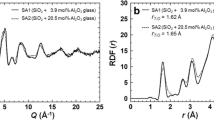
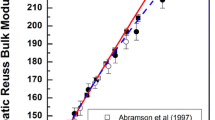
Abstract
Hydrous basalt glasses with water contents of 0–6.82% were synthesized using a multi-anvil press at 1.0–2.0 GPa and 1200–1400 °C. The starting materials were natural Mesozoic basalts from the eastern North China Craton (NCC). Their sound velocities and elastic properties were measured by Brillouin scattering spectroscopy. The longitudinal (V P) and shear (V S) wave velocities decreased with increasing water content. Increasing the synthesis pressure resulted in the glass becoming denser, and finally led to an increase in V P. As the degree of depolymerization increased, the V P, V S, and shear and bulk moduli of the hydrous basalt glasses decreased, whereas the adiabatic compressibility increased. The partial molar volumes of water (\(\nu\)) under ambient conditions were independent of composition, having values of 11.6 ± 0.8, 10.9 ± 0.6 and 11.5 ± 0.5 cm3/mol for the FX (Feixian), FW (Fuxin), and SHT (Sihetun) basalt glasses, respectively. However, the \({{V}_{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}}}\) values measured at elevated temperatures and pressures are increasing with increasing temperature or decreasing pressure. The contrasting densities of these hydrous basalt melts with those previously reported for mid-ocean ridge basalt and preliminary reference Earth model data indicate that hydrous basalt melts may not maintain gravitational stability at the base of the upper mantle.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agee CB (1998) Crystal-liquid density inversions in terrestrial and lunar magmas. Phys Earth Planet Inter 107:63–74
Armstrong J (1989) CITZAF: combined ZAF and phi-rho (Z) electron beam correction programs. California Institute of Technology, Pasadena
Bercovici D, Karato, S-i (2003) Whole-mantle convection and the transition-zone water filter. Nature 425(6953):39–44
Bouhifd AM, Whittington A, Richet P (2001) Partial molar volume of water in phonolitic glasses and liquids. Contrib Mineral Petrol 142(2):235–243
Chopelas A, Boehler R (1989) Thermal expansion measurements at very high pressure, systematics, and a case for a chemically homogeneous mantle. Geophys Res Lett 16(11):1347–1350
Fan W and Menzies M (1992) Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and accretion of asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China. Geotecton et Metallog 16:171–180
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Carlson RW, McDonough WF, Liu Y-S (2002) Re–Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 198:307–322
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Xu W-L, Yuan H-L, Liu Y-S, Walker RJ, Puchtel IS, Liu X, Huang H, Wang X-R (2008) Recycling deep cratonic lithosphere and generation of intraplate magmatism in the North China Craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 270:41–53
Guillermet AF (1986) The pressure dependence of the expansivity and of the Anderson–Grüneisen parameter in the Murnaghan approximation. J Phys Chem Solids 47:605–607
Hirschmann MM (2006) Water, melting, and the deep Earth H2O cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 34:629–653
Ihinger PD, Zhang Y, Stolper EM (1999) The speciation of dissolved water in rhyolitic melt. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:3567–3578
Karato SI (1995) Effects of water on seismic wave velocities in the upper mantle. Proceedings of the Japan Academy. Ser B Phys Biol Sci 71(2):61–66
Karato SI, Jung H (1998) Water, partial melting and the origin of the seismic low velocity and high attenuation zone in the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 157(3–4):193–207
Kawamoto T, Holloway JR (1997) Melting temperature and partial melt chemistry of H2O-saturated mantle peridotite to 11 gigapascals. Science 276(5310):240–243
Lee SK, Yi YS, Cody GD, Mibe K, Fei Y, Mysen BO (2011) Effect of network polymerization on the pressure-induced structural changes in sodium aluminosilicate glasses and melts: 27Al and 17O solid-state NMR study. J Phys Chem C 116(3):2183–2191
Litasov K, Ohtani E (2002) Phase relations and melt compositions in CMAS–pyrolite–H2O system up to 25 GPa. Phys Earth Planet Inter 134(1):105–127
Liu DY, Nutman AP, Compston W, Wu JS, Shen QH (1992) Remmants of ≥ 3800 Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology 20:339–342
Malfait WJ, Xue X (2010) The nature of hydroxyl groups in aluminosilicate glasses: Quantifying Si–OH and Al–OH abundances along the SiO2–NaAlSiO4 join by 1H, 27Al–1H and 29Si-1H NMR spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:719–737
Malfait WJ, Sanchez-Valle C, Ardia P, Medard E, Lerch P (2011) Amorphous materials: properties, structure, and durability: compositional dependent compressibility of dissolved water in silicate glasses. Am Mineral 96:1402–1409
Malfait WJ, Seifert R, Petitgirard S, Mezouar M, Sanchez-Valle C (2014a) The density of andesitic melts and the compressibility of dissolved water in silicate melts at crustal and upper mantle conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 393:31–38
