Abstract
Introduction
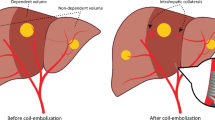
In planning Yttrium-90 (90Y)-radioembolizations, strategy problems arise in tumours with multiple arterial supplies. We aim to demonstrate that tumours can be treated via one main feeding artery achieving flow redistribution by embolizing accessory vessels.
Methods
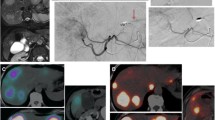
One hundred 90Y-radioembolizations were performed on 90 patients using glass microspheres. In 19 lesions/17 patients, accessory branches were found feeding a minor tumour portion and embolized. In all 17 patients, the assessment of the complete perfusion was obtained by angiography and single photon emission computerized tomography–computerized tomography (SPECT–CT). Dosimetry, toxicity, and tumor response rate of the patients treated after flow redistribution were compared with the 83 standard-treated patients. Seventeen lesions in 15 patients with flow redistribution were chosen as target lesions and evaluated according to mRECIST criteria.
Results
In all patients, the complete tumor perfusion was assessed immediately before radioembolization by angiography in all patients and after the 90Y-infusion by SPECT–CT in 15 of 17 patients. In the 15 assessable patients, the response rate in their 17 lesions was 3 CR, 8 PR, and 6 SD. Dosimetric and toxicity data, as well tumour response rate, were comparable with the 83 patients with regular vasculature.
Conclusions
All embolization procedures were performed successfully with no complications, and the flow redistribution was obtained in all cases. Results in term of toxicity, median dose administered, and radiological response were comparable with standard radioembolizations. Our findings confirmed the intratumoral flow redistribution after embolizing the accessory arteries, which makes it possible to treat the tumour through its single main feeding artery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geschwind JF, Salem R, Carr BI et al (2004) Yttrium-90 microspheres for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 127:S194–S205
Carr BI (2004) Hepatic arterial 90-yttrium glass microspheres (TheraSphere) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: interim safety and survival data on 65 patients. Liver Transplant 10:S107–S110
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Atassi B et al (2005) Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with use of 90Y microspheres (TheraSphere): safety, tumor response, and survival. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:1627–1639
Hilgard P, Hamami M, Fouly AE et al (2010) Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 glass microspheres in hepatocellular carcinoma: European experience on safety and long-term survival. Hepatology 52(5):1741–1749
Mazzaferro V, Sposito C, Bhoori S et al (2013) Yttrium (90) radioembolization for intermediate-advanced hepatocarcinoma: a phase II study. Hepatology 57(5):1826–1837
Ibrahim SM, Lewandowski RJ, Sato KT et al (2008) Radioembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a clinical review. World J Gastroenterol 14:1664–1669
Young JY, Rhee TK, Atassi B et al (2007) Radiation dose limits and liver toxicities resulting from multiple Yttrium-90 radioembolization treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1375–1382
Riaz A, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik LM et al (2009) Complications following radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres: a comprehensive literature review. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(9):1121–1130
Kennedy A, Nag S, Salem R et al (2007) Recommendations for radio-embolization of hepatic malignancies using yttrium-90 microsphere brachytherapy: a consensus panel report from the Radio-embolization Brachytherapy Oncology Consortium (REBOC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:13–23
Abdelmaksoud MH, Louie JD, Kothary N et al (2011) Embolization of parasitized extrahepatic arteries to re-establish intrahepatic arterial supply to tumors before yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22(10):1355–1362
Abdelmaksoud MH, Louie JD, Kothary N et al (2011) Consolidation of hepatic arterial inflow by embolization of variant hepatic arteries in preparation for yttrium-90 radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22(10):1364–1371
