Abstract
Background
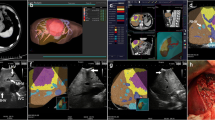
The clinical feasibility and usability of intraoperative ultrasonography (IOUS) tracked by computed tomography (CT) images have been proposed; however, it requires technically demanding manual registration procedure.
Study design
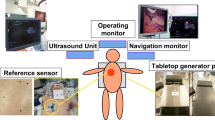
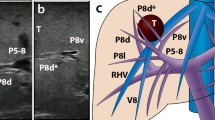
A prospective study using real-time virtual sonography (RVS) with novel automatic registration system was conducted in four high-volume centers of liver resection from 2015 to 2016. The requiring time for registration of IOUS and CT images and positional error of confluence of middle hepatic venous tributaries (V8-MHV, V5-MHV) were measured in patients undergoing laparotomy.
Results
Automatic registration was successful in 43 of 52 enrolled patients (83%), with error ranges of 11.4 (3.1–69.4) mm for V8-MHV and 16.2 (4.3–66.8) mm for V5-MHV. Time required for total registration process was 36 (27–74) s.
Conclusions
The RVS with novel automatic registration system can provide quick and easy registration and acceptable accuracy, which can promote the usage of IOUS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imamura H, Seyama Y, Kokudo N et al (2003) One thousand fifty-six hepatectomies without mortality in 8 years. Arch Surg 138:1198–1206 discussion 1206
Are C, Gonen M, Zazzali K et al (2007) The impact of margins on outcome after hepatic resection for colorectal metastasis. Ann Surg 246:295–300
de Haas RJ, Wicherts DA, Flores E et al (2008) R1 resection by necessity for colorectal liver metastases: is it still a contraindication to surgery? Ann Surg 248:626–637
Andreou A, Aloia TA, Brouquet A et al (2013) Margin status remains an important determinant of survival after surgical resection of colorectal liver metastases in the era of modern chemotherapy. Ann Surg 257(1079–108):8
Saito S, Yamanaka J, Miura K et al (2005) A novel 3D hepatectomy simulation based on liver circulation: application to liver resection and transplantation. Hepatology 41:1297–1304
Radtke A, Sotiropoulos GC, Molmenti EP et al (2010) Computer-assisted surgery planning for complex liver resections: when is it helpful? A single-center experience over an 8-year period. Ann Surg 252:876–883
Mise Y, Hasegawa K, Satou S et al (2011) Venous reconstruction based on virtual liver resection to avoid congestion in the liver remnant. Br J Surg 98(1742–175):1
Takamoto T, Hashimoto T, Ogata S et al (2013) Planning of anatomical liver segmentectomy and subsegmentectomy with 3-dimensional simulation software. Am J Surg 206:530–538
Makuuchi M, Hasegawa H (1985) Yamazaki S Ultrasonically guided subsegmentectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 161:346–350
Kawasoe H, Eguchi Y, Mizuta T et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation with the real-time virtual sonography system for treating hepatocellular carcinoma difficult to detect by ultrasonography. J Clin Biochem Nutr 40(66–7):2
Sandulescu L, Saftoiu A, Dumitrescu D et al (2009) The role of real-time contrast-enhanced and real-time virtual sonography in the assessment of malignant liver lesions. J Gastrointest Liver Dis 18(103–10):8
Satou S, Aoki T, Kaneko J et al (2014) Initial experience of intraoperative three-dimensional navigation for liver resection using real-time virtual sonography. Surgery 155(255–26):2
Sofuni A, Itoi T, Itokawa F et al (2013) Real-time virtual sonography visualization and its clinical application in biliopancreatic disease. World J Gastroenterol 19(7419–742):5
Beller S, Hunerbein M, Eulenstein S et al (2007) Feasibility of navigated resection of liver tumors using multiplanar visualization of intraoperative 3-dimensional ultrasound data. Ann Surg 246:288–294
Kingham TP, Scherer MA, Neese BW et al (2012) Image-guided liver surgery: intraoperative projection of computed tomography images utilizing tracked ultrasound HPB (Oxford) 14(594–60):3
Peterhans M, vom Berg A, Dagon B et al (2011) A navigation system for open liver surgery: design, workflow and first clinical applications. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 7(1):7–16
Torzilli G, Montorsi M, Donadon M et al (2005) “Radical but conservative” is the main goal for ultrasonography-guided liver resection: prospective validation of this approach. J Am Coll Surg 201:517–528
Araki K, Conrad C, Ogiso S et al (2014) Intraoperative ultrasonography of laparoscopic hepatectomy: key technique for safe liver transection. J Am Coll Surg 218(e37–4):1
Kawaguchi Y, Velayutham V, Fuks D, et al (2017) Operative techniques to avoid near misses during laparoscopic hepatectomy. Surgery 161:341–346
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Hitachi, Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Takeshi Takamoto designed the study. Takeshi Takamoto, Yoshihiro Mise, Shouichi Satou, and Yuta Kobayashi acquired the data. Takeshi Takamoto contributed to analysis and interpretation and drafted the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and approved the final draft of the article.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takamoto, T., Mise, Y., Satou, S. et al. Feasibility of Intraoperative Navigation for Liver Resection Using Real-time Virtual Sonography With Novel Automatic Registration System. World J Surg 42, 841–848 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4210-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4210-5