Malfait WJ, Seifert R, Petitgirard S, Perrillat J P, Mezouar M, Ota T, Sanchez-Valle C (2014b) Melt buoyancy in large silicic magma chambers as a viable trigger of supervolcano eruptions. Nat Geosci 7:122–125
Manghnani MH, Williams Q, Dingwell DB (2013) A high-temperature Brillouin scattering study on four compositions of haplogranitic glasses and melts: high-frequency elastic behavior through the glass transition. Am Mineral 98:367–375
Matsukage KN, Jing Z, Karato S-i (2005) Density of hydrous silicate melt at the conditions of Earth’s deep upper mantle. Nature 438:488–491
Menzies MA, Fan WM, Zhang M (1993) Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. In: Prichard HM, Alabaster T, Harris NBW (eds.) Magmatic Processes and Plate Tectonics. Geological Society London Special Publications, London 76:71–81
Mock R, Hillebrands B, Sandercock R (1987) Construction and performance of a Brillouin scattering set-up using a triple-pass tandem Fabry-Perot interferometer. J Phys E Sci Instrum 20(6):656
Ochs FA, Lange RA (1997) The partial molar volume, thermal expansivity, and compressibility of H2O in NaAlSi3O8 liquid: new measurements and an internally consistent model. Contrib Mineral Petrol 129(2–3):155–165
Ochs FA, Lange RA (1999) The density of hydrous magmatic liquids. Science 283(5406):1314–1317
Ohlhorst S, Behrens H, Holtz F (2001) Compositional dependence of molar absorptivities of near-infrared OH-and H2O bands in rhyolitic to basaltic glasses. Chem Geol 174:5–20
Ohtani E, Maeda M (2001) Density of basaltic melt at high pressure and stability of the melt at the base of the lower mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 193(1):69–75
Pei F, Xu W, Wang Q, Wang D, Lin J (2004) Mesozoic basalt and mineral chemistry of the mantle-derived xenocrysts in Feixian, Western Shandong, China: constraints on nature of Mesozoic lithospheric mantle. Geological Journal of China Universities 10:88
Peslier AH, Luhr JF, Post J (2002) Low water contents in pyroxenes from spinel-peridotites of the oxidized, sub-arc mantle wedge. Earth Planet Sci Lett 201:69–86
Revenaugh J, Sipkin S (1994) Seismic evidence for silicate melt atop the 410-km mantle discontinuity. Nature 369:474–476
Richet P, Whittington A, Holtz F, Behrens H, Ohlhorst S, Wilke M (2000) Water and the density of silicate glasses. Contrib Mineral Petrol 138(4):337–347
Sakamaki T, Suzuki A, Ohtani E (2006) Stability of hydrous melt at the base of the Earth’s upper mantle. Nature 439:192–194
Sakamaki T, Ohtani E, Urakawa S, Suzuki A, Katayama Y (2009) Measurement of hydrous peridotite magma density at high pressure using the X-ray absorption method. Earth Planet Sci Lett 287:293–297
Seifert WK, Moldowan JM (1981) Paleoreconstruction by biological markers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:783–794
Seifert R, Malfait WJ, Petitgirard S, Sanchez-Valle C (2013) Density of phonolitic magmas and time scales of crystal fractionation in magma chambers. Earth Planet Sci Lett 381:12–20
Stolper E (1982) Water in silicate glasses: an infrared spectroscopic study. Contrib Mineral Petrol 81:1–17
Suzuki A, Ohtani E, Kato T (1998) Density and thermal expansion of a peridotite melt at high pressure. Phys Earth Planet Inter 107:53–61
Tammann G, Jenckel E (1929) Die Zunahme der Dichte von Gläsern nach Erstarrung unter erhöhtem Druck und die Wiederkehr der natürlichen Dichte durch Temperatursteigerung. Zeitschrift für anorganische allgemeine Chemie 184:416–420
Tkachev S, Manghnani M, Williams Q (2005) In situ brillouin spectroscopy of a pressure-induced apparent second-order transition in a silicate glass. Phys Rev Lett 95:57402
Wan Y, Wang S, Liu D, Wang W, Kröner A, Dong C, Yang E, Zhou H, Hangqian X, Ma M (2012) Redefinition of depositional ages of Neoarchean supracrustal rocks in western Shandong Province, China: SHRIMP U–Pb zircon dating. Gondwana Res 21:768–784
Wang D, Xu W, Feng H, Lin J, Zheng C (2002) Nature of Late Mesozoic lithospheric mantle in western Liaoning Province: evidences from basalt and the mantle-derived xenoliths. J Jilin Univ 32:319 (Chinese)
Wang W, Yang EX, Zhai MG, Wang SJ, Santosh M, Du LL, Xie HQ, Lv B, Wan YS (2013) Geochemistry of ~2.7 Ga basalts from Taishan area: constraints on the evolution of early Neoarchean granite-greenstone belt in western Shandong Province, China. Precambrian Res 224:94–109
Whitfield CH, Brody EM, Bassett WA (1976) Elastic moduli of NaCl by Brillouin scattering at high pressure in a diamond anvil cell. Rev Sci Instrum 47:942–947
Whittington AG, Richet P, Polian A (2012) Water and the compressibility of silicate glasses: a Brillouin spectroscopic study. Am Mineral 97:455–467
Williams Q, Garnero EJ (1996) Seismic evidence for partial melt at the base of Earth’s mantle. Science 273:1528
Wu F-Y, Ge W-C, Sun D-Y (2003) Discussions on the lithospheric thinning in eastern China. Earth Sci Front 10:51–60 (in Chinese).
