Abstract
Objective
To explore the causes, diagnosis and treatment of post-pancreaticoduodenectomy hemorrhages (PPHs).
Methods
A database of 703 pancreaticoduodenectomy patients in our institution (January 2008–July 2013) was analyzed retrospectively.
Results
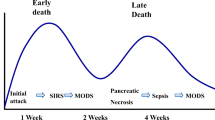
PPHs occurred in 62 patients of which, 38 had clear causes and 15 died because of uncontrolled bleeding and multiple organ failure. Pancreatic fistula and abdominal infection rates were significantly higher in the PPH group compared to the group who did not experience hemorrhages (P < 0.05) but did not significantly increase the mortality of PPH patients. Hemostasis was attempted by endotherapy in 7 patients and was successful in 4 (57.1 %). Angioembolization was performed in 12 patients and was successful in 10 (83.3 %) and relaparotomy in 24 patients successful in 13 (54.2 %). All deceased patients belonged to International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery clinical grade C and sentinel bleeding occurred in 60 % of PPH mortalities (9/15) (P = 0.005).
Conclusion
Pancreatic fistulae and abdominal infections are associated with PPH. Control of early mild upper gastrointestinal hemorrhages could be attempted by endotherapy, but angiography with intervention or surgical treatments were always required for delayed bleeding. The mortality in cases with sentinel bleedings was obviously increased.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Correa-Gallego C, Brennan MF, D’Angelica MI et al (2012) Contemporary experience with postpancreatectomy hemorrhage: results of 1,122 patients resected between 2006 and 2011. J Am Coll Surg 215:616–621
Blanc T, Cortes A, Goere D et al (2007) Hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy: when is surgery still indicated? Am J Surg 194:3–9
de Castro SM, Kuhlmann KF, Busch OR et al (2005) Delayed massive hemorrhage after pancreatic and biliary surgery: embolization or surgery? Ann Surg 241:85–91
Koukoutsis I, Bellagamba R, Morris-Stiff G et al (2006) Haemorrhage following pancreaticoduodenectomy: risk factors and the importance of sentinel bleed. Dig Surg 23:224–228
Rajarathinam G, Kannan DG, Vimalraj V et al (2008) Post pancreaticoduodenectomy haemorrhage: outcome prediction based on new ISGPS Clinical severity grading. HPB (Oxford) 10:363–370
Sanjay P, Fawzi A, Fulke JL et al (2010) Late post pancreatectomy haemorrhage. Risk factors and modern management. JOP 11:220–225
Sato N, Yamaguchi K, Shimizu S et al (1998) Coil embolization of bleeding visceral pseudoaneurysms following pancreatectomy: the importance of early angiography. Arch Surg 133:1099–1102
Yekebas EF, Wolfram L, Cataldegirmen G et al (2007) Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage: diagnosis and treatment: an analysis in 1669 consecutive pancreatic resections. Ann Surg 246:269–280
Choi SH, Moon HJ, Heo JS et al (2004) Delayed hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 199:186–191
Gao QX, Lee HY, Wu WH et al (2012) Factors associated with post-pancreaticoduodenectomy hemorrhage: 303 consecutive cases analysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 125:1571–1575
Manas-Gomez MJ, Rodriguez-Revuelto R, Balsells-Valls J et al (2011) Post-pancreaticoduodenectomy hemorrhage. Incidence, diagnosis, and treatment. World J Surg 35:2543–2548
Tien YW, Lee PH, Yang CY et al (2005) Risk factors of massive bleeding related to pancreatic leak after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 201:554–559
Wei HK, Wang SE, Shyr YM et al (2009) Risk factors for post-pancreaticoduodenectomy bleeding and finding an innovative approach to treatment. Dig Surg 26:297–305
Ricci C, Casadei R, Buscemi S et al (2012) Late postpancreatectomy hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy: is it possible to recognize risk factors? JOP 13:193–198
Lee HG, Heo JS, Choi SH et al (2010) Management of bleeding from pseudoaneurysms following pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 16:1239–1244
Brodsky JT, Turnbull AD (1991) Arterial hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy. The ‘sentinel bleed’. Arch Surg 126:1037–1040
Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C et al (2007) Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH): an International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery 142:20–25
Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G et al (2005) Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery 138:8–13
Cameron JL, Riall TS, Coleman J et al (2006) One thousand consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies. Ann Surg 244:10–15
Reddy JR, Saxena R, Singh RK et al (2012) Reoperation following Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Int J Surg Oncol 2012:218248
Hur S, Yoon CJ, Kang SG et al (2011) Transcatheter arterial embolization of gastroduodenal artery stump pseudoaneurysms after pancreaticoduodenectomy: safety and efficacy of two embolization techniques. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:294–301
Robinson K, Rajebi MR, Zimmerman N et al (2013) Post-pancreaticoduodenectomy hemorrhage of unusual origin: treatment with endovascular embolization and the value of preoperative CT angiography. J Radiol Case Rep 7:29–36
Rumstadt B, Schwab M, Korth P et al (1998) Hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann Surg 227:236–241
Khorsandi SE, Limongelli P, Jackson JE et al (2008) Management of delayed arterial hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. A case series. JOP 9:172–178
Beyer L, Bonmardion R, Marciano S et al (2009) Results of non-operative therapy for delayed hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Gastrointest Surg 13:922–928
Limongelli P, Khorsandi SE, Pai M et al (2008) Management of delayed postoperative hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a meta-analysis. Arch Surg 143:1001–1007
Meng XF, Wang J, Wang ZJ et al (2012) Delayed massive hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 92:1119–1121
Zhang J, Zhu X, Chen H et al (2011) Management of delayed post-pancreaticoduodenectomy arterial bleeding: interventional radiological treatment first. Pancreatology 11:455–463
Treckmann J, Paul A, Sotiropoulos GC et al (2008) Sentinel bleeding after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a disregarded sign. J Gastrointest Surg 12:313–318
Acknowledgments
None.
Grant support for the research reported
None.
Conflict of interests
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jian-feng Chen and Shi-feng Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Jf., Xu, Sf., Zhao, W. et al. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies to Manage Post-Pancreaticoduodenectomy Hemorrhage. World J Surg 39, 509–515 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2809-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2809-3