Bilbao JI, Garrastachu P, Maria J, Herraiz MJ et al (2010) Safety and efficacy assessment of flow redistribution by occlusion of intrahepatic vessels prior to radioembolization in the treatment of liver tumors. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 33(3):523–531
Lencioni R, Llovet JM (2010) Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 30(1):52–60
National Cancer Institute (29 May 2009) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.0 NCI, NIH, DHHS. NIH publication number 09-7473
Chiesa C, Maccauro M, Romito R, Spreafico C et al (2011) Need, feasibility and convenience of dosimetric treatment planning in liver selective internal radiation therapy with 90Y microspheres: the experience of National Cancer Institute of Milan. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 55:168–197
Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik L et al (2011) Radioembolization results in longer time-to-progression and reduced toxicity compared with chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 140(2):497–507
Chiesa C, Mira M, Maccauro M, Romito R, Spreafico C, Sposito C, Bhoori S, Morosi C, Pellizzari S, Negri A, Civelli E, Lanocita R, Camerini T, Bampo C, Carrara M, Seregni E, Marchianò A, Mazzaferro V, Bombardieri E (2012) A dosimetric treatment planning strategy in radioembolization of hepatocarcinoma with 90Y glass microspheres. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 56(6):503–508
Sebastian AJ, Szyszko T, Al-Nahhas A, Nijran K, Tait NP (2008) Evaluation of hepatic angiography procedures and Bremsstrahlung imaging in selective internal radiation therapy: a two-year single-center experience. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31:643–649
Redman HC, Reuter SR (1970) Arterial collaterals in the liver hilus. Radiology 94:575–579
Chuang VP, Wallace S (1980) Hepatic arterial redistribution for intraarterial infusion of hepatic neoplasms. Radiology 135:295–299
Charnsangavej C, Chuang VP, Wallace S, Soo CS, Bowers T (1982) Angiographic classification of hepatic arterial collaterals. Radiology 144:485–494
Arai Y, Yakeuchi Y, Inaba Y et al (2007) Percutaneous catheter placement for hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 10:30–37
Ganeshan A, Upponi S, Hon LQ, Warakaulle D, Uberoi R (2008) Arterial infusion of chemotherapy: the role of diagnostic and interventional radiology. Ann Oncol 19:847–851
Tanaka T, Arai Y, Inaba Y et al (2003) Radiologic placement of side-hole catheter with tip fixation for hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:63–68
Cho A, Gunji H, Koike N et al (2007) Intersegmental arterial communication between the medial and left lateral segments of the liver. Dig Surg 24:328–330
Gunji H, Cho A, Tohma T et al (2006) The blood supply of the hilar bile duct and its relationship to the communicating arcade located between the right and left hepatic arteries. Am J Surg 192:276–280
Tohma T, Cho A, Okazumi S et al (2005) Communicating arcade between the right and left hepatic arteries: evaluation with CT and angiography during temporary balloon occlusion of the right or left hepatic artery. Radiology 237:361–365
Miyazaki M, Ito H, Nkagawa K et al (2000) Unilateral hepatic artery reconstruction is unnecessary in biliary tract carcinomas involving lobar hepatic artery: implications of interlobar hepatic artery and its preservation. Hepatogastroenterology 47:1526–1530
Sone M, Kato K, Hirose A et al (2008) Impact of multislice CT angiography of radiological catheter placement for hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31:91–97
Wallace MJ, Murthy R, Kammat PP et al (2007) Impact of C-arm CT on hepatic arterial interventions for hepatic malignancies. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:1500–1507
Conflict of interest
Carlo Spreafico, Carlo Morosi, Marco Maccauro, Raffaele Romito, Rodolfo Lanocita, Enrico M. Civelli, Carlo Sposito, Sherrie Bhoori, Carlo Chiesa Ph, Laura F. Frigerio, Alice Lorenzoni, Tommaso Cascella, Alfonso Marchianò and Vincenzo Mazzaferro have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spreafico, C., Morosi, C., Maccauro, M. et al. Intrahepatic Flow Redistribution in Patients Treated with Radioembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 322–328 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0921-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0921-2