Wu L, Yang D-B, Xie H-S, Li F-F, Hu B, Yu Y, Xu W-L, Gao C-X (2014) Pressure-induced elastic and structural changes in hydrous basalt glasses: the effect of H2O on the gravitational stability of basalt melts at the base of the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 406:165–173
Xia Q-K, Hao Y, Li P, Deloule E, Coltorti M, Dallai L, Yang X, Feng M (2010) Low water content of the Cenozoic lithospheric mantle beneath the eastern part of the North China Craton. J Geophys Res 115:B07207
Xie H-S, Zhang Y-M, Xu H-G, Hou W, Guo J, Zhao H (1993) A new method of measurement for elastic-wave velocities in minerals and rocks at high-temperature and high-pressure and its significance. Sci China Ser B-Chem 36(10):1276–1280
Xu Y-G (2001) Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archaean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: evidence, timing and mechanism. Phys Chem Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod 26:747–757.
Xu WL, Zheng CQ, Wang DY (1999) Discovery of mantle- and lower crust-derived xenoliths in Mesozoic trachybasalts from western Liaoning, and their geological implications. Geol Rev 45:444–449 (in Chinese).
Xu YG, Huang X-L, Ma J-L, Wang Y-B, Iizuka Y, Xu J-F, Wang Q, Wu X-Y (2004) Crust-mantle interaction during the tectono-thermal reactivation of the North China Craton: constraints from SHRIMP zircon U–Pb chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic plutons from western Shandong. Contrib Mineral Petrol 147:750–767
Xu WL, Hergt JM, Gao S, Pei FP, Wang W, Yang DB (2008) Interaction of adakitic melt–peridotite: implications for the high-Mg# signature of Mesozoic adakitic rocks in the eastern North China Craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 265:123–137
Xu WL, Yang DB, Gao S, Pei FP, Yu Y (2010) Geochemistry of peridotite xenoliths in Early Cretaceous high-Mg# diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton: the nature of Mesozoic lithospheric mantle and constraints on lithospheric thinning. Chem Geol 270:257–273
Xu W-L, Zhou Q-J, Pei F-P, Yang D-B, Gao S, Li Q-L, Yang Y-H (2013) Destruction of the North China Craton: delamination or thermal/chemical erosion? Mineral chemistry and oxygen isotope insights from websterite xenoliths. Gondwana Res 23:119–129
Yan Z-T (2000) An approximate relation between cubical thermal expansion coefficient of solids and pressure. Chin J High Press Phys 14:4
Yang W, Li S (2008) Geochronology and geochemistry of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Western Liaoning: implications for lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton. Lithos 102:88–117
Yang D-B, Xu W-L, Pei F-P, Yang C-H, Wang Q-H (2012) Spatial extent of the influence of the deeply subducted South China Block on the southeastern North China Block: constraints from Sr–Nd–Pb isotopes in Mesozoic mafic igneous rocks. Lithos 136–139:246–260
Yin CQ, Zhao GC, Guo JH, Sun M, Zhou XW, Zhang J, Xia XP, Liu CH (2011) U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of zircons of the Helanshan Complex: constrains on the evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the Western Block of the North China Craton. Lithos 122:25–38
Yoshino T, Manthilake G, Matsuzaki T, Katsura T (2008) Dry mantle transition zone inferred from the conductivity of wadsleyite and ringwoodite. Nature 451:326–329
Zhai M, Guo J, Liu W (2005) Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic continental evolution and tectonic history of the North China Craton: a review. J Asian Earth Sci 24:547–561
Zhang Y, Stolper EM (1991) Water diffusion in a basaltic melt. Nature 351:306–309
Zhang H-F, Zheng J-P (2003) Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of Mesozoic basalts from the North China Craton: a case study in Fuxin, Liaoning Province. Chin Sci Bull 48(9):924–930
Zhao G-C, Guo J-H (2012) Precambrian geology of China: preface. Precambrian Res 221–222:1–12
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Sun M (2002) SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of the Fuping Complex: implications for accretion and assembly of the North China Craton. Am J Sci 302:191–226
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun M, Li SZ, Li XP, Zhang J (2008) SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages of granitoid rocks in the Lüliang Complex: implications for the accretion and evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Res 160:213–226
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Xia Qun-ke for technical support on the electron microprobe and infrared absorption spectroscopy experiments. We also thank Professor Liu Qiong for hospitality and stimulating discussions. This work was financially supported by (Grant No. 91014004, 11374121 and 11074094), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2013M540243), the Fundamental Research Funds for Jilin University, China (Grant No. 450060491500) and the Special fund of the West Light Foundation of CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Yang, DB., Liu, JX. et al. A Brillouin scattering study of hydrous basaltic glasses: the effect of H2O on their elastic behavior and implications for the densities of basaltic melts. Phys Chem Minerals 44, 431–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0870-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0870-9