patients, and no major AEs were observed. Mean VAS score was 7.1 before treatment, 1.6 at 1 week, 0.3 at 4 weeks, and 0.2 at 3 months. All procedures were classified as SE. Pain recurrence was not noted in any patient during follow-up (mean: 15.1 months).
Conclusion
RFA is a safe, highly effective, and fast-acting treatment for painful extraspinal OO. Future studies with a greater number of patients are needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehara S, Rosenthal DI, Aoki J, Fukuda K, Sugimoto H, Mizutani H, et al. Peritumoral edema in osteoid osteoma on magnetic resonance imaging. Skelet Radiol. 1999;28(5):265–70.
Assoun J, Richardi G, Railhac JJ, Baunin C, Fajadet P, Giron J, et al. Osteoid osteoma: MR imaging versus CT. Radiology. 1994;191(1):217–23.
Kransdorf MJ, Stull MA, Gilkey FW, Moser RP Jr. Osteoid osteoma. Radiographics. 1991;11(4):671–96.
Helms CA, Hattner RS, Vogler JB. Osteoid osteoma: radionuclide diagnosis. Radiology. 1984;151(3):779–84.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Wolfe MW, Jennings LC, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(6):815–21.
Rosenthal DI, Alexander A, Rosenberg AE, Springfield D. Ablation of osteoid osteomas with a percutaneously placed electrode: a new procedure. Radiology. 1992;183(1):29–33.
Miyazaki M, Aoki J, Miyazaki A, Nakajima T, Koyama Y, Shinozaki T, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma using cool-tip electrodes without the cooling system. Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29(2):138–43.
Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Kubisch CH, Trumm CG, Weber C, Duerr HR, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma-5-year experience. Eur J Radiol. 2009;73:374–9.
Cioni R, Armillotta N, Bargellini I, Zampa V, Cappelli C, Vagli P, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2004;14(7):1203–8.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Torriani M, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy. Radiology. 2003;229(1):171–5.
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR, Bloem JL. Osteoid osteoma: clinical results with thermocoagulation. Radiology. 2002;224(1):82–6.
Woertler K, Vestring T, Boettner F, Winkelmann W, Heindel W, Lindner N. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and follow-up in 47 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12(6):717–22.
Kobayashi T, Arai Y, Takeuchi Y, Nakajima Y, Shioyama Y, Sone M, et al. Phase I/II clinical study of percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) as palliation for painful malignant vertebral compression fractures (PMVCF): JIVROSG-0202. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(12):1943–7.
Cribb GL, Goude WH, Cool P, Tins B, Cassar-Pullicino VN, Mangham DC. Percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation of osteoid osteomas: factors affecting therapeutic outcome. Skelet Radiol. 2005;34(11):702–6.
Sung KS, Seo JG, Shim JS, Lee YS. Computed-tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermoablation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma-2–5 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2009;33(1):215–8.
Peyser A, Applbaum Y, Khoury A, Liebergall M, Atesok K. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided radiofrequency ablation using a water-cooled probe. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(2):591–6.
Kjar RA, Powell GJ, Schilcht SM, Smith PJ, Slavin J, Choong PF. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteoma: experience with a new treatment. Med J Aust. 2006;184(11):563–5.
Rimondi E, Bianchi G, Malaguti MC, Ciminari R, Del Baldo A, Mercuri M, et al. Radiofrequency thermoablation of primary non-spinal osteoid osteoma: optimization of the procedure. Eur Radiol. 2005;15(7):1393–9.
Martel J, Bueno A, Ortiz E. Percutaneous radiofrequency treatment of osteoid osteoma using cool-tip electrodes. Eur J Radiol. 2005;56(3):403–8.
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR, van den Berg-Huysmans AA, Bloem JL. Osteoid osteoma: factors for increased risk of unsuccessful thermal coagulation. Radiology. 2004;233(3):757–62.
Cantwell CP, O’Byrne J, Eustace S. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma with cooled probes and impedance-control energy delivery. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(5 Suppl):S244–8.
Martel J, Bueno A, Nieto-Morales ML, Ortiz EJ. Osteoid osteoma of the spine: CT-guided monopolar radiofrequency ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2008;71(3):564–9.
Sutphen SA, Murakami JW. Radiofrequency ablation of a cervical osteoid osteoma: a trans-thyroid approach. Pediatr Radiol. 2007;37(1):83–5.
Cristante AF, Barros Filho T, Oliveira RP, Barbarini AF, Teixeira WG. Treatment of osteoid osteoma in the vertebral body of the lumbar spine by radiofrequency ablation. Clinics. 2007;62(6):791–4.
Funding
This study was funded by a Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant (Number 01901625) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, M., Arai, Y., Myoui, A. et al. Phase I/II Multi-Institutional Study of Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation for Painful Osteoid Osteoma (JIVROSG-0704). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 1464–1470 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1438-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1438-7